Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global 11 Apr, 2024 Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
The CHIPS Act and Semiconductor Supply Chains
Semiconductor supply chains are neither flexible nor resilient. Constructing a new chip-building facility costs billions of dollars, and the bulk of high-end semiconductor manufacturing is centralized in geopolitical hot spots. The Biden administration is attempting to reverse a decadeslong trend of allowing manufacturing to be relocated out of the US with the CHIPS and Science Act. The act is intended to subsidize manufacturing and workforce development to revitalize the US domestic semiconductor industry. But the impact of the CHIPS Act on the US economy and global supply chains may be years away.
“The US government is going to spend around $50 billion over the next five or so years to bolster the chip industry, and a quarter of that will go to [research and development] and workforce development, around three quarters will go to subsidizing manufacturing costs,” explained Chip War author Christopher Miller in a recent S&P Global podcast. “And the reason for this is that building a new chip-making facility in the US costs at least 20% more than it does in many parts of East Asia. The US wants to close the cost gap with places like Taiwan and Korea.”
According to Chris Rogers, head of supply chain research at S&P Global Market Intelligence, the chip industry merits this attention because it sits at the nexus of US national security and economic development policies. US policymakers are attempting to address supply chain weakness, boost national security and maintain a competitive position in the face of competition that enjoys significant foreign government support.
Government subsidies are already attracting private investment to semiconductor manufacturing. According to S&P Global Market Intelligence estimates, investment will rise 85% in 2024 versus 2019 in inflation-adjusted terms. The CHIPS Program Office has announced over $10 billion in grant awards and about $12.6 billion in loans to date to four semiconductor manufacturers across investments in eight states, according to S&P Global Ratings. However, many projects that have received grants and loans have gotten off to a rocky start due to demand uncertainty, permitting issues and pending environmental reviews.
Current demand for semiconductors is undergoing some cyclical weakness. New orders have been down in 18 of the past 19 months, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence. However, the requirements of generative AI and the needs of hyperscalers to invest to meet the growing demand for large language models seem to indicate brighter days ahead for semiconductor demand. Even if this increase in demand intersects with new facilities made possible by the CHIPS Act, success in rebuilding US semiconductor manufacturing is not guaranteed.
“The challenge is going to be, can this be sustainable over time?” Miller said. “Because I don’t think we should expect multiple CHIPS acts into the future. There’s going to be one, I think. And the goal is to have this initial expenditure of funds catalyze an industry that the US hopes will grow more over time.”
Today is Monday, April 8, 2024, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
- Written by Nathan Hunt.
UK Recruiters Signal Coolest Pay Growth For Over Three Years In March
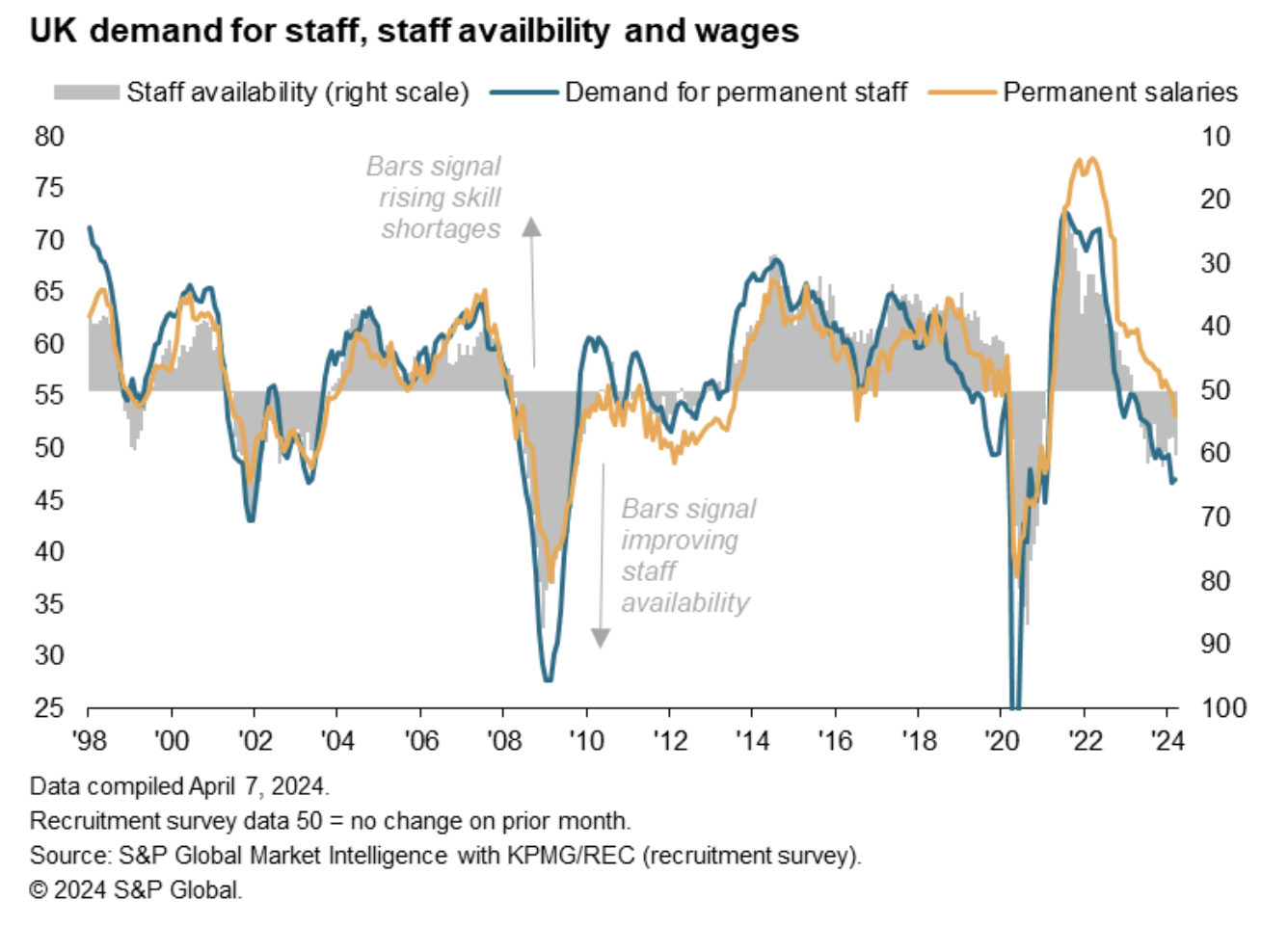
Recruitment industry survey data are particularly useful as they provide a leading indicator of the tightness of the labour market in terms of the balance of supply and demand for staff, as well as resulting pay pressures. With policymakers at the Bank of England eager to see signs of moderating pay growth prior to cutting interest rates, the latest data paint an encouraging picture. The March survey showed the slowest pay growth for over three years, as recruiters report reduced demand for staff and improving staff availability.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on the global economy >
Proceeds From REIT At-The-Market Programs Near All-Time Highs In Q4 2023

Proceeds raised by US equity real estate investment trusts through at-the-market programs increased in the fourth quarter of 2023, reaching nearly an all-time quarterly high for the sector. US REITs raised just over $6.65 billion in aggregate during the fourth quarter, a 30.1% increase over the $5.11 billion raised the quarter prior and a 13.6% rise year over year.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on capital markets >
Seaborne Trade In Russian Oil Under G7 Price Cap
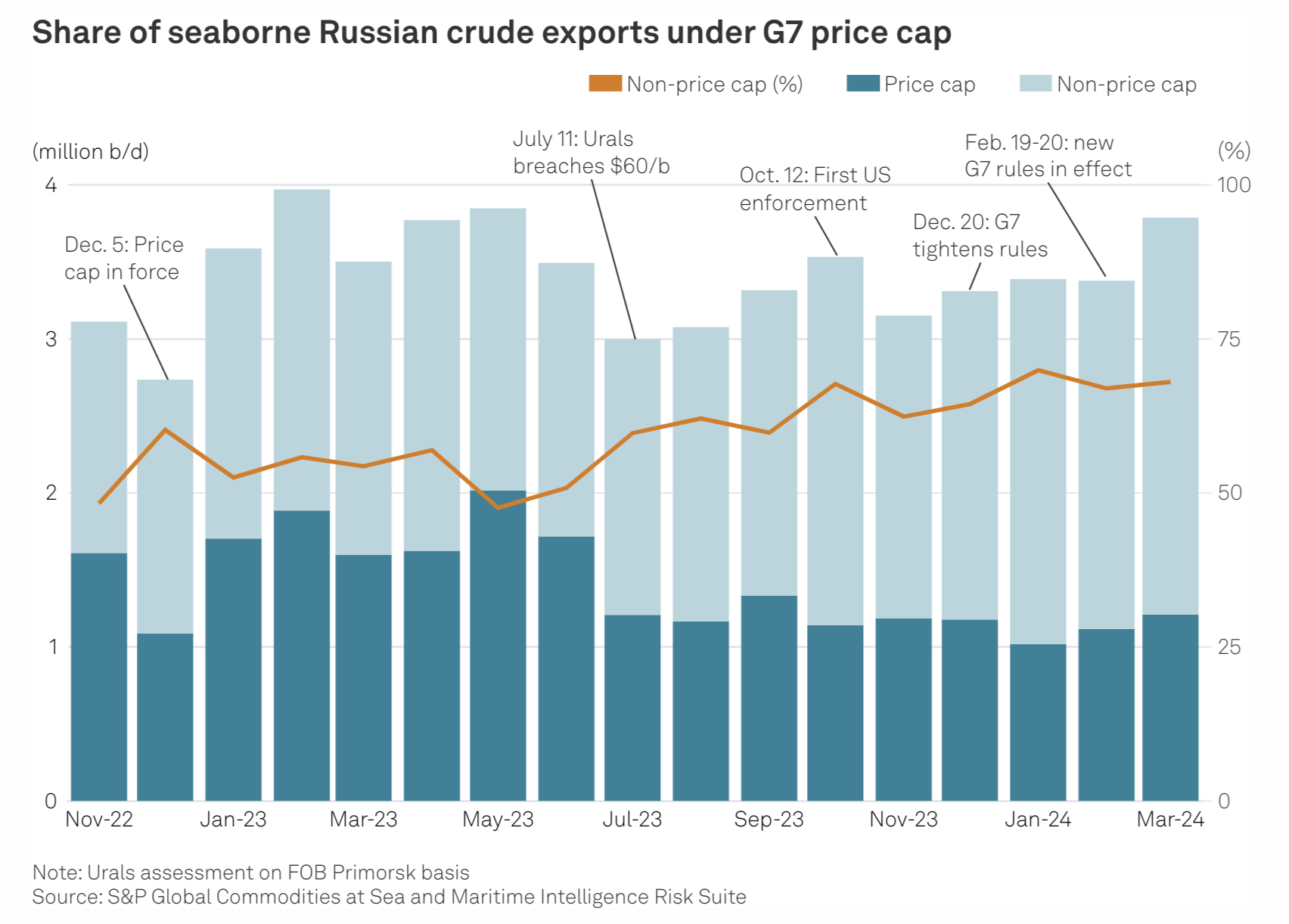
Russia, one of the world’s largest oil suppliers, has increasingly turned to non-Western firms to transport its crude to overseas buyers during its ongoing war with Ukraine. With a dual goal of undermining Russia’s war chest without creating significant disruptions to global supplies amid inflation pressure, G7 countries and their allies have banned tanker operators, insurers and other services firms from facilitating seaborne Russian crude exports unless the barrels are sold for no more than $60/b.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
Listen: CERAWeek: How Energy Transition Discussions Are Shifting
This week the ESG Insider podcast is covering key themes from one of the world’s largest energy conferences — the annual CERAWeek gathering hosted by S&P Global in Houston, Texas. The event convenes stakeholders from across sectors to discuss solutions to the biggest challenges facing the future of energy, the environment and climate — and the messaging from many speakers differed from what we hear about the pace of the energy transition at the climate or sustainability-focused events we have covered on this podcast.
—Listen and subscribe to ESG Insider, a podcast from S&P Global Sustainable1
Access more insights on sustainability >
Asian Iron Ore Spot Activity Picks Up In 2023 As Mills Sought To Shield Margins
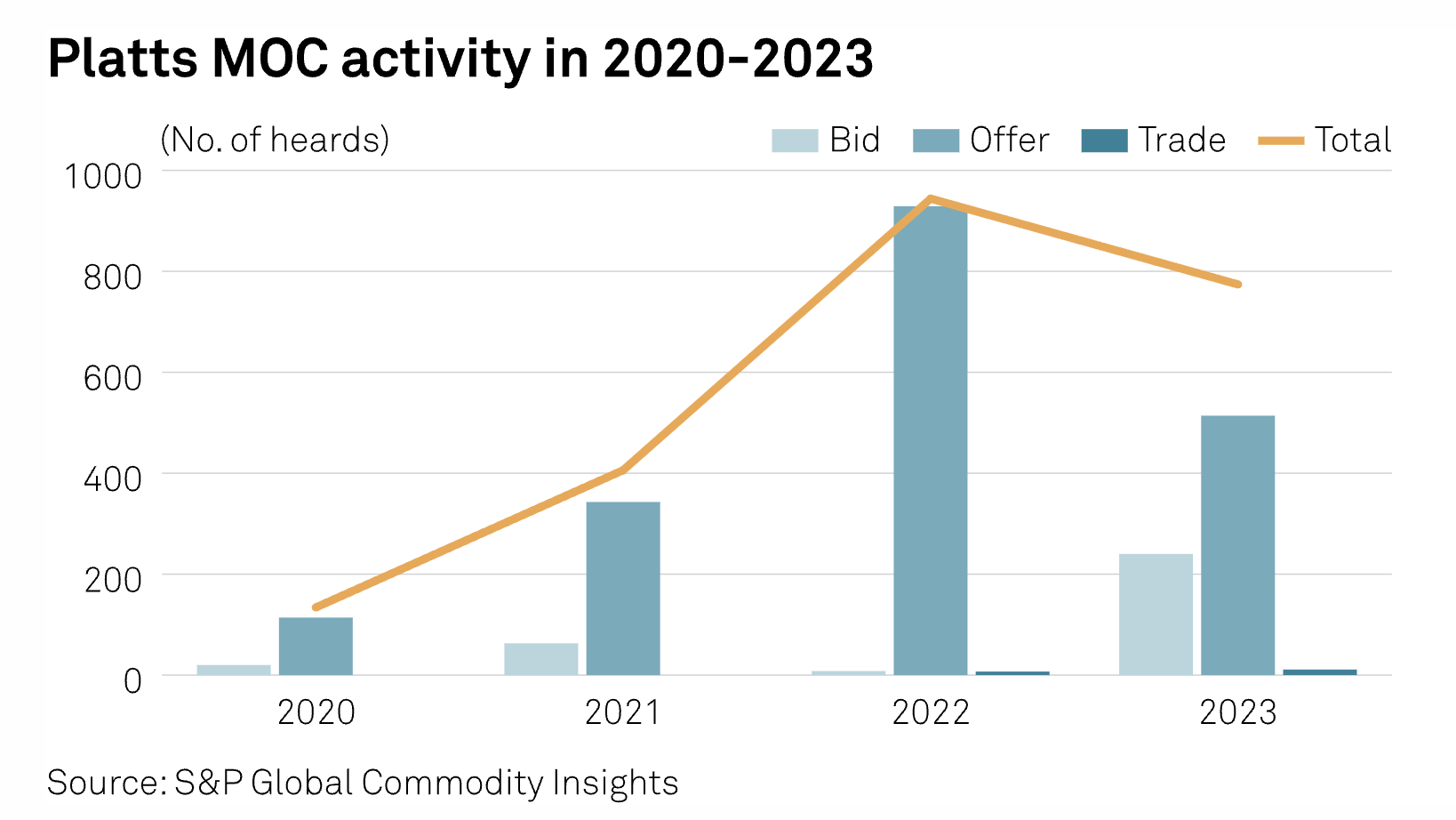
Spot activity in the Asian seaborne market for iron ore nudged higher in 2023, a year that saw Chinese steelmakers drift between positive and negative margins, as market participants placed bets on government policies to shore up a post-pandemic economy. As firm demand by Chinese mills pushed the country's iron ore imports to a record volume of 1.18 billion mt, the quantity of iron ore price data points – or heards – published by Platts, part of S&P Global Commodity Insights, rose 2.9% to 26,958 last year. These were in relation to fines, lump, pellet and concentrate cargoes.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
China E-Commerce Giants Face Their Biggest Test
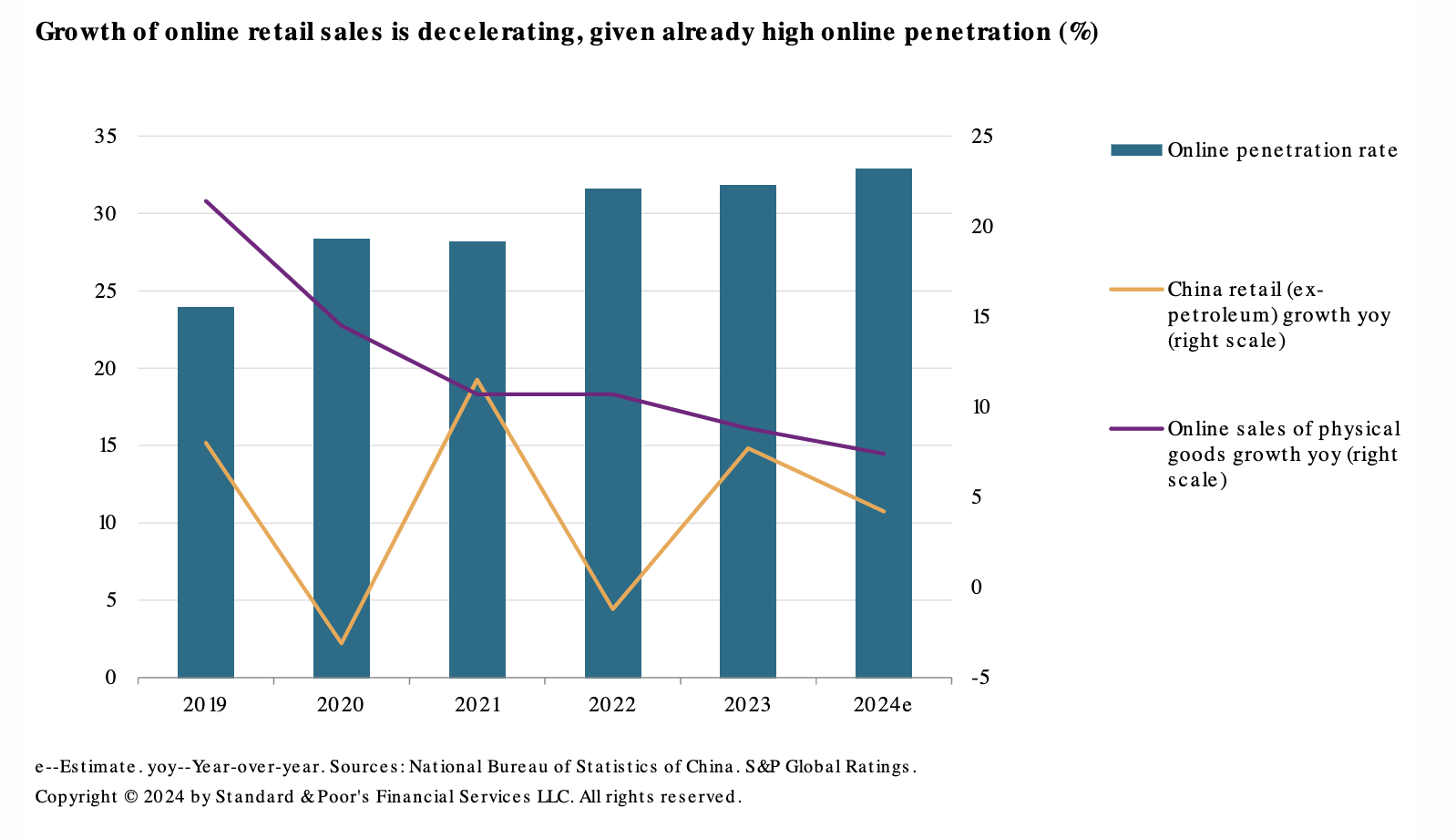
The pioneers of China e-commerce are on notice. Sector growth is stalling, competition is rising and consumers are tightening belts. The credit profiles of Alibaba Group Holding Ltd., JD.com Inc. and Vipshop Holdings Ltd. remain intact for now. But they're increasingly looking over their shoulders at PDD Holdings Inc., which is snapping for more market share. PDD has leveraged consumer desire for value-for-money deals. The company's focus on cheap unbranded products has catapulted it to the second most popular e-commerce platform in China. And its business model has been very profitable.
—Read the article from S&P Global Ratings
