Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
ECONOMICS COMMENTARY — Jul 01, 2022
The S&P Global Eurozone Manufacturing PMI® fell from 54.6 in May to 52.1 in June, its lowest reading since August 2020 and a fifth consecutive month of decline in the headline measure.
Driving the deterioration was a contraction of output in June, which dropped for the first time in two years.
Worse looks set to come, according to the survey's other sub-indices. Several survey gauges are now consistent with an imminent industrial recession and period of economic distress, as explored further in the following analysis.
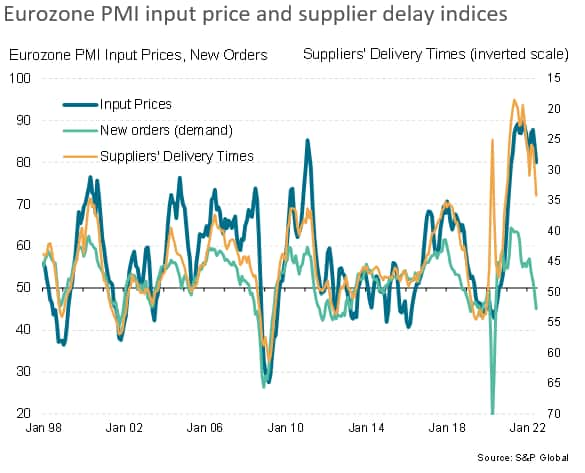
One upside to the weakening of business conditions in the sector was a cooling of price pressures, albeit with energy and food supply remaining major concerns in the outlook for inflation.

The first drop in production for two years was primarily a function of a steepening downturn in demand. Orders for goods have fallen at an accelerating rate over the past two months, dropping in June in every country surveyed with the exception of the Netherlands, and even here the rate of growth has weakened markedly in recent months. The overall drop in eurozone manufacturing new orders was among the steepest seen over the past decade, with demand falling across the board for consumer goods, investment goods and intermediate goods (the latter referring to inputs supplied to other companies).
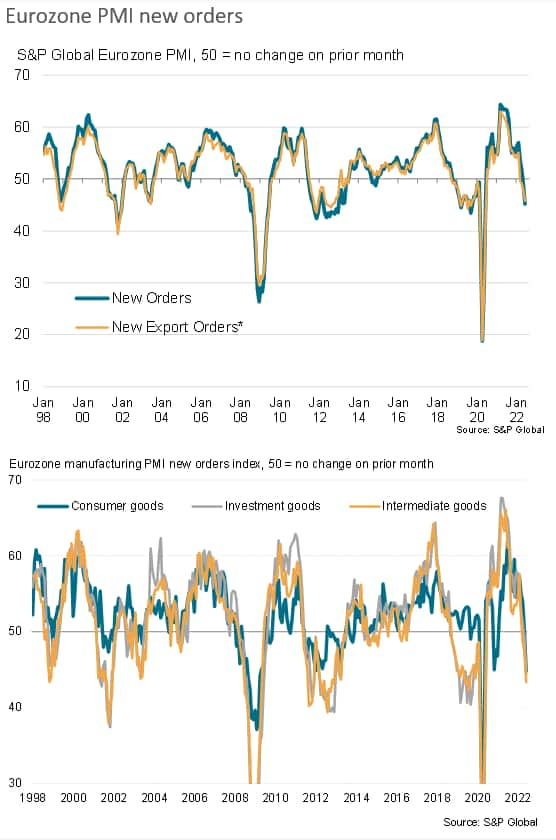
Demand is now weakening as firms report customers to be growing more cautious in relation to spending due to rising prices and the uncertain economic outlook.
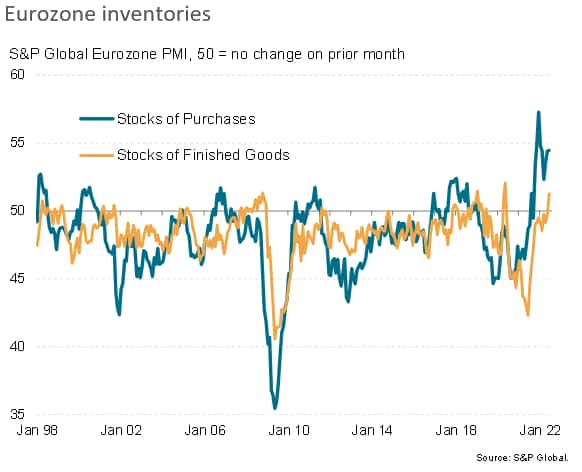
Looking at inventories, both raw materials and unsold stock are now rising due to lower than expected production and sales volumes respectively, hinting that an inventory correction will act as an additional drag on the sector in coming months.
Looking at the resulting new-orders-to-inventory ratio, which acts as a reliable lead indicator of output, this gauge has fallen to a level for which only the global financial crisis and initial impact of the pandemic saw more distressed readings.
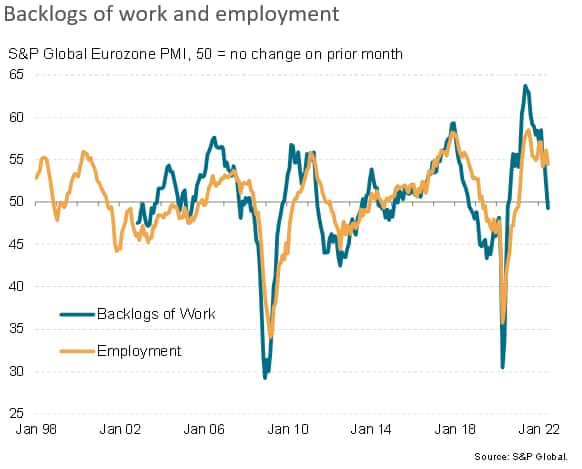
Backlogs of work are meanwhile falling, which is often a prelude to firms reducing operating capacity. This reduction normally takes the form of both lower employment and lower business investment in capital equipment.
In fact, as noted above, new orders for investment goods are already falling sharply, which is in turn linked to business confidence in the outlook having fallen to the gloomiest for just over two years and a level consistent with economic stress.
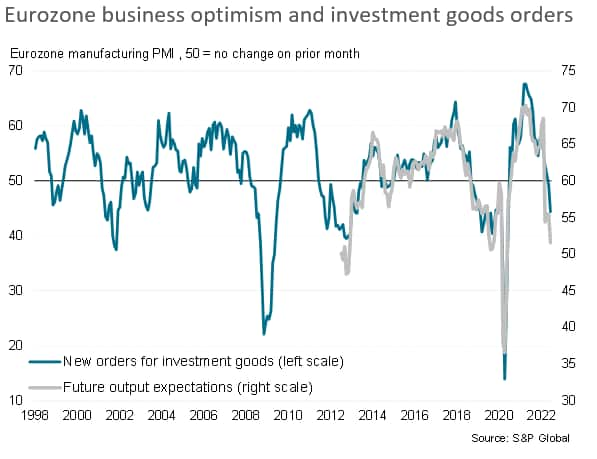
One upside to the recent weakening of demand is an alleviation of some supply chain constraints, which has in turn helped cool inflationary pressures for industrial goods. With the survey data indicating an increasing likelihood of the manufacturing sector slipping into a recession, these price pressures should ease further in the third quarter.
Chris Williamson, Chief Business Economist, S&P Global Market Intelligence
Tel: +44 207 260 2329
chris.williamson@spglobal.com
© 2022, IHS Markit Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI™) data are compiled by IHS Markit for more than 40 economies worldwide. The monthly data are derived from surveys of senior executives at private sector companies, and are available only via subscription. The PMI dataset features a headline number, which indicates the overall health of an economy, and sub-indices, which provide insights into other key economic drivers such as GDP, inflation, exports, capacity utilization, employment and inventories. The PMI data are used by financial and corporate professionals to better understand where economies and markets are headed, and to uncover opportunities.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
Location
