Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global — 15 Sep, 2023 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
A Geopolitical Competition in Renewable Energy
China, the US and the EU are locked in an accelerating race to lead the world in green energy production, manufacturing, storage and industrial decarbonization. China has a commanding lead in most aspects of the renewable energy race, but new government initiatives in the US and the EU are designed to create homegrown industries and manufacturing to gain on China. Each region’s approach to funding renewable energy projects reflects its market and funding conditions. But the similarities in approach outweigh the differences. A group of researchers at S&P Global published an in-depth analysis of this developing geopolitical competition over renewable energy: “Renewable Energy Funding in 2023: A ‘Capital Transition’ Unleashed.”
There is a substantial shortfall in funding for renewable energy if the world intends to meet a 2050 net-zero target. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, an estimated annual investment of $1.4 trillion in renewable generating assets is required through 2050 to achieve net-zero. S&P Global Commodity Insights forecasts about $700 billion in annual investment leading up to 2050. To compensate for this expected shortfall, many governments are attempting to mobilize private capital to accelerate the energy transition by providing incentives, favorable financing terms and tax breaks.
China, the US and the EU have been particularly active in their efforts to mobilize private capital. All three governments appear to have identified renewable energy production, manufacturing and storage as strategic growth areas to boost their domestic economies. The passage of the Inflation Reduction Act in the US seems to have accelerated a geopolitical competition to support renewable energy investment. In the US and Europe, this support focuses on seeding new renewable energy projects. In China, the focus is on defending its manufacturing dominance and expanding its supply chains. Each region has structured support and incentives to play to regional strengths in its investment markets.
China has enlisted top-down policy decision-making and state-owned banks and enterprises to accelerate investments in renewable power. Because lending rates have been kept low to boost the economy’s sluggish growth after lockdowns, Chinese companies favor debt financing. Government policies also allow renewables projects to access preferential rates.
In the US, the American Jobs Plan, Inflation Reduction Act and CHIPS for America Act contain funding and incentives for the energy transition. The Inflation Reduction Act, in particular, has unleashed the substantial US private equity market to invest directly in renewable energy through incentives and revisions to the tax code.
In the EU, regulation acts as both support and an impediment to renewable energy investment. The EU requires renewable energy projects with government support or subsidies to include two-way contracts for differences to protect the interests of energy providers and consumers. While these contracts may appear to be a burden for generators, they confirm the long-term viability of a project and establish a consistency of demand that is required to obtain financing. The lengthy permitting process for grid connection in the EU causes delays of at least three to six years for renewable energy projects. This creates tension in the EU between the intention to build out renewable capacity and the reality of regulatory bottlenecks.
“Financial and capital markets may be part of shaping the energy transition as they respond to government policy,” S&P Global’s authors wrote in the analysis. “But it is the realities of the energy transition that have created a vector along which governments are competing for economic preeminence.”
Today is Friday, September 15, 2023, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
Written by Nathan Hunt.
S&P U.S. Indices Mid-Year 2023: Analyzing Relative Returns To CRSP
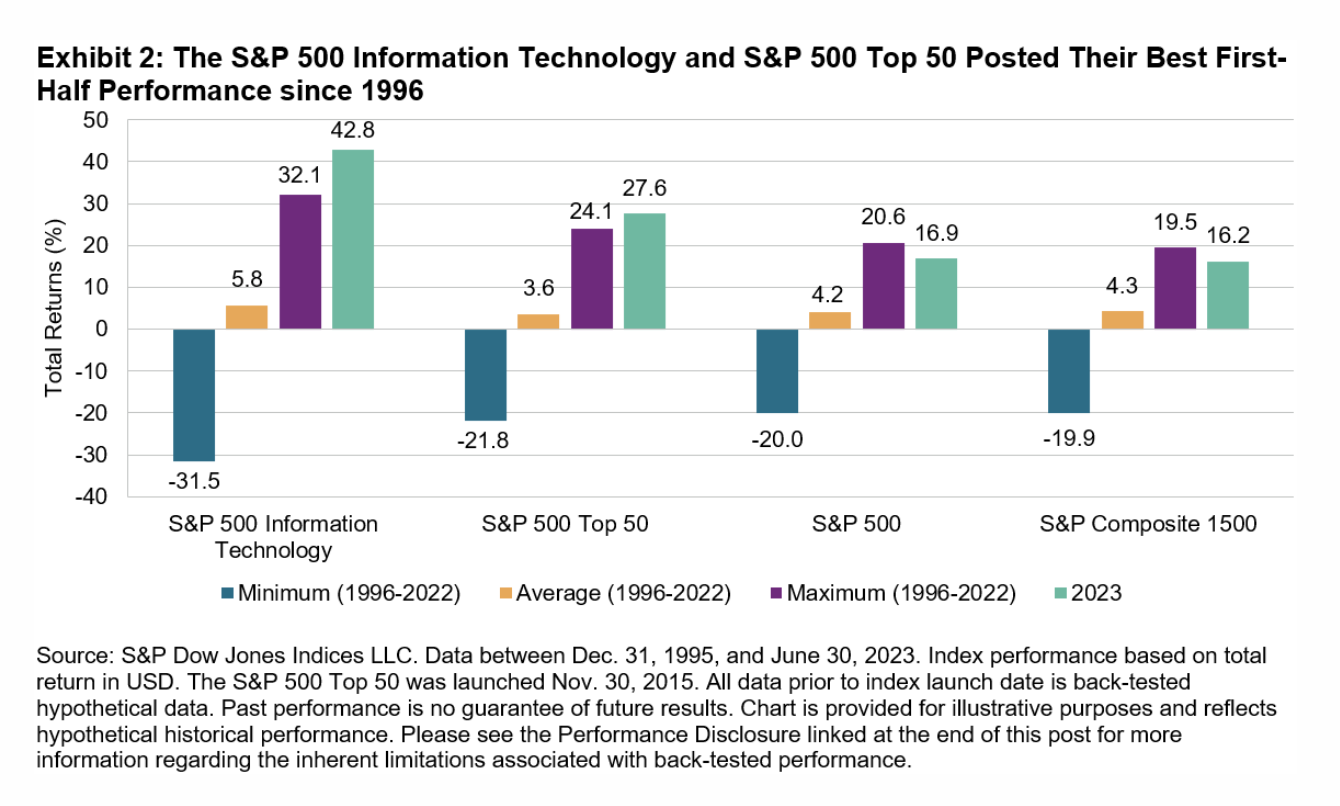
Following a challenging 2022, H1 2023 hosted a recovery among U.S. equities: the S&P 500® (up 16.9%) posted its fourth-best first half since 1996, and there were gains across the market cap spectrum. But on a relative basis, and in contrast to longer horizons, the S&P Core U.S. Equity Indices lagged their CRSP counterparts in H1 2023.
—Read the article from S&P Dow Jones Indices
Access more insights on the global economy >
Credit FAQ: What An Acceleration Of Quantitative Tightening Could Mean For Eurozone Banks

Amid a broad consensus that core inflation will remain above target for another two years, S&P Global Ratings' economists expect the European Central Bank's (ECB's) monetary policy to continue normalizing once rates have peaked. If inflation does indeed exceed the target for another two years, S&P Global Ratings believes the current passive form of quantitative tightening (QT) could give way to a more active form, which would involve the ECB starting to sell bonds on the market.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on capital markets >
US Soybean 2023-24 Production Woes Likely To Boost Brazilian Exports In 2024
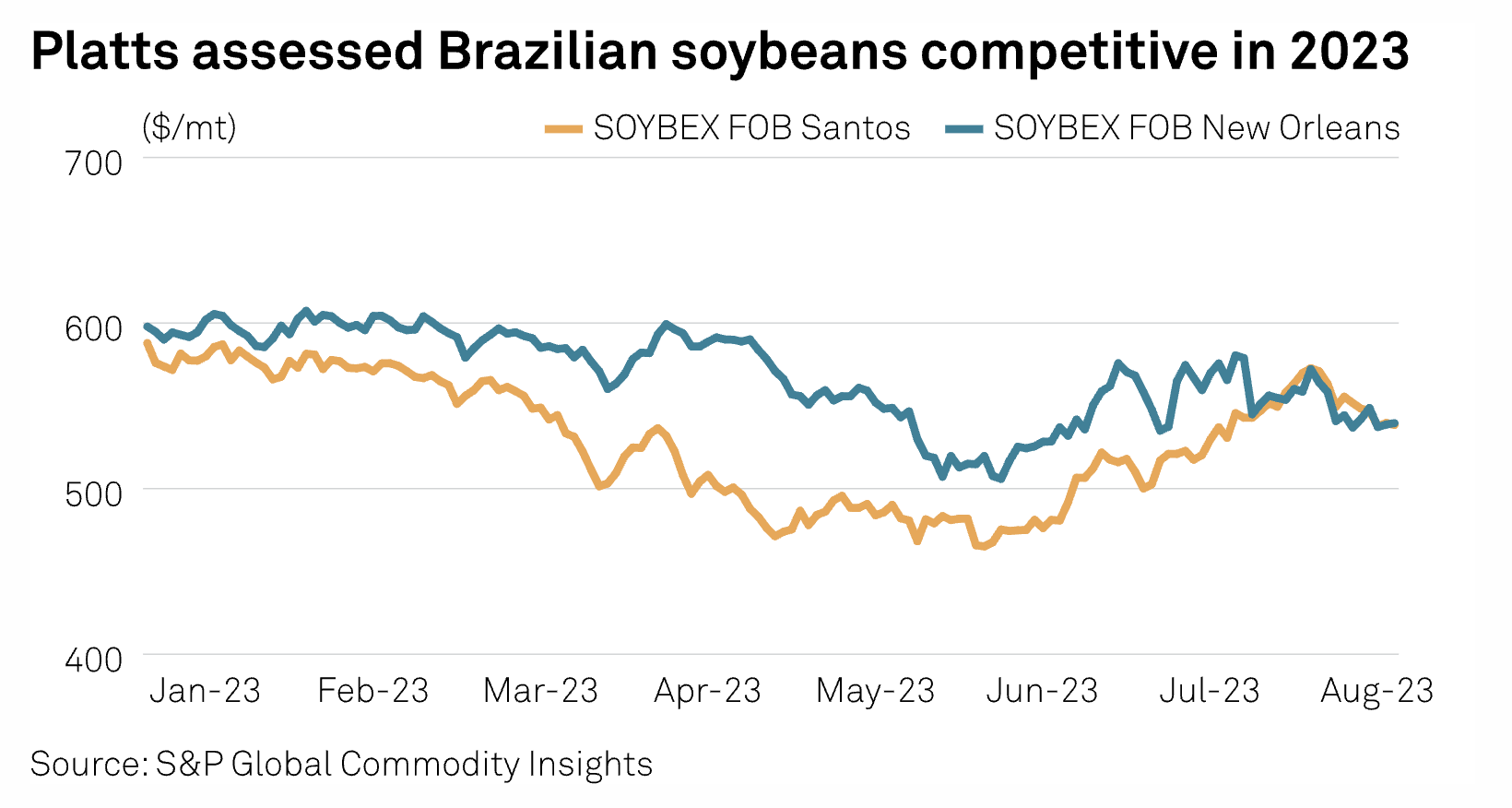
The US soybeans production forecast in marketing year 2023-24 (September-August) has been sliced significantly since pre-season estimates amid sizable acreage cut and prolonged unfavorable weather, likely supporting Brazil's oilseed exports early next year, analysts and market observers have told S&P Global Commodity Insights. Just before the oilseed sowing for MY 2023-24 began mid-May, the US soybean production was forecast at record 122.74 million mt with a yield of 52 bushels/acre, up 5% on the year and acreage estimates of 87.5 million acres, steady on the year, the US Department of Agriculture's May 12 World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates report showed.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
Cleaner Vs Cheaper Fuels: Asia's Policy Dilemma Is Here To Stay — For Now
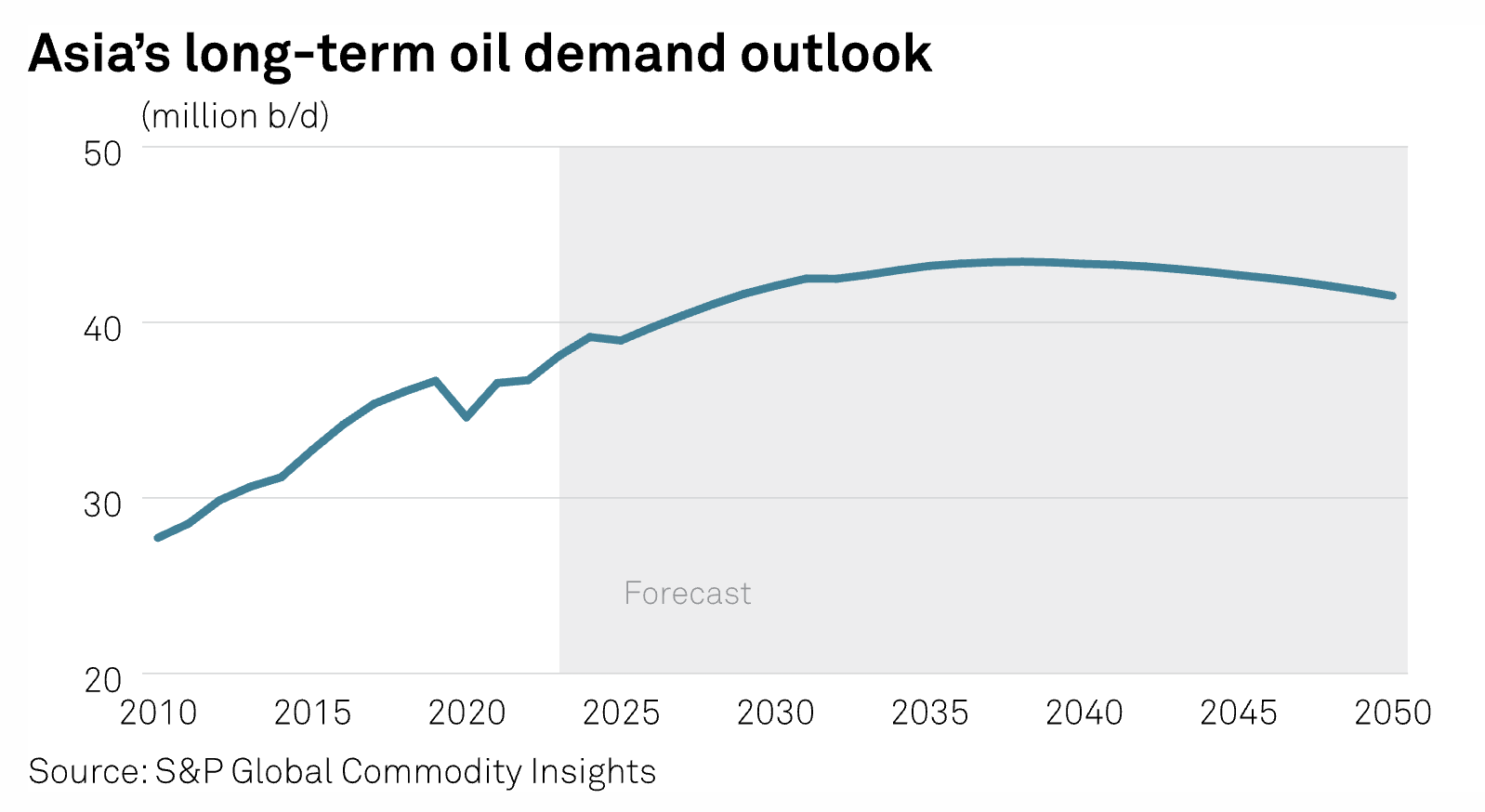
Embracing a new energy order will surely come at a hefty cost for Asia, but will it be higher than the price the region pays for its deep addiction to imported fossil fuels? For more than 1,000 delegates who attended the Asia Pacific Petroleum Conference by S&P Global Commodity Insights in early September, a key takeaway was that Asia today is relatively better placed to strike a balance between providing affordable and sustainable energy, as well as ensuring energy security, compared to where it was a few years ago.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on sustainability >
OPEC Launches Latest Broadside Against The IEA Over Peak Oil Prediction
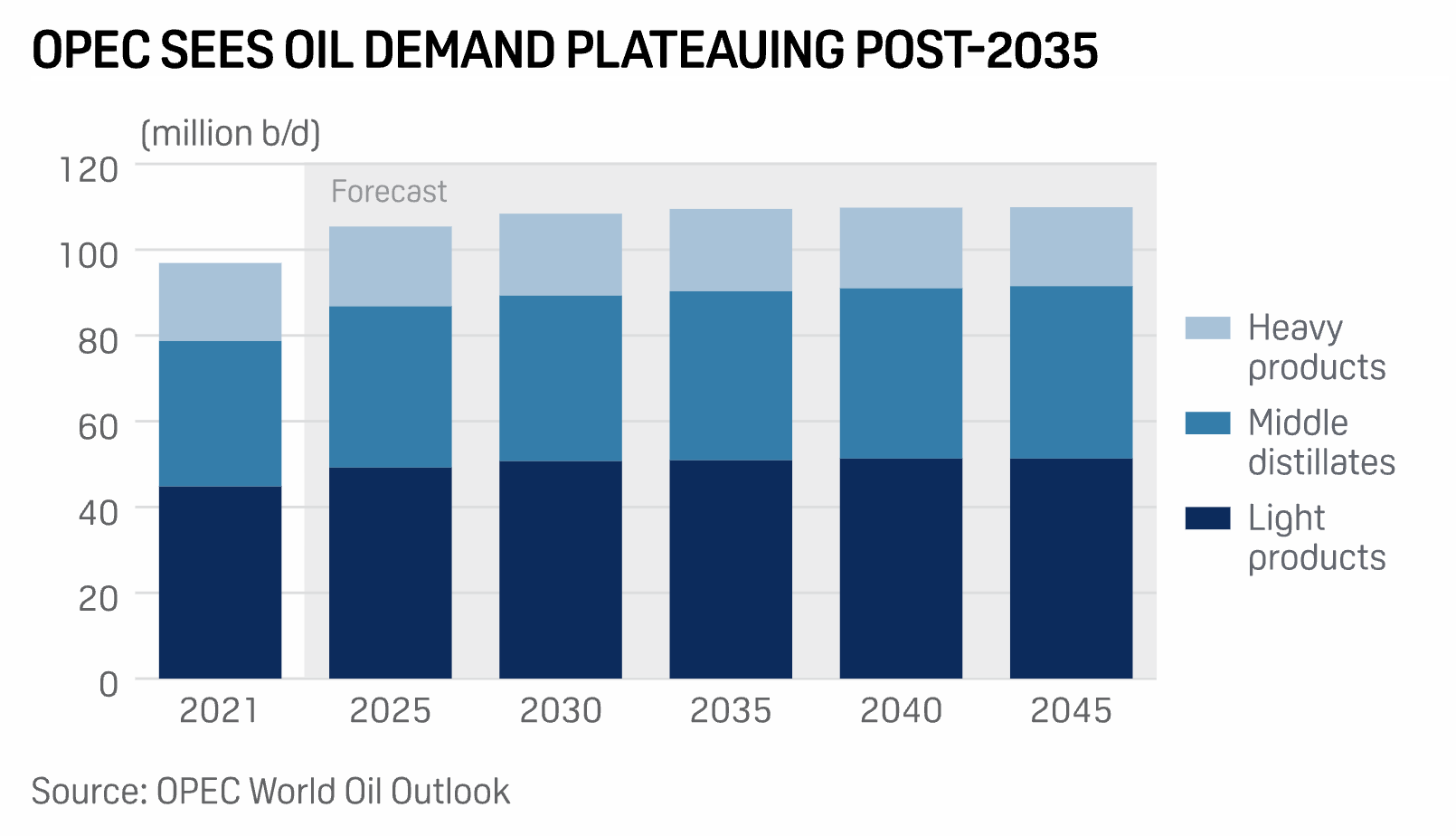
OPEC has hit out again at the International Energy Agency, saying its prediction of a peak in fossil fuel demand before 2030 presents a "dangerous" risk to global energy security by stoking calls to end investments in oil and gas projects. In a sharply worded response to IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol's Sept. 12 op-ed in the Financial Times that declared the hastening decline of hydrocarbons a "welcome sight," OPEC Secretary General Haitham al-Ghais accused the agency of ideologically driven fearmongering that would destabilize the world economy.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Generative AI Use Cases Could Boost Document And Content Management Software
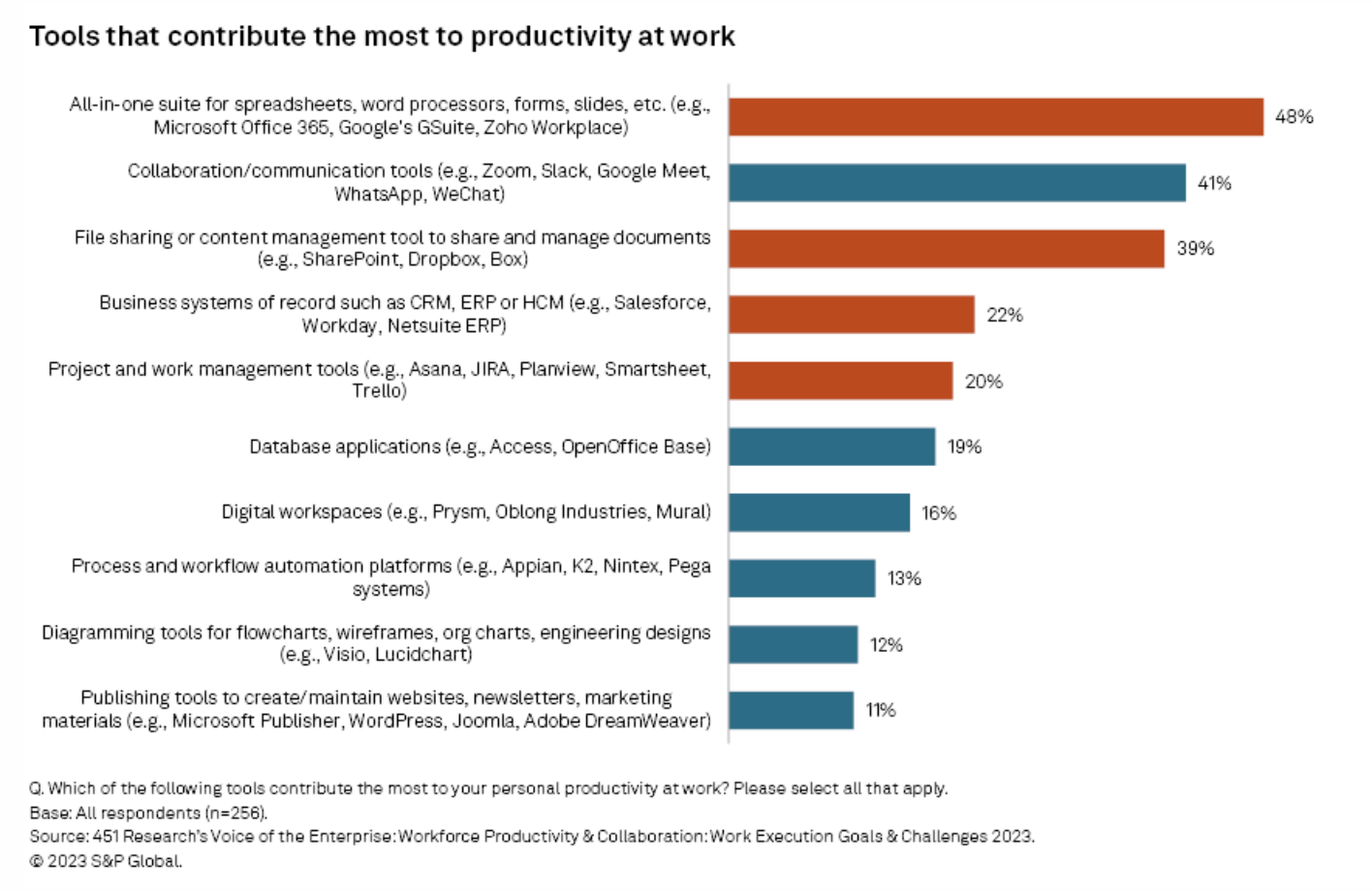
There is no denying that the hype around generative AI — a technology known for being able to generate complete pieces of content or gather relevant data and information from a short prompt — has thrust discussion about possible use cases for the technology into the limelight. This prominence has undoubtedly been aided by Microsoft Corp. 's $10 billion investment in ChatGPT-maker OpenAI LLC . As this investment shows, there is huge enterprise potential for the technology, and software vendors are racing to release their own generative AI (GenAI) products or partner with an established brand.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
