Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global — 26 Jan, 2023 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.

Climate Change: A Glass Half Full
Recent progress in addressing climate change comes in part from a recognition by companies that finding solutions to the problem can help the planet and their bottom line.
While the goals of big business and environmentalists have long seemed at odds, new legislation and a growing consensus around the urgency of the climate crisis have begun to align the interests of the two groups. Companies across all sectors are devoting resources to minimizing their carbon footprints or developing technology to combat climate change.
Big Tech companies are among the vanguard in the move away from fossil fuels, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence. Companies like Amazon are investing heavily in renewable generation to satisfy their appetite for abundant, reliable energy while meeting decarbonization commitments to consumers and shareholders. As the cost of renewables continues to fall — becoming cheaper than fossil fuels for the first time in 2021, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency — the transition to clean energy makes increasing business sense for companies that depend on energy-intensive datacenters, which can consume up to 200 times the power of a standard office space. Inflation Reduction Act tax credits are further driving down the cost of renewable energy projects, making them even more enticing for big electricity consumers.
The new tax credits and the falling cost of green energy are also converting power companies into climate allies. Once generally opposed to national clean energy standards, U.S. electric utilities are now capitalizing on the favorable economics of renewables to replace aging fossil fuel generation with wind and solar. Worldwide, the clear-cut business case for the energy transition has put renewables on track to comprise 90% of global electricity capacity expansion between 2022 and 2027, according to the International Energy Agency.
A slew of companies has cropped up in response to the growing demand for decarbonization technology, and they're attracting plenty of money from investors, S&P Global Market Intelligence reported. Some ventures are developing novel, carbon-free power sources, such as enhanced geothermal or fusion, while others are innovating processes for removing CO2 from the atmosphere — a service that could be monetized by selling carbon credits to businesses looking to meet their net-zero commitments. Keen investor interest in green tech insulated the sector from an overall venture capital slowdown, with funding to the space holding steady since 2021. According to a report from PwC, climate tech investments accounted for more than 25% of all venture capital invested in 2022.
A similar trend among environmental, social and governance funds further highlights the resilience of climate-focused investing. In the latest version of a report from US SIF, an industry group representing investment managers with ESG strategies, respondents for the first time identified climate change as the most important criterion they considered when incorporating ESG principles into their portfolios. Notably, this comes even as ESG assets under management in the U.S. dropped to $8.4 trillion in 2022 from $17.1 trillion in 2020, due in part to an SEC rule change that required ESG-labeled funds to invest 80% of assets in ESG investments, according to the report.
Unfortunately, the business community's apparent willingness to join the fight against climate change can only go so far in solving the problem. Amazon, for instance, is actively building renewable capacity for its own energy needs but has limited ability to decarbonize upstream and downstream operations across its supply chain. The tech and retail giant saw its overall greenhouse gas emissions increase 18% from 2020 to 2021 despite an almost 23% decrease in its emissions from purchased energy. Cement production, which contributes about 7% of the world's direct CO2 emissions, is similarly plagued by stubborn-to-decarbonize activities, according to a research report from S&P Global Ratings. A key step in the manufacturing process releases carbon from the raw materials used and accounts for two-thirds of the industry's CO2 emissions.
The cement case study also provides a reason for optimism, however. Faced with ambitious decarbonization targets in the EU, the industry has become a test bed for cutting-edge carbon capture technology, which could reduce emissions by up to 36%, according to the Global Cement and Concrete Association. Given enough incentive by consumers or government regulations, companies will continue to innovate such solutions to climate change.
Today is Thursday, January 26, 2023, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
Written by Adam Rihner.
U.S. January's Flash PMI Data Add To Recession Signals, But Also Point To Rising Cost Pressures
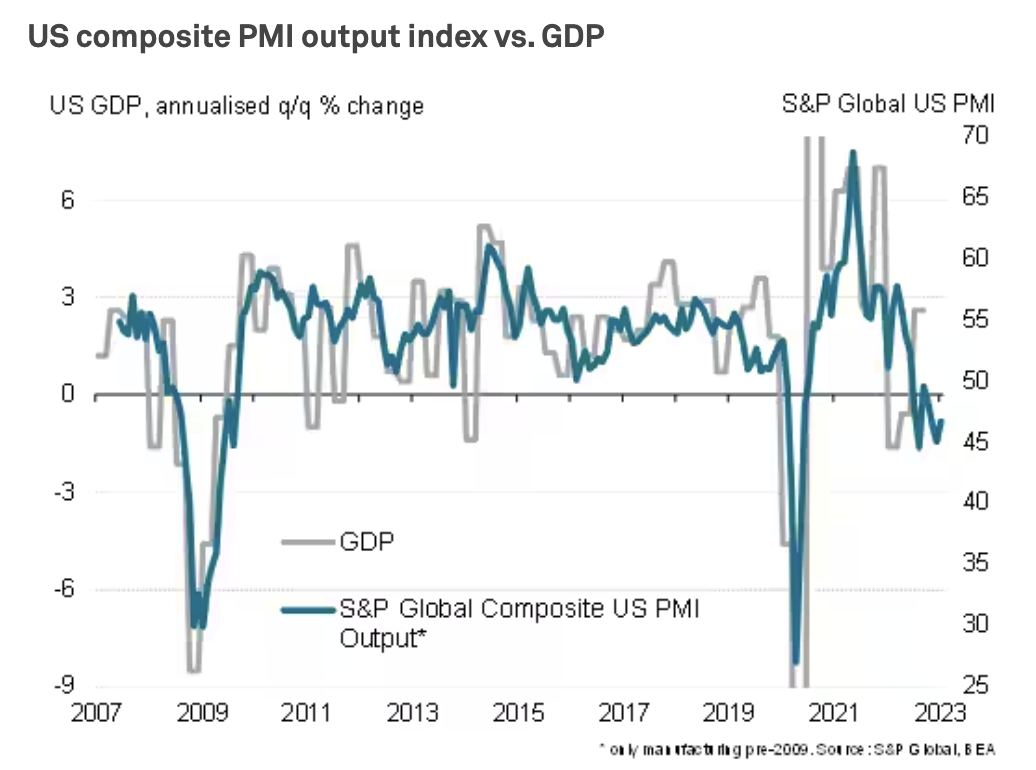
The U.S. economy has started 2023 on a disappointingly soft note, with business activity contracting sharply again in January according to the latest business survey data from S&P Global. Although moderating compared to December, the rate at which output is declining is among the steepest seen since the global financial crisis, reflecting falling activity across both manufacturing and services. Jobs growth has also cooled, with January seeing a far weaker increase in payroll numbers than evident throughout much of last year, reflecting a hesitancy to expand capacity in the face of uncertain trading conditions in the months ahead.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on the global economy >
A Mixed Bag For U.S. And Canadian Life Insurers In 2023

The U.S. and Canadian life insurance sectors are facing a mix of good news and bad news at the start of the new year. Factors that could affect life insurers include rising rates, choppy equity markets, global geopolitical uncertainty and, above all, the looming threat of a recession sometime this year. Meanwhile, changes to financial reporting standards in the U.S. might cause more confusion than clarity, and COVID-19, while seemingly on the decline, still carries meaningful uncertainty.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on capital markets >
EU Ban On Russian Methanol Imports Delayed To Allow For Supply Diversification
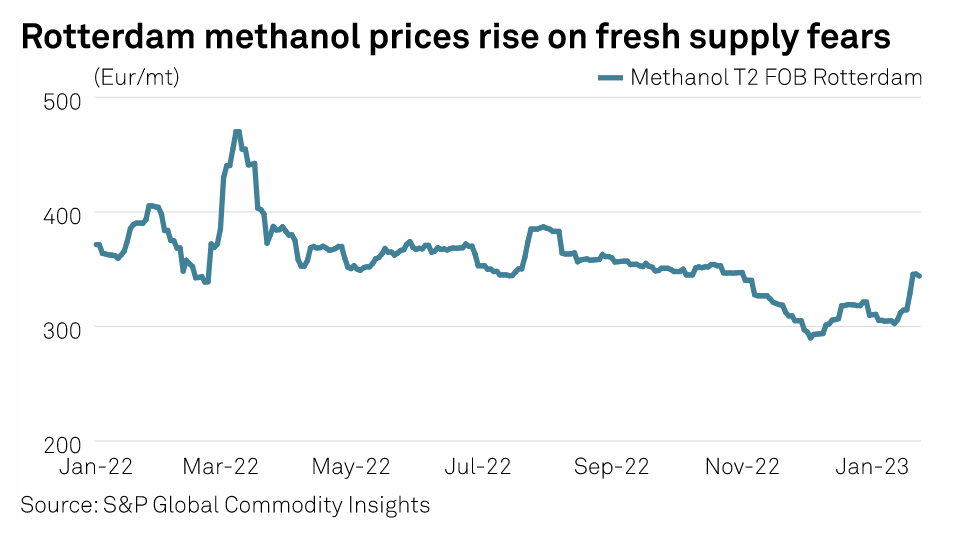
A multi-month delay on banning Russian methanol imports into the EU is intended to allow member states to find alternative sources of supply, the European Commission said Jan. 25. The EU's ban on methanol imports from Russia will not become effective until June 18. It was announced in October as part of the eighth package of EU economic sanctions against Russia and had originally been due to come into force early in January.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
The State Of Biodiversity
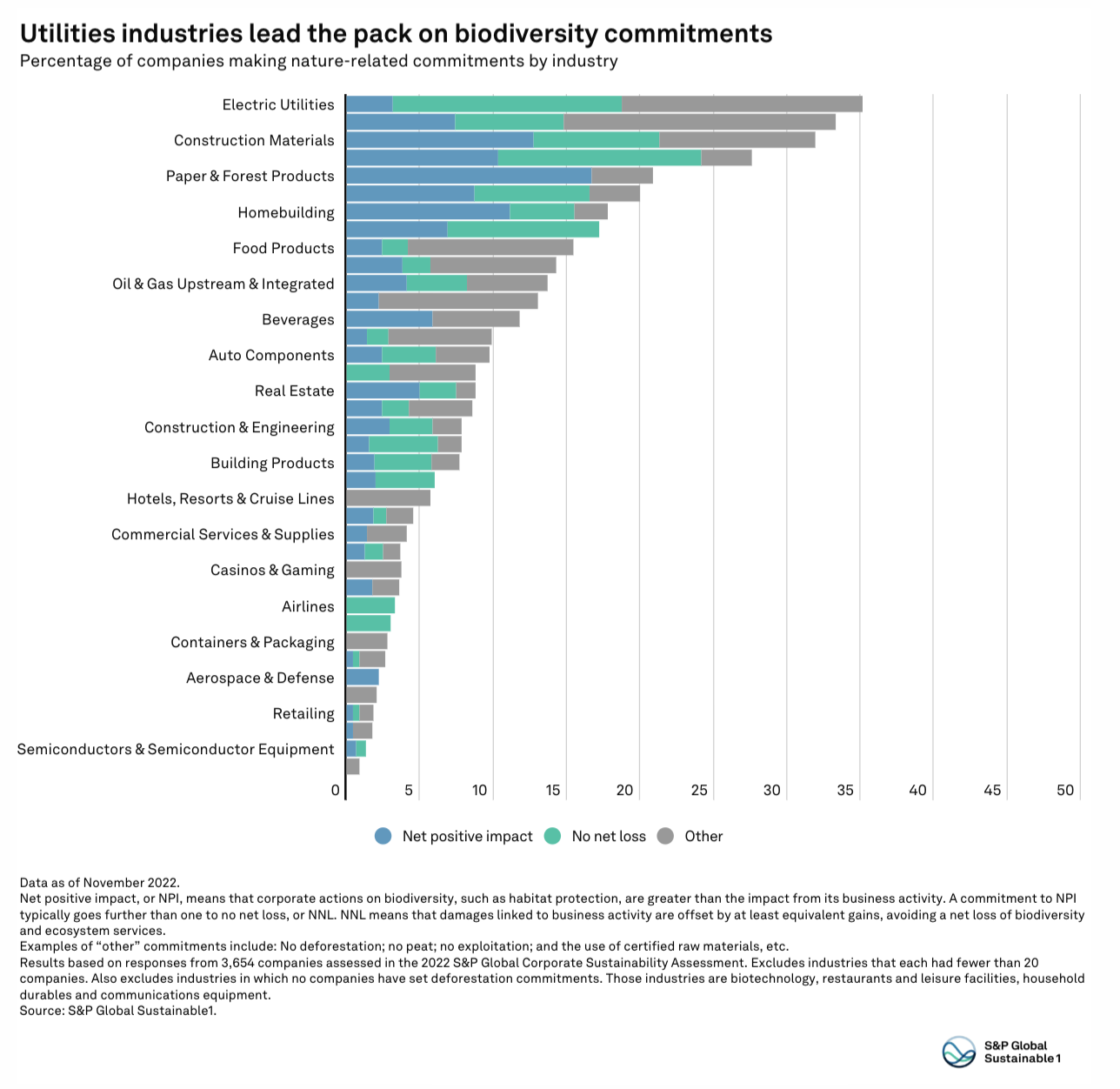
We're at a pivotal moment for the corporate world’s understanding of biodiversity’s connection to climate change and the financial implications of nature loss. This changing tide was apparent at the U.N.’s COP15 meeting in Montreal, Canada, last month, where more than 190 countries agreed to a historic package of goals and targets aimed at halting and reversing nature loss by 2030.
—Read the article from S&P Global Sustainable1
Access more insights on sustainability >
What Lies Ahead For Voluntary Carbon Markets In 2023
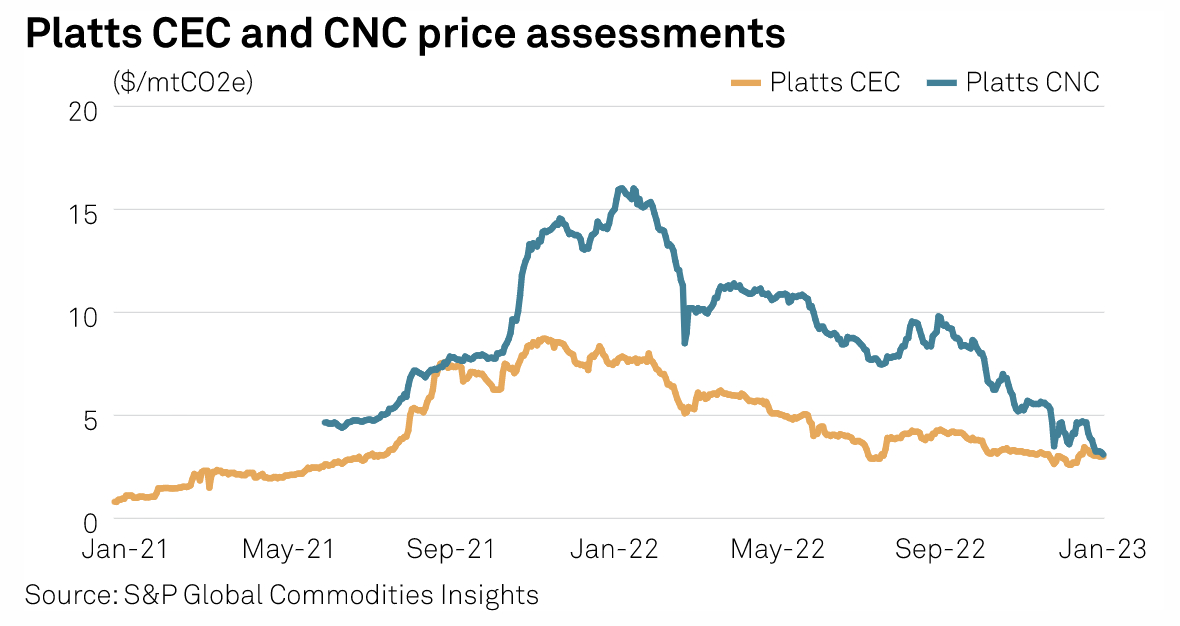
A quick glimpse at the price history of most types of voluntary carbon credits in 2021 and 2022 will reveal somewhat of a bell-shaped curve skewed to the right. It's a shape that tells a very simple story: a large part of the value that carbon credits quickly gained in 2021 was slowly but steadily lost in 2022. It's a shape that leaves market players wondering about what would come next — and the same line could offer the answer.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
In-Game NFTs Forecast To Grow Into $15B Market By 2027
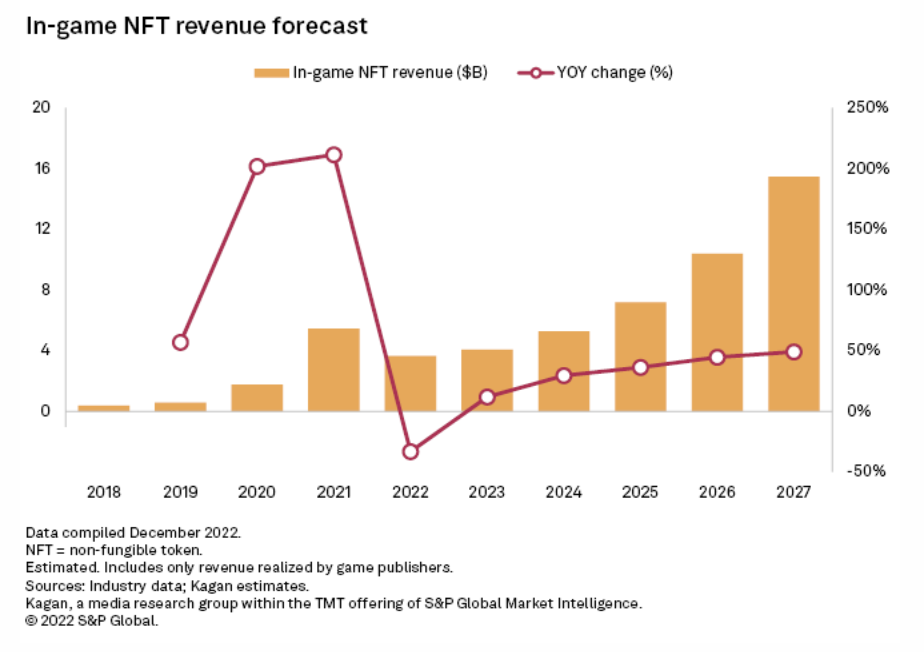
Kagan estimates that publishers made $3.64 billion in revenue from non-fungible tokens connected to items for use inside of video games in 2022, and S&P Global Market Intelligence expects that figure to grow at a 33.5.% compound annual growth rate through 2027 to $15.46 billion as more games with NFT mechanics come to market and attract a wider player base.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on technology and media >
CERAWeek by S&P Global — Navigating A Turbulent World: Energy , Climate and Security

Join global leaders, policymakers and executives from across energy, climate, finance, technology and industry at CERAWeek 2023 for timely dialogue, shared learning and connection.
—Register for CERAWeek