Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters

This guide highlights the key performance indicators (KPIs) for the cannabis industry and where investors should look to find an investment edge.
The cannabis industry encompasses all activities that are directly or indirectly involved in the production and sale of cannabis and its derived products. The primary activities of companies in the cannabis industry include the legal production, transportation, sale, and consumption or use of medical marijuana, recreational or adult-use marijuana, and hemp, as well as all products derived from them. The major stakeholders in the cannabis industry are cultivators, processors, medical and legal professionals, regulators, dispensaries, law enforcement, multinationals, and end-consumers.
The cannabis industry is a niche industry, which gained prominence around the late 1990s, but the industry growth was hindered by regulatory roadblocks in many countries. As the regulatory environment has evolved and continues to evolve, governments in many countries have now started to legalize cannabis for medical and adult use, prompting entrepreneurs and multinational companies to tap into this growing opportunity.
Regulations governing cannabis use, change in market perception, growth in the cannabis user base, usage frequency, medical advancements, and the development of new ways to consume cannabis are all major drivers that will determine the future of this industry. Companies in the cannabis industry are driving research, innovation, technology, and product development, to explore ways to increase their expertise in the application of cannabis, new forms of delivery, and expanding product range. The cannabis industry has grown and matured over the years as it continues to be advocated for its medicinal benefits. As a psychoactive drug, cannabis continues to find extensive favor among both recreational and medicinal users.

Key performance indicators (KPIs) are the most important business metrics for a particular industry. When understanding market expectations for Cannabis, whether at a company or industry level, some KPIs to consider are:
In the last two decades, the cannabis industry has grown significantly. Investors have increasingly shown interest and demonstrated participation in several aspects of the cannabis industry, with a key factor fueling the industry growth being the expanding demand for legal cannabis. As cannabis has steadily achieved legalized status in several U.S. states and also international markets, more companies are venturing into cannabis, its research and development, testing, and manufacturing.
Cannabis is a herbaceous plant, and also an umbrella term meant to refer to either marijuana and/or hemp. Cannabis products derived from its leaves, stems, seeds, and other parts can be used for both medicinal and adult-use purposes.
To understand its most popular uses, it is important to first define cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are a large group of chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant. Of these, two of note are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). THC is what creates the psychoactive effect– aka ‘high’– often associated with cannabis usage, while CBD does not. Instead, CBD is often utilized for health and relaxation purposes in that it offers medical benefits without the ‘high’. Some of the ways cannabinoids can be consumed include: smoking or vaping, ingesting it via drinking or eating, such as in brewed tea or edibles like brownies or candies, eating it raw, applying it as a topical treatment, or taking it as capsules or supplements.
(Sources: Medical News Today, and Investopedia)
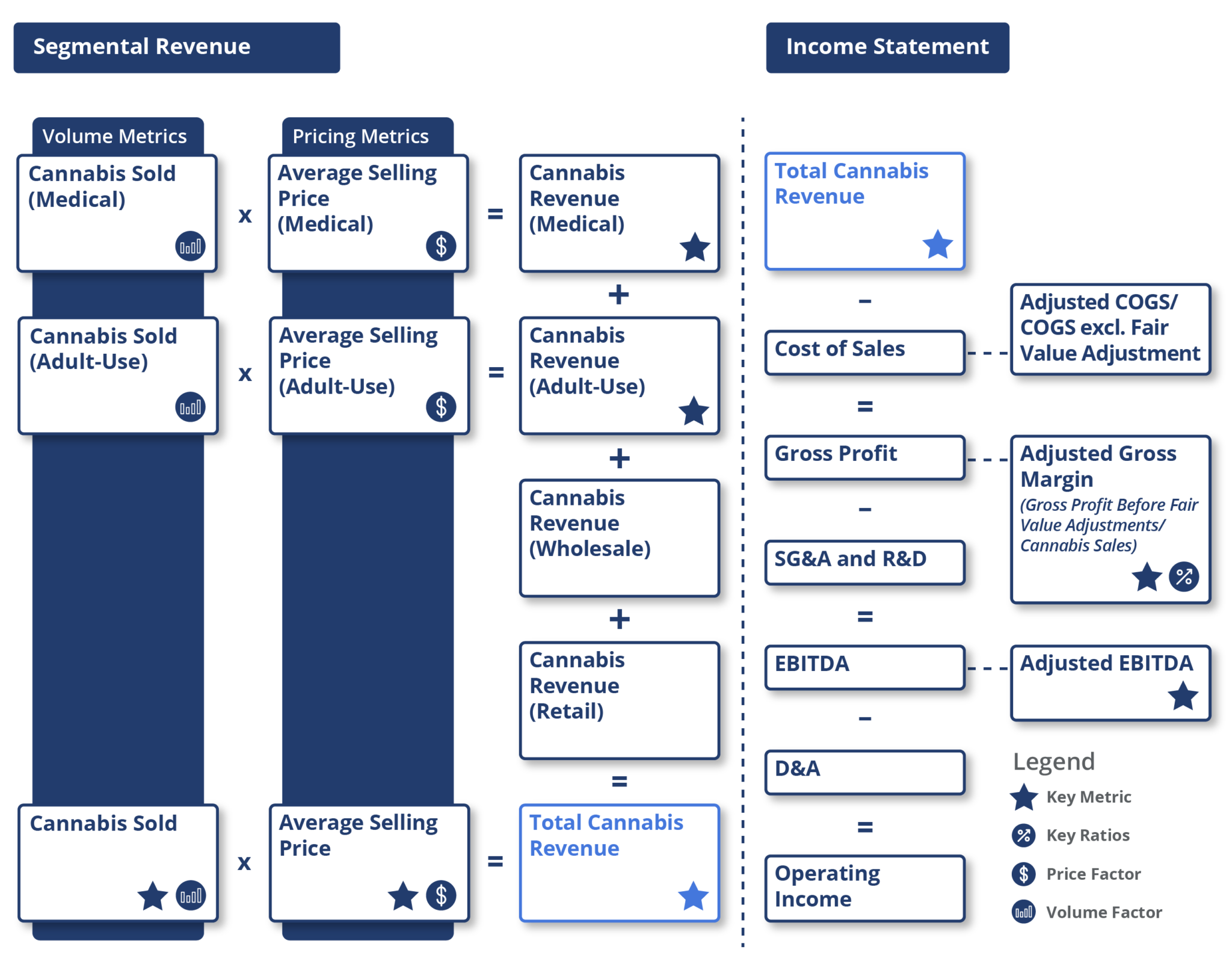
Companies in the cannabis industry generate revenue primarily from the volume of cannabis sold (kg/gram) and the average selling price (ASP) of cannabis per unit ($/gram or $/kg). This is applicable for both medical and adult-use cannabis segments.
Companies report both GAAP and fair value adjusted numbers for the cost of goods sold (COGS). Analysts primarily use the fair value of COGS for peer comparisons, which is generally adjusted for the aggregate gain/loss in the fair value of biological assets and inventory.
Gross margin and EBITDA margin are key profitability indicators that analysts look at in conjunction with valuation multiples like enterprise value / sales and enterprise value / EBITDA. Other useful operating metrics include acreage, production volume, cannabis sold (adult-use/medical), average selling price (ASP), number of stores, among others.
The cannabis industry requires large capital investments and cash flows to increase production capacity, expand product ranges, and fund operations. Free cash flow is one of the indicators that analysts track to understand the amount of cash flow required to maintain and expand.
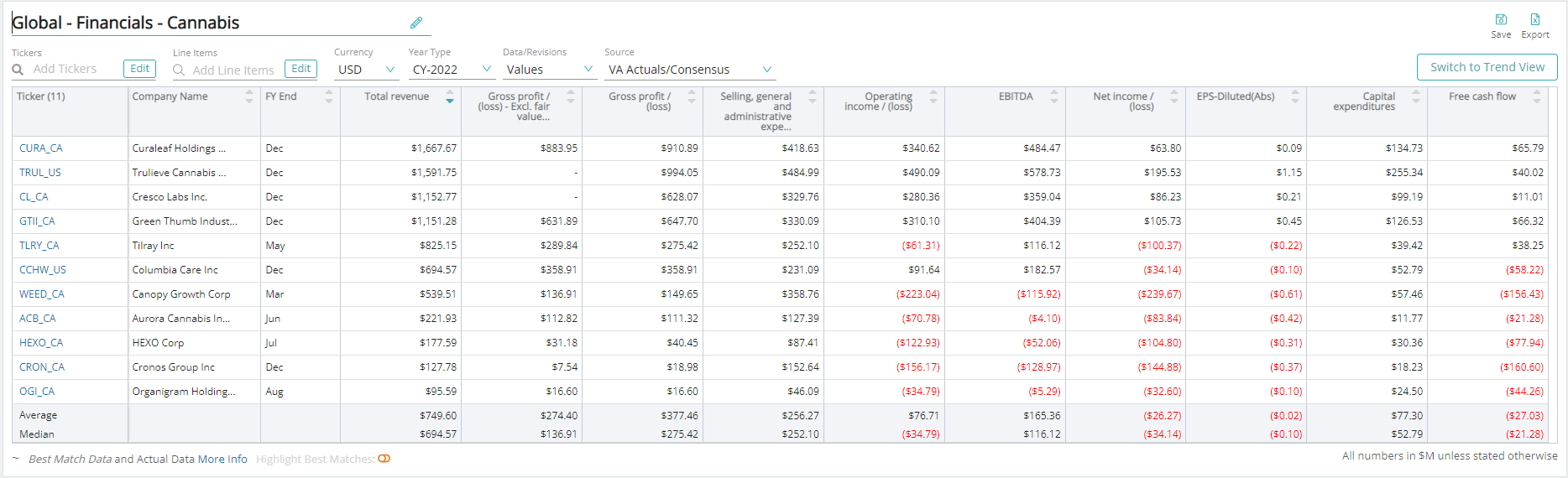
Visible Alpha offers five cannabis-related comp tables, comparing forecasts for key financial and operating metrics, to make it easy to quickly conduct relative analysis. Every pre-built, customizable comp table is based on region, sub-industry, or key operating metrics.
This guide highlights the key performance indicators for the cannabis industry and where investors should look to find an investment edge, including: