Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — March 10, 2025

By Jim O'Reilly
The aggregate transmission rate base for a group of 26 companies in the PJM Interconnection LLC rose to $67.94 billion in 2024 from $63.15 billion in 2023, or 7.6%, a modest increase from the 7.0% growth recorded in 2023 and reversing five consecutive years of slowing annual growth for the 26-company group.

➤ A modest uptick in transmission rate base growth in PJM in 2024 may mark a turnaround from recent slowing growth in the region, as a combination of newly announced transmission projects and stable returns on equity (ROEs) could serve as catalysts for accelerating growth. Recent developments include new projects to meet rapidly increasing datacenter load and private equity investments in existing transmission assets.
➤ Transmission base ROEs for utilities in PJM have remained unchanged for the last few years, providing a stable and attractive regulatory environment for new capital investments in the transmission grid. A 50-basis-point ROE adder for most companies in PJM for participating in a regional transmission organization (RTO) remains in place, and 10 of the 26 companies have been authorized additional ROE incentive adders from 25 to 150 basis points for the companies' investments in specific transmission projects.
➤ While overall rate base growth year over year in PJM was moderate, growth among the parent companies and individual companies in PJM was very mixed based on data reported to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission in annual transmission formula rate updates filed by the companies. Two companies recorded declining rate base, while the remaining 24 companies recorded growth of 1.0% to 35.5%. The average growth recorded by the 26 companies was 9.6%.

Overview
Regulatory Research Associates annually publishes a series of transmission ratemaking analyses covering the six RTOs and independent system operators (ISOs) in the US, and an additional report covering 14 utilities in the West and Southeast regions of the US that are not members of an RTO/ISO. RRA also compiles the seven regional reports annually into one national report that analyzes a total of nearly 100 companies.
The 26 PJM companies in RRA's analysis represent just eight parent companies — American Electric Power Co. Inc. (AEP), Dominion Energy Inc., DQE Holdings LLC, Duke Energy Corp., Exelon Corp., FirstEnergy Corp., PPL Corp. and Public Service Enterprise Group Inc. (PSEG). Eighteen of the 26 companies are vertically integrated utilities and eight are transmission-only companies (transcos).
Regional growth
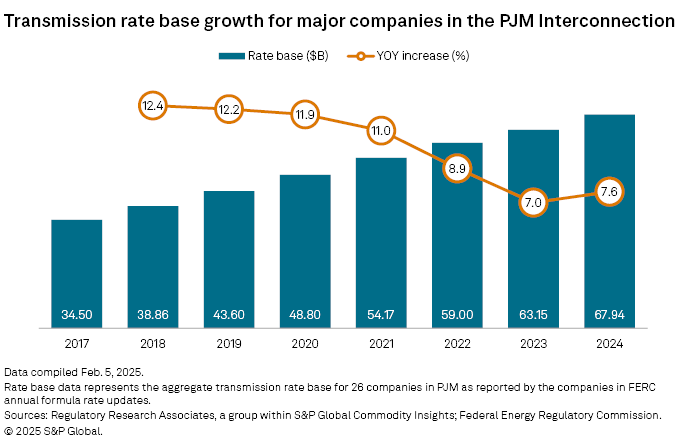
The aggregate rate base for the group of 26 companies in PJM rose to $67.94 billion in 2024 from $63.15 billion in 2023, or 7.6%. Prior to 2024, year-over-year annual growth for the 26-company group had slowed each year since 2018, from a high of 12.4% in 2018 to a low of 7.0% in 2023.
Despite the slowing growth from 2018 to 2023 and only the slight upturn in 2024, the 26-company group added approximately $5 billion in transmission rate base in each of the last seven years, nearly doubling the group's aggregate rate base from $34.50 billion in 2017 to $67.94 billion in 2024.
Recent developments in PJM point to the potential for accelerating capital investment in transmission by companies in the region. In April 2024, FERC approved PJM's cost allocation proposal for billions of dollars in transmission upgrades in large part to help meet datacenter demand growth in the region: FERC approves PJM's $5.1 billion transmission plan, dismisses datacenter cost concerns. On Dec. 31, 2024, a PSEG subsidiary asked the Maryland Public Service Commission to approve a new $424 million transmission project to help meet unprecedented load growth in Maryland and Virginia: PSEG unit files transmission application in Maryland to shore up PJM reliability.
In addition, in October 2024, leading transmission owners AEP, Dominion Energy and FirstEnergy agreed to jointly plan transmission projects throughout the PJM footprint: 3 utilities agree to partner on PJM transmission projects. Subsidiaries of the three utilities in the 26-company group combined represent approximately $35 billion in transmission rate base in PJM. Finally, in August 2024, PPL Corp. announced that nearly 5 GW of demand from datacenters in advanced development in Pennsylvania will require the company to make additional network investments of up to $450 million: PPL prepares for 17 GW of datacenter growth in Pennsylvania.
Parent companies
Rate base year-over-year growth for the 26-company group in PJM largely reflected modest growth for AEP, which represents approximately 26% of the total rate base for all 26 companies in this analysis. The aggregate rate base for all 11 AEP companies rose to $17.56 billion in 2024 from $16.47 billion in 2023, or 6.6%.
AEP's modest growth was mixed across the company's six operating utilities as a group and the company's five transcos as a group. AEP's six operating utilities combined recorded rate base growth of 7.6% in 2024, an increase from 5.6% in 2023, while AEP's five transcos recorded a growth of 5.9% in 2024, a decline from 8.2% growth in 2023.
Exelon's six operating utilities in PJM combined recorded somewhat higher year-over-year growth in 2024. The rate base for the six utilities rose to $11.97 billion in 2024 from $11.11 billion in 2023, or 7.7%. From 2022 to 2023, the rate base of the six companies combined rose 6.8%.
FirstEnergy, represented in the 26-company PJM group by three transco subsidiaries, recorded a more significant year-over-year increase in rate base growth in 2024. The transcos combined rate base of $8.00 billion in 2024 was an increase from $7.34 billion in 2023, or 8.9%, versus a 7.4% growth recorded by the same companies from 2022 to 2023.
Duke Energy's two subsidiaries in PJM recorded strong double-digit rate base growth for the second consecutive year. Duke Energy Kentucky Inc. and Duke Energy Ohio Inc. reported a combined rate base of $1.22 billion in 2024, an increase from $1.09 billion in 2023, or 11.8%. The combined rate base for the two Duke companies rose to $1.09 billion in 2023 from $990.0 million in 2022, or 10.6%.
The accompanying table highlights the 26 PJM companies covered in this analysis, their reported transmission rate base for 2023 and 2024, their base ROE and any ROE incentive adders where applicable.
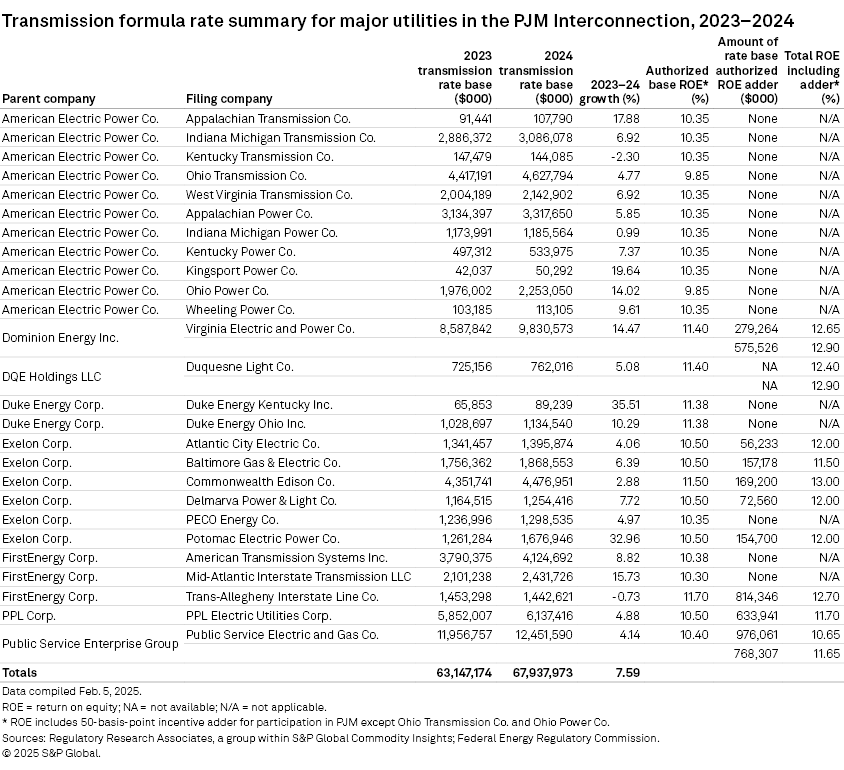
Refer to the linked data tables for transmission rate base, authorized ROEs and other ratemaking parameters from 2018 through 2024 for the 26 companies in PJM by parent company and an appendix containing transmission rate base data for the same companies from 2011 through 2024 as available.
Individual companies
Year-over-year rate base growth among the 26 individual companies in PJM in the analysis ranged widely regardless of parent company, geography, company size or business model. From 2023 to 2024, eight of the 26 companies recorded strong growth of more than 10%, nine recorded moderate growth between 5% and 10% and nine companies recorded relatively slow growth of less than 5%.
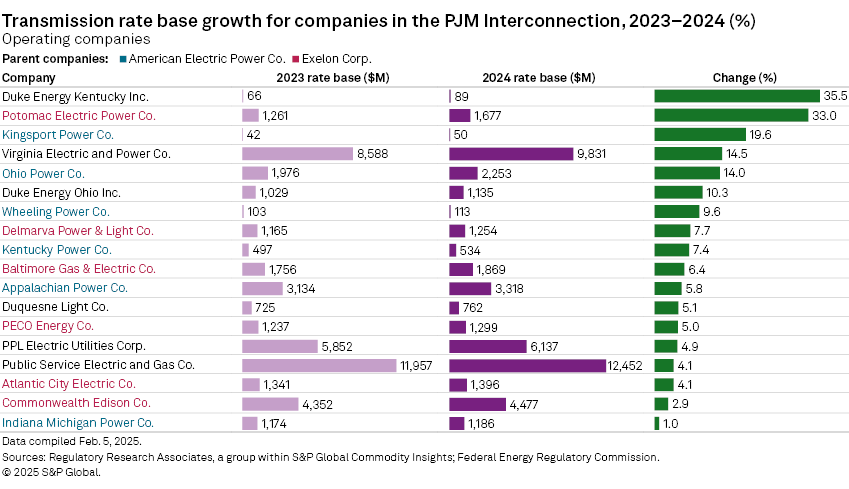
Thirteen companies in the 26-company group reported a rate base of more than $1.5 billion in 2024. Growth for these 13 companies was led by 33.0% growth recorded by Exelon's Potomac Electric Power Co. (Pepco). The lowest growth among the 13 companies was also recorded by an Exelon subsidiary, Commonwealth Edison Co., which recorded growth of just 2.9%. PSEG subsidiary Public Service Electric and Gas Co. (PSE&G), the largest company in the overall group of 26 companies and representing more than 18% of the total rate base in this analysis, recorded year-over-year growth of only 4.1%.
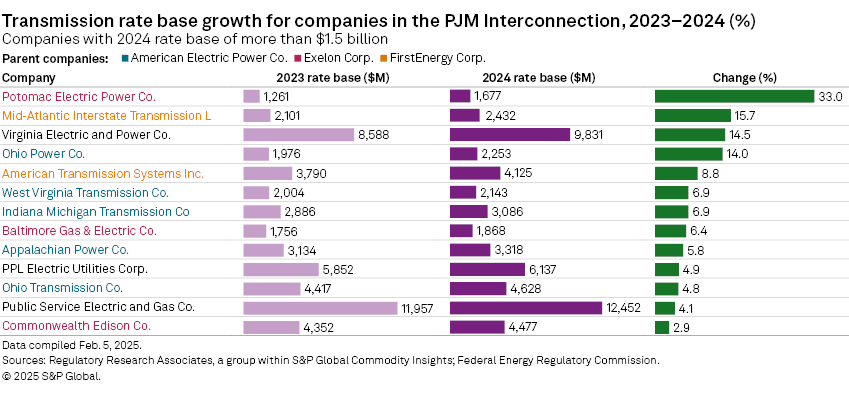
Of the 13 companies that reported a rate base of less than $1.5 billion, year-over-year growth was led by the 35.5% growth recorded by Duke Energy Kentucky, one of the smallest companies in the PJM group.
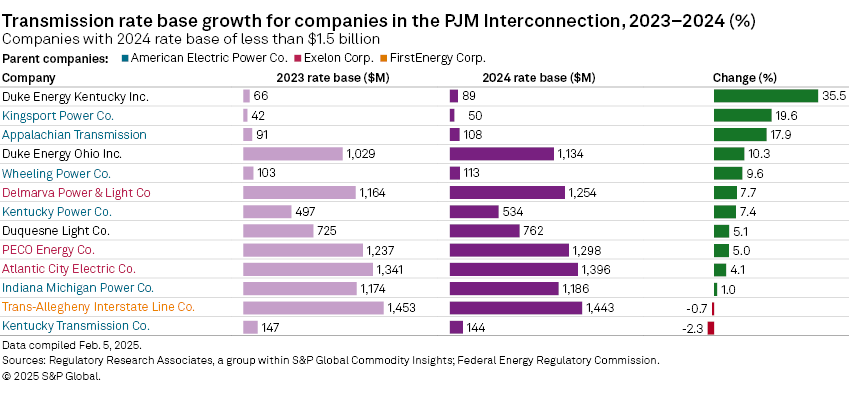
Segmented by business model, the eight transcos in the analysis combined — all subsidiaries of either AEP or FirstEnergy — represented $18.11 billion in rate base and recorded year-over-year growth of 7.2%. Within the group of transcos, below average growth or declining rate base for AEP Ohio Transmission Co. Inc. and AEP Kentucky Transmission Co. Inc. and FirstEnergy's Trans-Allegheny Interstate Line Co. (TrAILCo) was offset by relatively strong growth recorded by FirstEnergy's American Transmission Systems Inc. (ATSI) and Mid-Atlantic Interstate Transmission. (MAIT).
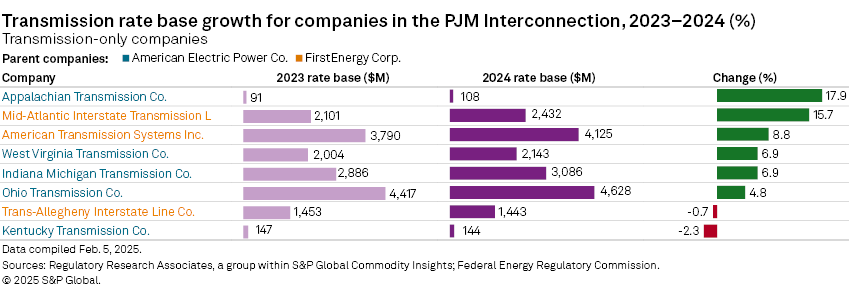
FirstEnergy and AEP have recently sold equity stakes in certain transco subsidiaries in PJM. In 2024, FirstEnergy completed the sale of an additional 30% stake in FirstEnergy Transmission LLC to Brookfield Super-Core Infrastructure Partners LP: FirstEnergy receives final proceeds from $3.5B transmission stake sale. Brookfield previously purchased a 19.9% interest in FirstEnergy Transmission for $2.4 billion in 2022. FirstEnergy Transmission is the holding company of the three FirstEnergy transcos in this analysis — ATSI, MAIT and TrAILCo.
AEP announced on Jan. 9, 2025, that it will sell a 19.9% equity interest in its AEP Ohio Transmission and AEP Indiana Michigan Transmission Co. subsidiaries to a 50/50 partnership between KKR & Co. Inc. and Canada's Public Sector Pension Investment Board: AEP to sell minority stake in transmission assets to investment firms for $2.8 billion. The two companies are AEP's largest transcos in PJM and represent over $7 billion in transmission rate base, more than the transmission rate base of AEP's six operating utilities in PJM combined.
The 18 operating utilities in the analysis, which accounted for $49.83 billion in rate base in 2024, recorded year-over-year growth of 7.7%. Among the operating companies, PSE&G and PPL Electric Utilities Corp. — two of the largest companies in the group — recorded slow growth of less than 5%, while Exelon subsidiary Pepco, Dominion Energy's Virginia Electric and Power Co. and AEP's Ohio Power Co. recorded strong growth of 14% or higher.
Return on equity in PJM
FERC has established base ROEs for transmission owners in PJM on a company-by-company basis, ranging from 9.80% for MAIT to 11.20% for TrAILCo. While MAIT and TrAILCo are both FirstEnergy transcodes, the two companies have significantly different origins and asset profiles.
TrAILCo's primary asset is the Trans-Allegheny Interstate Line (TrAIL) project, a 240-mile, 500-kV transmission line from southwestern Pennsylvania through West Virginia to Northern Virginia. The project had an estimated cost of over $1 billion and was completed in 2011. In 2008, FERC approved a settlement that established an 11.20% base ROE for TrAILCo, plus a 50-basis-point ROE adder for the company's participation in the PJM RTO (RTO adder). FERC also authorized an additional incentive ROE of 100 basis points for the TrAIL project for a total ROE of 12.70%. The commission determined an enhanced ROE was warranted for the TrAIL project because, among other things, the project's length, scope and multistate nature presented substantial risks and challenges in siting and obtaining required permits.
MAIT was formed in 2017 as a stand-alone transco to acquire the existing transmission assets owned by FirstEnergy utility subsidiaries Metropolitan Edison Co. and Pennsylvania Electric Co. in Pennsylvania. MAIT's 9.80% base ROE was established by a settlement of the company's initial formula rate proceeding at FERC in 2018. The settlement also authorized the 50-basis-point RTO adder for MAIT's participation in PJM.
The other 24 companies in RRA's PJM analysis were also previously authorized the 50-basis-point RTO adder for participating in PJM. However, in 2021, FERC determined that The Dayton Power and Light Co. (DP&L) did not qualify for the RTO adder because state law required the company to join an RTO: Split FERC pulls RTO participation rate adder for Dayton, orders refunds: DP&L is known legally as AES Ohio.
In 2022, FERC found that AEP's two Ohio subsidiaries — Ohio Power Co. and AEP Ohio Transmission Co. — also no longer qualified for the RTO adder due to the Ohio law that requires the utilities to join an RTO: FERC yanks ROE boost for AEP Ohio utilities, retains for Duke, FirstEnergy. In the same order, however, FERC declined to remove the RTO adder for FirstEnergy's ATSI and Duke Energy Ohio. The commission noted the adder for the two companies was agreed to as part of separate, uncontested settlements between the utilities and their customers and "we do not find it would be appropriate to change unilaterally a single aspect of such a comprehensive settlement, at least absent evidence that the overall ROE has become unjust and unreasonable…."
After the utilities appealed FERC's orders to the US Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit, the court issued a decision on Jan. 17, 2025, that upheld the commission's decisions, removing the RTO adder for DP&L and AEP's two Ohio subsidiaries. However, the court found that FERC acted arbitrarily and capriciously in continuing to authorize the RTO adder for ATSI and Duke Energy Ohio because it was part of negotiated settlement agreements. The court stated, "[c]ontrary to FERC's assertion, whether it approved the RTO adder explicitly on a 'single issue' basis or impliedly as part of a settlement makes little difference to how the three utilities approached rate negotiations." The court remanded the case to FERC to revise its decision for ATSI and Duke Energy Ohio: Court upholds FERC's denial of RTO incentives for Dayton Power.
Apart from the 50-basis-point RTO adder, 10 of the 26 PJM companies in RRA's analysis have been authorized additional ROE incentive adders from 25 to 150 basis points for the companies' investments in specific transmission projects.
RRA's transmission analyses and PJM companies
Given the complexities inherent in determining a company's rate base from an outside perspective, the RRA analyses of transmission ratemaking, with very limited exceptions, include transmission rate base only for those companies that report such data in their annual updates under a formula-based rate framework. The mechanics of determining rate base — the items that may be reflected in rates at a given time and how their value should be calculated for ratemaking purposes — are explained in greater detail in Rate base: it's more complicated than it sounds.
The transmission rate base and other data in RRA's analyses are drawn from the companies' initial formula rate updates filed each year and may not reflect subsequent revisions or true-ups filed by any of the companies.
RRA first published this analysis of utilities in PJM in 2015. The first report compiled five years of rate base and other data — 2015 data and four years of historical data. RRA has subsequently published annual updates to that first report for a total historical dataset covering 14 full years from 2011 through 2024, where available.
To arrive at the roster of 26 companies in this analysis, RRA initially selected 25 companies in PJM for the first report published in 2015 with formula rates that had been in effect for at least five years. In 2017, FirstEnergy subsidiary MAIT and Exelon subsidiary PECO Energy were added to the group after FERC approved the two companies' proposals to transition from stated transmission rates to formula rates.
In 2018, the canceled Potomac-Appalachian Transmission Highline LLC (PATH) project was removed from the group after the company's transmission rate base dropped to $3.4 million. PATH, a joint venture formed in 2007 between AEP and FirstEnergy, was a proposed $2.1 billion transmission line between West Virginia and Maryland. In 2012, PJM canceled PATH after determining reliability needs, justifying the project development no longer existed.
Data visualization by Chrisallen Villanueva.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
For a complete, searchable listing of RRA's in-depth research and analysis, please go to the S&P Capital IQ Pro Energy Research Library.
Regulatory Research Associates is a group within S&P Global Commodity Insights.
S&P Global Commodity Insights produces content for distribution on S&P Capital IQ Pro.
Theme
Location
Products & Offerings
Segment