APAC equity markets closed mixed, while all major US and European equity indices closed lower. US government bonds closed higher, while benchmark European bonds closed lower. CDX-NA closed wider across IG and high yield, iTraxx-Xover was wider, and iTraxx-Europe was almost flat on the day. Oil, natural gas, gold, and silver were higher, while the US dollar and copper were lower on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- US equity indices closed lower; Nasdaq -0.4%, Russell 2000 -0.9%, S&P 500 -1.2%, and DJIA -1.6%, with the S&P 500 and Nasdaq having the worst monthly declines (-4.8% and -5.3%, respectively) since March 2020.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -3bps/1.49% yield and 30yr bonds -1bp/2.05% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/53bps and CDX-NAHY +5bps/302bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.1%/94.23.
- Gold closed +2.0%/$1,757 per troy oz, silver +2.6%/$22.05 per troy oz, and copper -2.6%/$4.09 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +0.3%/$75.03 per barrel and natural gas closed +7.1%/$5.87 per mmbtu.
- Cotton closed +3.9%/$1.06 per pound, which is the highest closing level in 10 years.
- IHS Markit provisionally expects that key global markets will show steep declines during September. High-frequency data and other intelligence gathered by our analysts provisionally estimates that the mainland China market will fall by around 30% year on year (y/y) in September. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Furthermore, we believe registration volumes in the US market are on course to retreat by around 25% y/y during September as well. The estimated performance, which is weaker than previously thought, is mainly due to the fallout from the semiconductor shortage that has hit production since the beginning of the year. This has been compounded by a multitude of factors which have emerged during the year and has exacerbated capacity and production constraints for this key component. These include poor weather, fires and the COVID-19 virus pandemic.
- The disruption has already caused IHS Markit to significantly revise its light-vehicle production in the September forecast, has meant that OEMs have struggled to supply vehicles despite otherwise strong customer demand. In addition, inventory has been depleted to very low levels with little opportunity to replenish it, losing the buffer to meet demand from vehicles in stock; this has compounded the direct and immediate shortages and is showing up as an aggressive impact on sales. This is also likely to be indicative of the performance in these markets through the remaining months of the year.
- Given the situation regarding production disruptions and the movement in the IHS Markit Production Loss tracker for Europe, it would not be a surprise to see September sales volumes here down by a similar rate. However, it is likely to hinge on registration volumes in the UK during the important September age-related number plate change, which makes the month hugely influential.
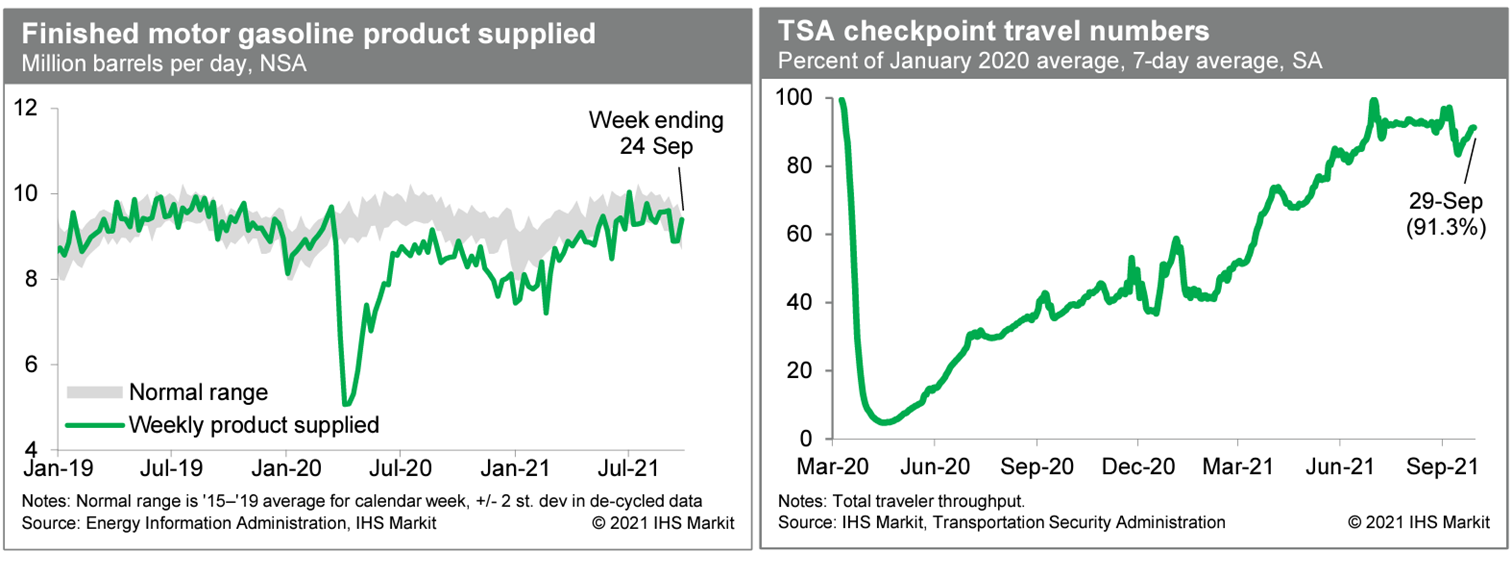
- Consumption of gasoline jumped last week, according to the Energy Information Administration, to the upper end of a normal range (for this time of year). This indicates no concern about internal mobility. Meanwhile, averaged over the last seven days, and after seasonal adjustment, passenger throughput at US airports was running at 91.3% of the January 2020 average, close to readings prior to some volatility around the Labor Day holiday. This suggests no progress has been made in air travel since mid-June. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Joel Prakken)
- US seasonally adjusted initial claims for unemployment insurance increased by 11,000 to a seven-week high of 362,000 in the week ended 25 September. California reported the largest increase in initial claims among all states for the second straight week—unadjusted claims there rose by 17,978 to 86,792 in the week ended 25 September. Initial claims in Michigan also turned up—rising by 6,432 to 18,727—as the auto industry continues to struggle with supply-chain issues. The recent trend in initial claims is at best flat as the spread of the Delta variant and supply-chain issues weigh on activity. (IHS Markit Economist Akshat Goel)
- Seasonally adjusted continuing claims (in regular state programs) fell by 18,000 to 2,802,000 in the week ended 18 September. The insured unemployment rate edged down 0.1 percentage point to 2.0%.
- In the week ended 11 September, continuing claims for Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC) fell by 2,652,742 to 991,813.
- In the week ended 11 September, continuing claims for Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) fell by 3,836,877 to 1,059,248.
- In the week ended 11 September, the unadjusted total of continuing claims for benefits in all programs fell by 6,222,725 to 5,027,581.
- The US spice processor McCormick has reported that its net sales rose by 11.4% y/y to $1.54 billion in the quarter ending on 31 August, bringing year-to-date sales to $4.58 billion in the FY2021 (December-November), thanks to a robust spice home consumption and hostelry recovery. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jose Gutierrez)
- Asian markets have been the drivers of growth, with a 20% increase.
- As a result, the company has upgraded its sales outlook, expecting to rise by 12-13%, up from 11-12% in its previous estimate.
- "We are capitalizing on the sustained shift to cooking more at home, increased digital engagement, clean and flavorful eating, and trusted brands, which we are confident will persist beyond the pandemic," the chief officer, Lawrence E. Kurzius, explained.
- Flavor solutions segment sales rose by 21% y/y to 627.5 million, bringing year-to-date sales to 1.77 billion (+21 y/y) due to higher sales of packaged food, beverages and away-from-home products in restaurants.
- Eli Lilly (US) has announced that it will reduce the list price of its generic insulin lispro injection (100 units/mL) in the United States by 40% from 1 January 2022. The new list price for the generic will be USD82.41 for individual vials and USD159.12 for a pack of five pens. This is 70% less than the branded version of the drug, which is sold by Lilly as Humalog U-100. According to Lilly, the 40% price cut will in effect reduce the price of insulin lispro injection to 2008 levels. The company noted that the greatest benefit would be seen by people who face higher out-of-pocket (OOP) costs, which include those without insurance and those insured under high-deductible plans. The reduction comes amid ongoing political pressure over the high cost of insulin, including Humalog, whose price per vial reportedly rose from USD21 in 1996 to USD275 in 2019. Against this background, in June Walmart launched a new private label analog insulin, ReliOn NovolLog Insulin (insulin aspart) injection, which the company said represented a saving of between 58% and 75% on the cash price of branded insulin products. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Milena Izmirlieva)
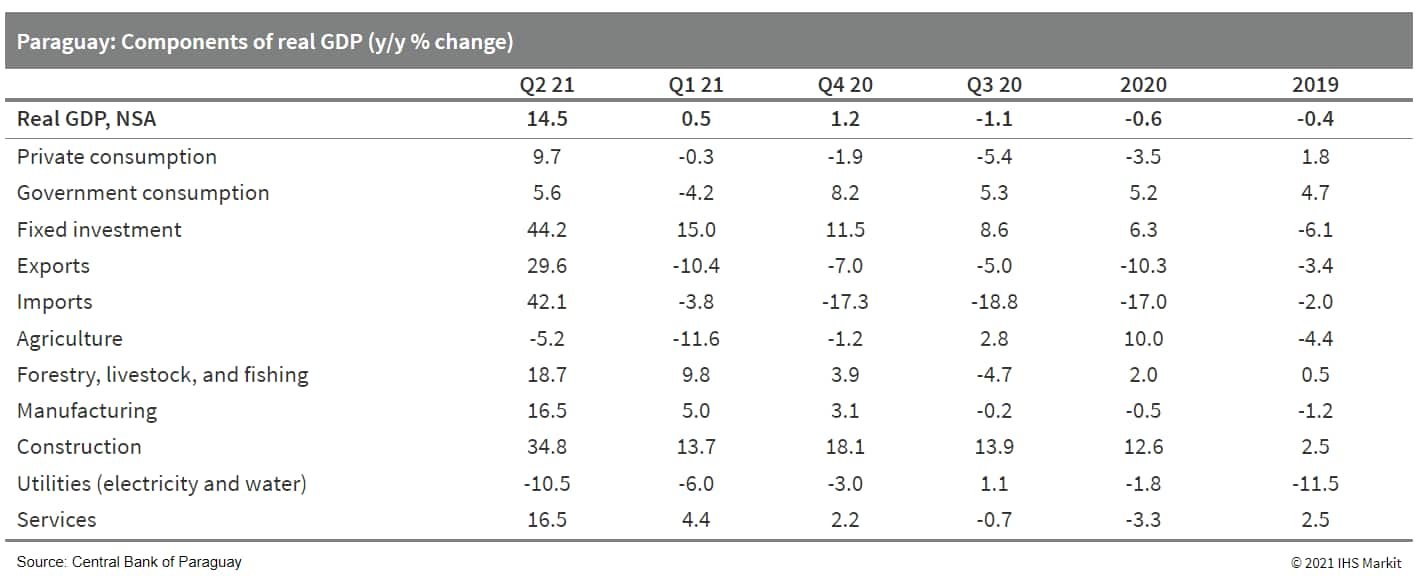
- Paraguay's second-quarter real GDP grew by 14.5% year on year (y/y) on favorable base effects and robust activity in industrial sectors. Services will continue to rebound, but a drought will weigh on agriculture, hydroelectric output, government revenue, and exports. (IHS Markit Economist Jeremy Smith)
- Following a 2.4% quarter-on-quarter (q/q) expansion, the fastest since the third quarter of 2020, real GDP in the second quarter of 2021 was as much as 4.1% higher than in the fourth quarter of 2019.
- As expected, a surge in the number of COVID-19 infections from April to June and the subsequent tightening of containment measures dampened the recovery of private consumption. The monthly sales index dropped sharply in April while the consumer confidence index dipped well into negative territory.
- Even so, however, the impact was not as significant as anticipated and robust growth in industrial sectors such as manufacturing and construction more than compensated for pandemic-related disruptions.
- Although fixed investment accounts for just one-quarter of real output by expenditure, it explains half of the overall year-on-year (y/y) expansion, increasing by 44.2% y/y after declining by just 2.5% y/y in the second quarter of 2020.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- All major European equity indices closed lower; Italy -0.2%, UK -0.3%, France -0.6%, Germany -0.7%, and Spain -0.9%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed lower; Germany +1bp, France/Spain +2bps, and Italy/UK +4bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed flat/50bps and iTraxx-Xover +5bps/253bps.
- Brent crude closed +0.3%/$78.31 per barrel.
- Rolls-Royce has announced that it will launch its first battery electric vehicle (BEV) during the next couple of years. According to a statement released by the brand, the new model will be known as the Spectre, which will reflect "the beginning of a new legacy for our brand", and also fit with Phantom, Ghost and Wraith nameplates that it currently uses. CEO Torsten Müller-Ötvös has said that it is now starting a test program for the vehicle that will cover 2.5 million km - 400 years' use for the typical owner - and that it will take place across the world. This will be completed before the first deliveries take place to customers during the fourth quarter of 2023. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Perrigo (US/tax-domiciled in Ireland) has resolved a long-running tax dispute in Ireland, which will result in the company making a one-off EUR297-million (USD343 million) settlement to Ireland's Revenue Commissioners. The case dates back to 2018 when Ireland's Revenue Commissioners issued an EUR1.64-billion tax claim in relation to a 2013 deal to sell multiple sclerosis drug Tysabri (natalizumab) to Biogen. Despite paying only a fraction (18.1%) of the original tax bill and avoiding any penalties or interest payments, the EUR297-million figure represents the largest single settlement in the history of Ireland's Revenue Commissioners. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Eóin Ryan)
- The European Parliament's Industry, Research, and Energy Committee voted on 27 September to phase out eligibility for natural gas pipelines in the Projects of the Common Interest (PCI) program, but to do so more slowly than advocated by environmental groups. (IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Kevin Adler)
- According to the EU, "PCIs link the energy systems of EU countries and can benefit from accelerated permitting procedures and funding." Recent examples in the gas sector include a pipeline between Greece and Bulgaria, completed in 2020, and a pipeline between Poland and Lithuania, completed in 2019.
- The PCI criteria is being revised to align the Trans-European Networks in Energy (TEN-E) regulation with the objectives of the European Green Deal. The EU has set a goal of a 55% reduction in GHG emissions by 2030 from a 2005 baseline, as its key measure of progress towards meeting a goal of net-zero emissions by 2050.
- However, coming at a time when gas prices are surging in Europe and dragging power prices up with them, the committee members' vote reflected concerns that moving away from fossil fuels too quickly could be costly. As a result, the new eligibility rules will not go into effect until 2027.
- According to IHS Markit's tracking of international gas prices, the benchmarks in Europe known as the Dutch TTF and the UK NBP showed spot prices this week surpassing €75/MWh. This is up more than 500% from a year ago, when they were about €12/MWh. High demand, low inventories, and inadequate imports are all being credited for the price spike, which is expected to last through the upcoming winter, unless temperatures are unusually warm.
- Germany's Federal Statistical Office (FSO) has reported, based on data from various regional states, that the country's national consumer price index (CPI) is flat month on month (m/m) in September. This has driven up the annual inflation rate from 3.9% in August to 4.1% year on year (y/y), a level not observed since 1993. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- The EU-harmonized CPI measure even increased by 0.3% m/m, its y/y rate thus rising sharply from 3.4% to 4.1%. The recent differential between the national and the harmonised measures in y/y terms - linked to the latter using weights derived from the consumer spending pattern of 2020 rather than 2015, thus underweighting package-tour prices that always spike around mid-year - has disappeared now.
- The detailed breakdown of the German national data will only be published with the final numbers on 13 October, but components are available, for instance, from the largest and most populous state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW). CPI inflation in this state stands at 0.0% m/m and 4.4% y/y, the latter rising from 4.2% y/y in August.
- In NRW, energy prices have increased by 0.4% m/m, boosting their annual rate once more from 12.6% in August to 13.6% in September. Food prices have added to inflationary pressure as their 0.2% monthly increase has lifted their y/y rate from 4.4% to 4.9%. In addition, loosened restrictions have facilitated price increases with respect to holiday travel and recreation/entertainment in general. The inflation rate for package tours has risen from 1.5% to 3.4% and the overall category of recreation/entertainment/culture from 3.4% to 4.0%.
- Durable goods prices provide a mixed picture as the y/y rate for clothing/shoes has softened once more from 4.2% to 2.1% whereas inflation of furniture/household goods has increased from 3.8% to 4.0% and that of 'miscellaneous goods and services' remains at a historically elevated level of 3.6%.
- Seasonally adjusted German unemployment has declined by 30,000 month on month (m/m) in September, one-third of the particularly large drop in July 2021 and broadly matching the average monthly decline since July 2020 (the start of the initial recovery after the first wave of the pandemic). A total of 64% of the initial, pandemic-related unemployment surge in the second quarter of 2020 has now been unwound. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- The Labour Agency calculates a cumulative net boosting effect from the COVID-19 pandemic on unemployment of 232,000 as of September, down from 261,000 by August 2021 and an interim peak of 638,000 in June 2020. This represents a comparison with a hypothetical continuation of the pre-pandemic trend if the pandemic had never occurred.
- Germany's (national) unemployment rate has remained steady at 5.5% in September. This compares with a peak of 6.4% after the end of the first wave of the pandemic in mid-2020 and a pre-pandemic 40-year low of 5.0% in March 2020.
- Employment, data for which regularly lag by one month, increased by 66,000 to 45.018 million in August. This reduces the gap with the pre-pandemic high in February 2020 to 0.9%. The sub-category of "regular" jobs - for which employers pay social security contributions, i.e., excluding the self-employed, "mini-jobs", or other forms of precarious employment - exceeded its level a year earlier by 1.4% in July (the latest data available). This outperformed July's 0.6% annual increase for total employment, confirming previous evidence that the recovery of precarious forms of employment still lags considerably. Meanwhile, among regular jobs, part-time employment outperformed full-time employment, up 2.6% versus 1.0% y/y.
- Daimler Truck and Torc Robotics have begun the third year of their partnership focusing on deploying Level 4 autonomous trucks in the United States, according to a company statement. Currently, the companies are testing their next-generation Level 4 autonomous trucks on public roads of the US states of New Mexico, Texas, and Virginia. These test trucks have more sensors at higher resolutions than previously to enhance object detection at longer ranges. Daimler Trucks announced in April 2019 an agreement to acquire a majority stake in Torc to commercialize highly automated trucks on US roads - specifically Level 4 autonomous trucks. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- South Africa's current-account surplus widened to 5.6% of GDP in the second quarter of 2021, from 4.3% of GDP in the previous quarter. The sizeable expansion of the trade surplus partly countered the larger shortfall on the services, income and transfer account, latest data in the South African Reserve Bank's (SARB) Quarterly Bulletin for September show. (IHS Markit Economist Thea Fourie)
- South Africa's export proceeds benefited from resilient global commodity prices, despite a smaller increase in volumes, while a rise in imports mostly reflected higher prices. The shortfall on the income account widened to 2.8% of GDP in the second quarter, from 1.0% of GDP in the previous quarter. Gross dividend payments rebounded, spurred by improved profit levels in the mining sector. Gross dividend receipts decreased sharply during the second quarter.
- The deficit on the financial account widened to 7.2% of GDP in the second quarter, from 4.4% of GDP in the first quarter, the SARB reports. "On a net basis, only direct investment recorded an inflow, while portfolio investment, financial derivatives, other investment and reserve assets all registered outflows," the SARB states.
- Foreign direct investment inflows strengthened in the second quarter on the back of higher equity investment by non-residents in domestic subsidiaries and the acquisition of a South African energy and chemicals group company by a foreign investor. Furthermore, the SARB data show that South African residents' foreign portfolio assets (foreign debt and equity securities) continued to increase in the second quarter, with a recorded outflow of ZAR71.0 billion (USD4.7 billion), from ZAR39.8 billion in the previous quarter.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Australia +1.9%, Mainland China +0.9%, South Korea +0.3%, Japan -0.3%, Hong Kong -0.4%, and India -0.5%.
- Chinese wine imports are showing signs of recovery in 2021, after three consecutive years of declining imports following a record year in 2017 when the country imported 751 million liters. All imported wine categories showed growth this year, except for bottled wines that were worst affected by China's import restrictions on Australian wine. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Vladimir Pekic)
- The overall volume of Chinese wine imports held relatively stable with a slight 1.4% contraction to 211.9 million liters in the first half of 2021, although the value of imports dipped 9.4% y/y to CYN5.30 billion ($819.1 million). The dip in value is primarily due to lower import prices this year which averaged CNY25/liter ($3.86/liter), according to a report published by the Spanish Wine Market Observatory (OeMv) on 23 September.
- The average price of Chinese wine imports amounted to CNY29.23/liter in 2020, up from CNY27.54/liter in 2019 and CNY27.40/liter in 2018.
- Last year, China reduced its wine imports by around 30% to 430 million liters, down from 613 million liters in 2019. Although part of the reduction can be attributed to Covid-19, Chinese wine purchases have been falling since they peaked in 2017. In 2020, the 15 largest wine suppliers to China all saw their exports shrink, save for Argentina that saw its bulk wine exports to China increase exponentially.
- The recent imposition of Chinese import tariffs of up to 200% on imported Australian bottled wines resulted in a sharp drop of Australian wine imports. Australian wine exports fell by 86.5% y/y in volume terms and by 85.5% y/y in value terms in H1 2021.
- Baidu's intelligent driving unit, Apollo, has released a report on its robotaxi service operations during the first half of 2021. The report, '2021 Baidu Autonomous Driving Service Semi-Annual Report', states that the Apollo robotaxi service covered four Chinese cities, Beijing, Guangzhou, Changsha and Cangzhou, involving an operating area of more than 600 square kilometers. Apollo has obtained over 410 test operation licenses for the service and it provided over 400,000 trips as part of the service, with a 95.3% rating on user experience, reports PanDaily. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Plus has delivered the initial production units of its PlusDrive autonomous solution to Chinese truck-maker FAW, according to a company statement. FAW will install PlusDrive on its factory production line with the aim of launching China's first driver-in autonomous trucks. Plus, which recently went public through a merger agreement with a special-purpose acquisition company (SPAC), focuses on developing Level 4 autonomous technology to make commercial freight transport safer, more efficient, and less expensive for its customers. This delivery is part of an agreement under which Plus sells PlusDrive units to FAW. The companies will introduce the Level 3 automated J7 heavy-duty truck, which is deployed with seven cameras, 5mm-wave radars, and one LiDAR, as well as an autopilot system. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
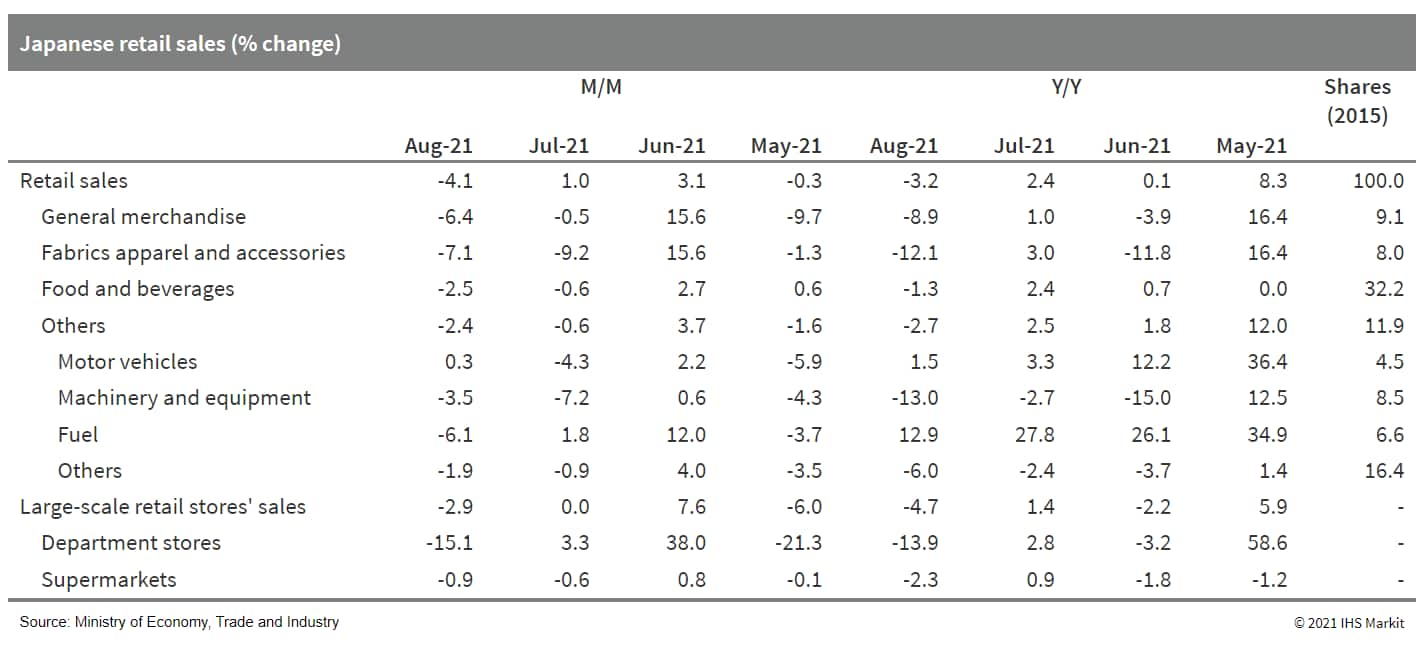
- Japan's retail sales fell by 4.1% month on month (m/m) and 3.1% year on year (y/y) in August following two consecutive months of m/m increases. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- The weakness reflected negative impacts from containment measures due to a surge of Delta variant COVID-19 infections and unusually heavy rainfall during the holiday season.
- Sales for all retail store groupings except for autos declined from the previous month. Because of tighter controls and temporary closures following mass infections in several stores, department store sales declined by 15.1% m/m.
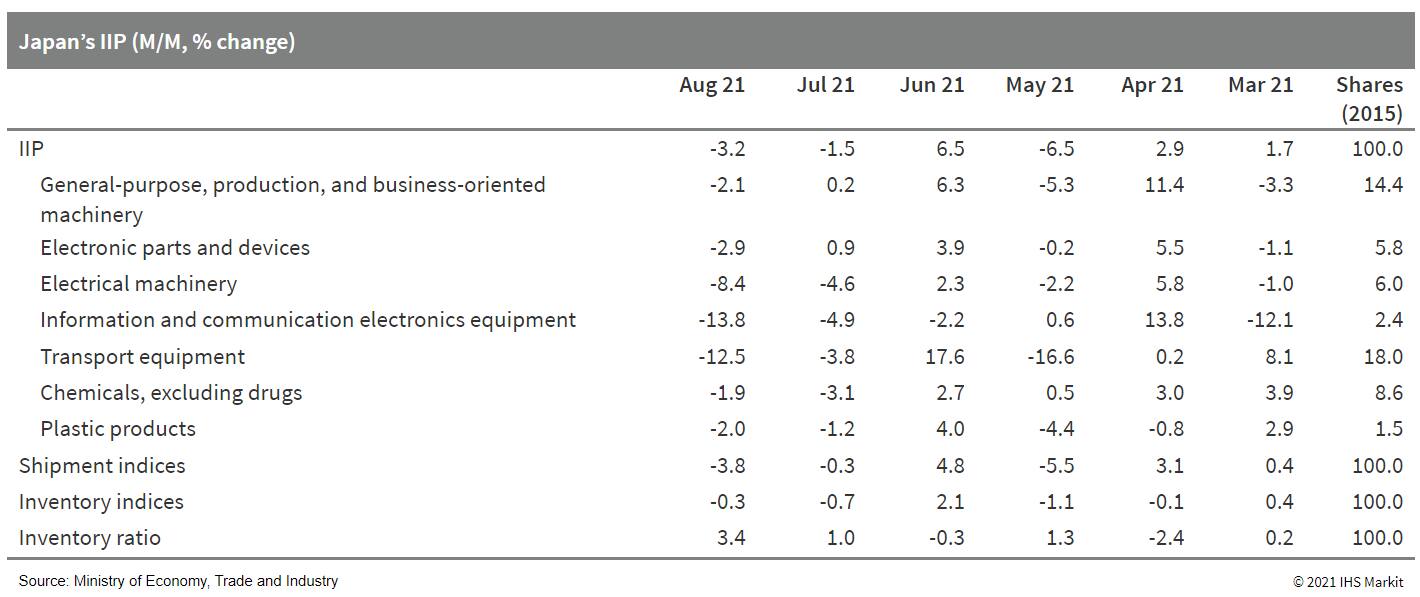
- Japan's index of industrial production (IIP) fell by 3.2% month on month (m/m) in August following a 1.5% m/m drop in July. A faster decline in manufacturers' shipments (down 3.8% m/m; 0.3% m/m drop in the previous month) and a softer drop in inventories (down 0.3% m/m; 0.7% m/m drop in the previous month) led the index of inventory ratio to rise by 3.4% m/m. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- Major factors behind the weakness were continued declines in a broad range of industry groupings, particularly autos and electrical machinery. Shortages of semiconductors and other components because of the Delta-variant infections and supply-chain disruption in Asia had a greater effect on auto production. The chip shortages and working-day adjustments during seasonal vacations also disrupted production of electrical machinery.
- The August results were weaker than IHS Markit's expectations. Supply-chain disruption is likely to remain an issue and continue to weigh on Japan's production over the short term. The recent situations involving Delta-variant infections in many Asian territories are improving, signaling an improvement of the supply-chain condition in the fourth quarter of 2021. However, fresh peaks for new daily cases in some territories and the relatively slow progress in vaccination rollouts in Southeast Asia mean that the risks of shortages of semiconductors and other components could persist for an extended period.
- Private equity firm Apollo Global Management has announced that funds managed by its affiliates have entered into a definitive agreement to acquire the thermal and emission control materials (Maftec) business of Mitsubishi Chemical, which produces and sells polycrystalline alumina fiber. Mitsubishi has confirmed that the deal is worth about ¥85 billion ($759 million). (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- Subject to customary closing conditions including regulatory approvals, the transaction is expected to be completed in March 2022. Mitsubishi says it expects to realize income of ¥54 billion related to the deal.
- The Maftec business makes polycrystalline alumina fiber from aluminum and silicon. It is a world leader in thermal and emission control protection materials, primarily for the industrial and automotive industry as original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) adapt their chemical fiber products to reduce emissions in traditional and hybrid vehicles, Apollo says. The business is also developing product applications for electric vehicle batteries, it says.
- Mitsui Chemicals and SKC Co. (Seoul, South Korea) plan to dissolve their joint venture (JV) Mitsui Chemicals & SKC Polyurethanes (MCNS; Seoul). The JV produces polyurethane (PU) raw materials including toluene diisocyanate (TDI), methylene di-para-phenylene isocyanate (MDI), polypropylene glycol (PPG), and PU system products. Mitsui says that customers will continue to receive products individually from Mitsui or SKC. Mitsui and SKC established MCNS in 2015 as a JV for their operations in PU raw materials. Mitsui says that over this period, discrepancies have started to arise in the policy of steadily improving earnings through high-performance products and bioproducts, and SKC's policy of quickly expanding scale. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- The Philippines' business confidence turned negative during the third quarter of 2021, undermined by the deterioration in local COVID-19 outbreak conditions and the reimposed strict containment measures in August. Meanwhile, consumer sentiment turned less pessimistic, but remained in the contraction territory, as consumers expect stronger labor and income conditions than those in previous quarters. Although the government has gradually eased containment measures despite elevated infections, concerns over the Delta variant, a slow vaccination campaign, and a still-challenging labor market will continue to weigh on domestic sentiment. (IHS Markit Economist Ling-Wei Chung)
- Business confidence over the Philippine economy turned negative during the third quarter of 2021, while consumer sentiment, although remaining in the contraction territory, improved, according to a quarterly survey conducted by the central bank Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP).
- Overall business confidence index for the current quarter dipped into the negative territory, coming in at -5.6%, which reversed from 1.4% in the second quarter. It followed three straight quarters of positive sentiment since recovering in the fourth quarter of 2020. In addition, the reading came in weaker than -5.3% posted in the third quarter of 2020 and was also the lowest level since the first quarter of 2009.
- Among sectors, business confidence worsened across the board in the third quarter of 2021, led by the hard-hit sectors by the pandemic. Sentiment of wholesale and retail trade sector came in especially weak, falling further to -16.9%, which widened from -9.5% in the second quarter and also marked the lowest reading since the first quarter of 2009. This was followed by -7.2% posted in the construction sector, with the sentiment turning negative for the first time since the third quarter of 2008. Confidence of the service sector also weakened to -2.4%, falling for the first time since the first quarter of 2009.

Posted 30 September 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.





