All major APAC, European, and US equity indices closed higher on the day and none were in negative territory at any point during the trading day. US government bonds closed sharply lower and benchmark European bonds were mixed. European iTraxx and CDX-NA closed tighter across IG and high yield. Natural gas, oil, copper, and silver closed higher, while the US dollar and gold were lower on the day. All eyes will be on tomorrow morning's 8:30am ET release of the US non-farm payroll report.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- All major US equity indices closed higher and none were in negative territory at any point during the trading day; Russell 2000 +1.6%, Nasdaq +1.1%, DJIA +1.0%, and S&P 500 +0.8%.
- 10yr US govt bond closed +5bps/1.58% yield and 30yr bonds +5bps/2.13% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed -1bp/53bps and CDX-NAHY -1bp/304bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.1%/94.22.
- Gold closed -0.1%/$1,759 per troy oz, silver +0.6%/$22.66 per troy oz, and copper +2.3%/$4.24 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +1.1%/$78.30 per barrel and natural gas closed +1.9%/$5.78 per mmbtu.
- The latest forecast from the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) reinforces messages that have been coming for the past year from international bodies, independent analysts, and climate advocates: at its current trajectory, humanity will fall far short of the Paris Agreement goal of reaching net-zero emissions by 2050. (IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Kevin Adler)
- EIA's conclusion in its "International Energy Outlook 2021," released 6 October is that global energy demand will rise by 50% between 2020 and 2050, and carry annual CO2 emissions from this sector 24.7% higher.
- Annual energy CO2 emissions in 2050 will total 42.839 billion metric tons (mt) globally, representing a yearly average gain of 0.7% from 2020 onwards.
- EIA projects that renewable energy will make significant inroads in the global power mix by 2050, rising by 3.3% per year (compared with 1% for oil and 0.9% for natural gas). It says that batteries will contribute to reliability. Yet it states that gas and coal will be needed to meet power demand as well.
- Renewable generation will nearly triple from 65.1 quadrillion Btu in 2020 to 191.7 quadrillion Btu in 2050. This will place its share of the power market at about 58.4% in 2050, compared with about 27.6% today.
- Considering all end uses for energy-residential, commercial, industrial, and transportation-fossil fuels still will provide a large share, particularly for industry and transportation in 2050. However, it is worth noting that EIA places renewables' share of energy consumption (235.2 quadrillion Btu) nearly on par with hydrocarbon-based liquid fuels (248.5 quadrillion Btu), and ahead of gas and coal.
- Rising consumption of fossil fuels will overwhelm the improvements anticipated in the carbon intensity of energy production and usage, thus leading to the net gain in CO2 emissions.
- US seasonally adjusted initial claims for unemployment insurance decreased by 38,000 to 326,000 in the week ended 2 October. The not seasonally adjusted (NSA) tally of initial claims fell by 41,431 to 258,909. While the level of initial claims has resumed its downward trend and is far below the pandemic-era high, initial claims closer to 200,000 would suggest a normal level of "churn" for an economy in its prime. (IHS Markit Economist Akshat Goel)
- Seasonally adjusted continuing claims (in regular state programs) fell by 97,000 to 2,714,000 in the week ended 25 September, hitting its lowest since 14 March 2020. The insured unemployment rate edged down 0.1 percentage point to 2.0%.
- In the week ended 18 September, continuing claims for Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC) fell by 360,999 to 630,814.
- Individuals who otherwise would not have qualified for benefits in regular programs were eligible for benefits under the Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) program; this program also ended on 4 September. In the week ended 18 September, continuing claims for PUA fell by 411,558 to 647,690.
- In the week ended 18 September, the unadjusted total of continuing claims for benefits in all programs fell by 854,638 to 4,172,943.
- US employers announced 17,895 planned layoffs in September, according to Challenger, Gray & Christmas, up 14% from a 24-year low of 15,723 in August. The total for September is 85% lower than the September 2020 reading. (IHS Markit Economist Juan Turcios)
- For the year to date, 265,221 job cuts have been announced, down from the 2,082,262 job cuts announced over the same period in 2020 and the lowest January-September total on record (Challenger began tracking job-cut announcements in January 1993).
- According to Andrew Challenger, senior vice president of Challenger, Gray & Christmas, "These numbers are still incredibly low. Employers are devising ways to meet the needs of their employees, whether by addressing burnout and the desire for flexibility, raising wages, offering support for child and family care issues, or being more deliberate in their workers' career development plans. They want to retain, not cut."
- So far this year, employers have cited COVID-19 as a reason for 8,684 planned job cuts. In September, only 234 planned job cuts were due to COVID-19 despite the elevated count in new cases due to the Delta variant. Employers have cited other reasons, including closing (53,571), market conditions (48,148), restructuring (47,297), demand downturn (45,614), and acquisition/merger (12,225) more frequently than COVID-19 as causes of job-cut announcements this year.
- Aerospace/defense has announced 33,646 job cuts this year, the highest number of any industry. Rounding out the five sectors that have reported the most job cuts this year are telecommunications (25,148), services (22,505), energy (19,545), and health care/products (18,936).
- US outstanding nonmortgage consumer credit rose $14.4 billion to $4.35 trillion in August, slower than earlier in the year. (US Regional Economics)
- The 12-month change in outstanding consumer credit was 4.8%, above the change in June, but most of that reflects 2020 moves.
- Revolving credit rose $3.0 billion, a far smaller rise than June's $18.2 billion; revolving credit has risen 2.1% over the past 12 months, far below consumer price gains.
- General Motors (GM) has announced the next evolution of its Super Cruise eyes-on-road, hands-free driver-assistance system, Ultra Cruise, which is due on premium vehicles in 2023. GM says the new-generation system can handle 95% of driving situations and adds lidar to the suite of sensors. When Ultra Cruise is launched, it will cover more than 2 million miles of road in the United States and Canada, compared with Super Cruise's current ability to handle 200,000 miles of highway. GM plans to expand the road coverage to more than 3.4 million miles. GM's Doug Parks says the Ultra Cruise system was developed completely in-house. Ultra Cruise is to be offered alongside Super Cruise, with Ultra Cruise to be offered on premium products and Super Cruise on more mainstream products. GM says that, ultimately, this strategy will help speed deployment of hands-free driver-assistance systems across its product line-ups, with one tailored for a more-affordable price point. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Uber is piloting new app features designed to improve the air travel experience, reports TechCrunch. The Uber Reserve feature will allow users at 20 major airports across the US to book a ride up to 30 days in advance. The new feature also allows sharing of flight information with drivers so they can track the progress in real-time. In addition, the company is deploying machine-learning technology to improve curbside pickups. Uber is also offering 60 minutes of complimentary wait time at no additional charge. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Autonomous mobility solutions provider Beep will launch a trial project by deploying a new fleet of autonomous shuttles for residents in the city of Peachtree Corners, Georgia (United States). The project, named PAUL (Piloting Autonomous Use Locally), will use autonomous shuttles manufactured by Navya and Local Motors. The vehicles will operate along the Technology Parkway and will include seven stops at popular destinations in the area. Each shuttle is equipped with a 5G gateway to power telematics data and enable interaction using T-Mobile's 5G connected infrastructure. In addition, cloud provider OVHcloud will allow the city and select technology partners to gain critical insights and make informed decisions using the data generated from the autonomous vehicles (AVs) and sensors. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Kyte, a fleet-logistics platform, has raised USD30 million in a Series A funding round led by Park West Asset Management and Sterling Road, according to a company statement. DN Capital, Amplo, 1984 Ventures, FundersClub, Moving Capital, Rosecliff Ventures, Seraph Group, Unpopular Ventures, Urban Innovation Fund, and the founders of German transportation unicorn FlixBus also participated in the round. The company plans to use the infused capital for product development, geographic expansion, and growth across new product lines. Kyte, which was founded in 2019, allows customers to order rental cars through its platform to be delivered at their doorsteps. The company currently operates in 10 major US cities and has raised USD40 million in funding. Kyte's on-demand cars are currently delivered by drivers, but in the future, the company plans to build a platform that can deliver vehicles via teleoperation or an autonomous system. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Canada's Ivey Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) rose 4.4 points to 70.4. The price index was the biggest mover, sharply rebounding as purchasing managers are noting strong inflation pressures. (IHS Markit Economist Chul-Woo Hong)
- The supplier deliveries index increased, but well within the contraction reading since conditions deteriorated in November 2020.
- The employment index fell to 63.7, suggesting moderate job growth.
- The 2.6-point decline in the inventories indexes suggests that inventory accumulation is more modest given supply chain constraints.
- German pharma major Bayer announced a USD200-million investment in the construction of a new manufacturing plant for the production of long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) in Costa Rica. The plant will be located in the Coyol Industrial Park in the Alajuela district, and it is expected to become operational by 2024. The site will produce hormonal implants and hormonal intrauterine systems (IUS). The construction of the factory is part of a broader plan of investment announced by the company as a strategy to increase access to modern contraception in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), which also involves the expansion of manufacturing capabilities in Finland. The investment plan will help Bayer achieve the goal of supplying 100 million women and girls in LMICs with access to family planning by 2030. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Ewa Oliveira da Silva)
- The latest data from the National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE) showed that Colombia's consumer price index (CPI) edged up to 4.5% year on year (y/y) in September from 4.4% y/y in August, as IHS Markit had expected, remaining above the upper limit target set by Banrep. The central bank targets inflation at 3.0% +/- 1 percentage point. (IHS Markit Economist Dariana Tani)
- The year-on-year rise in September's CIP was also the highest since April 2017. Core inflation, as measured by the CPI that excludes food and energy prices, rose by 2.6% y/y, almost unchanged from the 2.7% y/y posted in August.
- On a month-on-month (m/m) basis, the consumer price index rose by 0.38% m/m compared with an increase of 0.45% m/m in August. This was the third consecutive month that the index posted a monthly increase and was slightly lower than our own September's monthly forecast (0.46%).

Europe/Middle East/Africa
- All major European equity indices closed higher and none were in negative territory at any point during the trading day; Spain +2.1%, Germany +1.9%, France +1.7%, Italy +1.5%, and UK +1.2%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy -4bps, Germany/France -1bp, Spain flat, and UK +1bp.
- iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/51bps and iTraxx-Xover -7bps/259bps.
- Brent crude closed +1.1%/$81.95 per barrel.
- UK-based startup Wayve has raised GBP10 million (USD13.6 million) in funding from British online grocer Ocado Group, according to a company statement. This investment is a strategic partnership under which Wayve's technology will be deployed in selected Ocado delivery vans that will be used in an autonomous delivery trial. Wayve's data-collection devices will be installed in Ocado's delivery fleet to provide data for training and validation of Wayve's technology. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Following its most recent policy-setting meeting on 10 September, the European Central Bank (ECB) announced one key policy change. Specifically, it said that favorable financing conditions could be maintained with a "moderately lower" pace of net asset purchases under the pandemic emergency purchase program. Below, IHS Markit summarizes the key aspects of the subsequently published account of September's meeting. The most significant point is that although the assessment of inflation prospects remained relatively benign, there was an increased emphasis on upside risks. (IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- An accommodative monetary policy stance remained necessary. However, financial conditions had improved notably since March's decision to significantly increase the pace of net asset purchases. This improvement was visible across a broad spectrum of indicators. A recalibration of the pace of net asset purchases was therefore required.
- Some Governing Council members argued in favor of "a more substantial reduction in the pace of purchases". Others argued against this, however, expressing concern that a slower pace might induce market perceptions of a tighter monetary policy. This could drive interest rates higher and thwart the incipient increase in inflation expectations.
- Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) inflation had increased to 3% in August but unusually high rates of inflation were assessed to be largely temporary and underlying price pressures building up only slowly. Measures of underlying inflation were, by and large, moving gradually upwards but remained subdued and quite far away from 2%. Wage pressures remained low and quite heterogenous across countries.
- Headline inflation was projected to rise further until the end of 2021, before falling back in the first half of 2022. Temporary and special effects had continued to have a substantial impact on inflation dynamics in recent months, complicating the assessment. These included shifts in seasonal sales, base effects, and also the change in HICP weights at the beginning of 2021.
- Measures of longer-term inflation expectations had continued to increase but remained some distance from the ECB's 2% inflation target. Inflation options markets continued to signal a low risk of recent high inflation rates extending into the medium term.
- As the economy recovered further, underlying inflation was expected to rise over the medium term. This was expected to be gradual as it would take time to reach full capacity and wages were therefore expected to grow moderately. However, if supply bottlenecks lasted longer and fed through into higher-than-anticipated wage rises, price pressures could be more persistent.
- August was an extremely weak month for German industrial output and orders, driven especially by the automotive and machinery/equipment sectors, which are suffering markedly from material shortages. The plunge in demand was exacerbated by an unwinding effect related to July's big-ticket (ship-building) orders from Asia. Germany's industrial sector will have a significant dampening effect on fourth-quarter GDP growth despite the ongoing support from the recovering service sector. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- Seasonally and calendar-adjusted German industrial production excluding construction declined by 4.1% month on month (m/m) in August, representing a setback to levels last seen in September 2020. Furthermore, the latest output level is about 10% below its February 2020 pre-pandemic high.
- Total production including construction similarly posted a 4.0% m/m decline in August, given a comparable 3.1% drop in construction output. In contrast, energy output rebounded by 4.1% m/m, following a cumulative decline of 7.5% during May-July.
- The split by type of good reveals that the investment goods sector, which had outperformed in July, weakened the most during August. Nevertheless, the intermediate and consumer goods sectors also registered sizeable declines. In the case of the latter, this was the first decline since April, as the loosening of COVID-19-related restrictions in May had given consumer goods output a boost.
- BMW Group, through its venture capital fund, BMW i Ventures, has invested an undisclosed amount in US-based lithium technology startup Lilac Solutions. Lilac is seeking to develop an "ion exchange technology" to make mining lithium from brine resources more efficient and cost-effective without the use of evaporation ponds. BMW participated in Lilac's USD150-million Series B funding round along with SK Materials, Presidio Ventures, MCJ Collective, and Earthshot Ventures. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- GE Renewable Energy has announced that its Haliade-X prototype has started operating at 14MW in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. The company has now officially started certification measurements on the Haliade-X 14MW. This 14MW turbine is an upgraded version of Haliade-X 13MW. The company will provide 87 Haliade-X 14MW offshore wind turbines as their first commercial offering at the Dogger Bank C offshore wind farm. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Monish Thakkar)
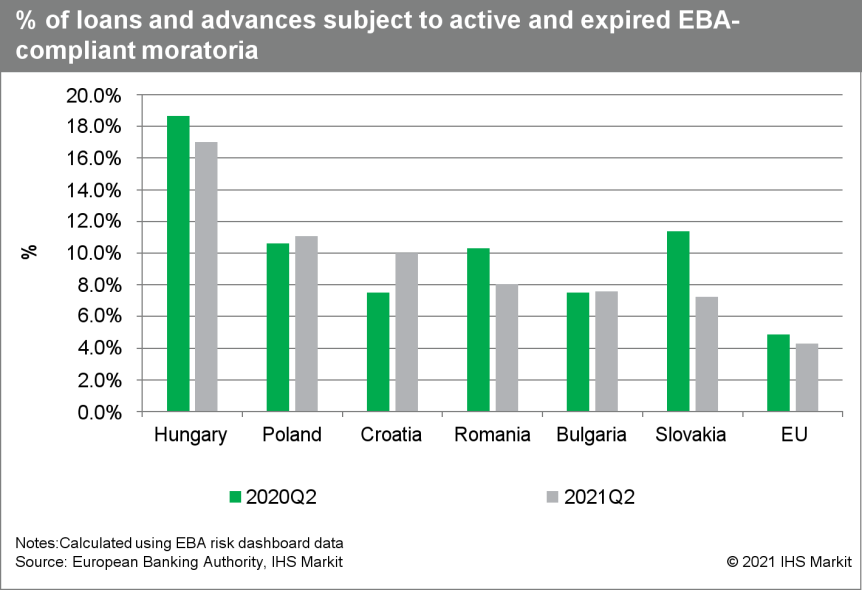
- The European Banking Authority (EBA) published on 6 October its latest quarterly risk dashboard covering banks' positions at the end of the second quarter of 2021. The dashboard was based on a sample of 131 banks covering 80% of the EU banking sector. Reported impairment remained stable - with the sample reporting an average non-performing loan (NPL) ratio of 2.3% - but assets under moratoria and state-relief schemes continued to face quality deterioration. Although there is a divergence at the sectoral level, the latest data reveal overall improving asset quality in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE). (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Greta Butaviciute, Brian Lawson, and Natasha McSwiggan)
- NPL and Stage 2 loan ratios have fallen for many countries but not all. Although NPL ratios have decreased in most countries, they have risen in sectors most affected by the remaining social distancing and travel restrictions measures, such as accommodation and food services, arts, entertainment, and recreation.
- The volume of loans under active EBA-eligible moratoria continued to fall in all countries for which data are available in the second quarter. However, the NPLs for loans still under moratoria rose in some countries, in particular Poland and Croatia, although they decreased in Bulgaria, Romania, and Slovakia.
- The total capital ratio stood comfortably at 19.6% in June 2021, while the leverage ratio rose by 0.1 percent to 5.7%, well above the EBA's recommended minimum of 3% for EU banks. The strong capital position reflected higher capital and a reduction in total assets on a quarterly basis, with the decline "driven by debt securities and derivatives". IHS Markit also assesses that temporary loan forbearance measures have prevented a rise in risk-weighted assets (RWAs), and capital ratios are likely to weaken when NPLs materialize.
- The return-on-assets ratio, despite having returned to a level recorded prior to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus outbreak, remains very low at just 0.47% in June. At the cut-off date of end-June, 27.8% of reporting banks had a return on equity (ROE) of below 6%, versus 33.4% in the prior quarter; in the last quarter of 2020, 78.8% of banks had reported such low returns.
- Cyber risks and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) are areas of growing concern for financial stability. The EBA notes that no major cyberattack has yet been reported but assesses that banks' information and communication technology (ICT) systems "remain vulnerable to significant disruptions", with cyber risks exacerbated by remote working and extensive use of third-party providers.
- After months of claiming that inflationary pressures are temporary, the National Bank of Poland (NBP) increased interest rates by 40 basis points at its 6 October session. (IHS Markit Economist Sharon Fisher)
- The NBP's monetary policy council (MPC) raised the policy rate to 0.5%, up from a historic low of 0.1% that had been in effect since May 2020.
- Alongside the hike in the policy rate, the MPC also increased the required reserve ratio (from 0.5% to 2.0%). Moreover, the Lombard, discount, and re-discount rates now stand at 1.00%, 0.52%, and 0.51%, respectively (from 0.50%, 0.12%, and 0.11% previously), with only the deposit rate remaining unchanged (at 0.00%).
Asia-Pacific
- All major APAC equity indices closed higher and none were in negative territory at any point during the trading day; Hong Kong +3.1%, South Korea +1.8%, India +0.8%, Australia +0.7%, and Japan +0.5%.
- China's slow progress on electricity market reforms has contributed to the country's worst power crunch in a decade this summer. Now, energy experts say Beijing needs to up its game if the world's largest GHG emitter is to meet future decarbonization targets. Despite promising to liberalize electricity pricing in 2015, the Chinese government has in general retained a tight grip on power tariffs, tamping down energy costs for retail and industrial users. While mitigating energy poverty and keeping the economic engine humming during the COVID-19 pandemic, the policy is widely blamed for the past few months of widespread power outages in nearly two-thirds of the country. Coal-fired power generators-which account for around half of China's electricity mix-have choked back supplies to end-users in the past month, as a result of coal prices soaring due to domestic shortages and reduced imports. Data from IHS Markit and Xinhua Infolink show China imported 50.7 million metric tons (mt) of steam coal between January and the end of August, down 25% from the same period of 2020. Coal prices rose by over 40% in north China last month. (IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Max Lin)
- MingYang Smart Energy's MySE 3.0-135 wind turbines have arrived in Italy for the 30MW Taranto offshore wind farm project. The company disclosed that the turbines were brought by the vessel Chipol Changan and arrived at the YILPORT last week and the turbines, where the offloading work is taking place. Renexia, the developer of the project placed an order with MingYang at the beginning of this year and the production of the ten turbines was completed in August 2021. According to MingYang, this is the first time a Chinese OEM is supplying turbines for the European offshore wind market. The 30MW offshore wind farm, also known as Beleolico, is scheduled to be put into operation in 2022. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Monish Thakkar)
- Spot sea 40-ft container prices halved to $8,000 in routes from China to the US west coast after many Chinese factories temporarily closed due to power cuts. In addition, spot 40 ft. container prices fell by a quarter to $15,000 between Chinese ports and the US east coast. However, US sea shipping companies are still increasing their long-term contracts, following trends led by the Shanghai Ocean Shipping Exchange (SSE), the Vietnamese Cashew Association (Vinacas) reported. The research company Caixin Global has explained that this sudden fall is due to the combination of manufacturing halt and the Chinese Golden Week (1-7 October) festival, with most players expecting rising prices in mid and long-term contracts until Q1 2022. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jose Gutierrez)
- Hyundai Mobis has held a ground-breaking ceremony for its new fuel-cell stacks production plant at the Industrial Complex in Cheongna International City, Incheon, according to a company press release. The company plans to invest KRW1.3 trillion (USD1.1 billion) in this facility and also a new fuel-cell systems assembly plant in Ulsan. The new plants are expected to become operational from the second half of 2023. When fully operational, the facilities are expected to produce 100,000 hydrogen fuel cells every year. Once construction of these facilities is completed, Hyundai Mobis will operate a total of three fuel-cell plants. Hyundai Mobis is part of South Korea's leading automaker Hyundai Motor Group, which has a strong focus on hydrogen fuel-cell technology. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
- Indonesia's parliament passed into law an overhaul of tax regulations on 7 October, integrating five tax laws into one law. Eight out of nine parties represented in parliament approved the Tax Regulation Harmonisation law. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Anton Alifandi)
- The passage of the law indicates the government's intent to increase tax revenue as part of its budget consolidation plan. The law consolidates previous laws, including those on income tax and value-added tax (VAT), a law on tax procedures, and a law on tax amnesty, into one tax law to simplify general tax administration.
- The law signals the government's prioritization of increased revenue over regional tax competitiveness. President Joko "Jokowi" Widodo in 2019 made a campaign pledge to reduce Indonesia's corporate taxation in line with some of its regional peers.
- The law for the first time introduces carbon tax into Indonesian law, but it is unlikely to be imposed in the next 12 months. The law lays the foundation for the government to impose a carbon tax as part of its Paris Accord commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 29% by 2030. It sets a minimum carbon tax of IDR30 (USD0.0021) per kg of carbon dioxide equivalent of emissions, 60% lower than the rate that the government had proposed in an earlier draft.
- The law provides the government with the option of further increasing and expanding the scope of VAT. The government withdrew an earlier plan to introduce VAT on basic foodstuffs following objections from groups representing workers, consumers, and market traders, significantly reducing the risk of large-scale protests.
- During its 6 October meeting, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to raise the OCR by 25 basis points to 0.50% - its first move since the OCR was lowered to its previous setting in March 2020. The decision was made to help counter rising inflation and support maximum sustainable employment. There were no changes to the RBNZ's alternative monetary policy tools such as the Large Scale Asset Purchase (LSAP) program or the Funding for Lending Programme (FLP). (IHS Markit Economist Andrew Vogel)
- The MPC's rate hike was "consistent with their assessment at the time of the August Statement". The MPC argued that, although the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus outbreak lockdowns - which kept the MPC from raising the OCR at its August meeting - are expected to have caused a sharp economic contraction (particularly in Auckland), it is likely not as severe as the one observed in the June (second) quarter of 2020 or otherwise bad enough to materially change the RBNZ's medium-term inflation or employment outlooks from what was projected in the August meeting.
- Additionally, the MPC noted the continued recovery in global economic activity and rising COVID-19 vaccination rates as positive indicators for domestic demand, while also highlighting the persistent strong price pressures caused by supply disruptions, labor shortages, and rising energy costs.

Posted 07 October 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.



