All major US equity indices and most APAC equity markets closed higher, while Europe was lower. US government bonds closed sharply lower and most benchmark European bonds were also lower on the day. The US dollar continued to sell-off today, while gold, silver, and copper were all higher. Oil prices rallied on an unexpected sizable production cut by Saudi Arabia announced at the conclusion of this week's OPEC+ meeting. The first wave of vote counts in the two US Senate runoff elections in Georgia indicates that both Republican candidates are in the lead, but it may take days to tally the significant quantity of mail-in ballots to determine the winners.
Americas
- US equity markets closed higher; Russell 2000 +1.7%, Nasdaq +1.0%, S&P 500 +0.7%, and DJIA +0.6%.
- Georgia voters returned to the polls to vote in two Senate runoff races after no candidate in either race broke the 50% threshold in November. The outcome of these two contests will determine the balance of the Senate for the next two years. Similar to the vote count in November's general election, early returns in the runoffs could skew Republican, as Georgia officials were only allowed to begin counting mail-in ballots, which are likely to lean Democratic, starting at 7 a.m. on Election Day. It could take several days or more to know the winner if the races are close—ABC and CNN took 10 days to call the state's competitive presidential race in November. As of 9:36pm EST Republican David Perdue has 50.7% of the votes vs Democrat challenger Jon Ossoff and Republican Kelly Loeffler has 50.3% of the votes vs Democrat challenger Raphael Warnock. (Bloomberg)
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +4bps/0.96% yield and 30yr bonds +5bps/1.71% yield.
- CDX-NAIG -1bp/52bps and CDX-NAHY -1bp/303bps.
- DXY US dollar index -0.5%/89.44.
- Gold +0.4%/$1,954 per ounce, silver +1.0%/$27.64 per ounce, and copper +2.5%/$3.64 per pound. Silver is +22% since 27 November.
- Crude oil +4.9%/$49.93 per barrel, which is its highest close since 24 February and it was as high as $50.19 at 2:22pm EST.
- Barely a few days into an agreed 500,000 b/d increase in production in January, the OPEC+ meeting on 4-5 January 2021 brought plenty of surprises to unsuspecting oil markets, chief among them Saudi Arabia's unilateral decision to cut production by 1 MMb/d through March. The group appeared set on Monday to roll over January output levels through February despite Russia's public dissent, and for the majority of OPEC+ that is indeed what was agreed, with production levels for all but three countries to remain steady through March. But market attention will be captivated by the three exceptions: Russia and Kazakhstan's decision to continue easing cuts over February and March by 65,000 b/d and 10,000 b/d a month, respectively, which was de facto endorsed by the OPEC+ group; and Saudi Arabia's 1 MMb/d voluntary cut commitment. While the latter far outweighs the former in terms of volumetric impact, Russia's divergence bears clear significance as it puts the strategic misalignment of the two largest producers in the OPEC+ group on full display. But where disagreement over policy in March 2020 led to a full breakdown as consensus was unable to be reached, Tuesday's announcement reflects a compromise to allow for divergent paths within the cooperation agreement. This evolution of the OPEC+ partnership could quickly go from convenient to unsustainable, but for the next two months at least, markets (and shale producers) will welcome Saudi Arabia's decision to buck internal consensus-building in favor of supply cuts that were much needed given demand headwinds. (IHS Markit Energy Advisory's Roger Diwan, Karim Fawaz, Edward Moe, and Sean Karst)
- Hospitalizations in the US topped 130,000 for the first time as several Sunbelt states experienced their highest levels of coronavirus patients since the pandemic began. The number of people currently in US hospitals with coronavirus rose to 131,195 from 128,210 on Monday, according to Covid Tracking Project data. California and Texas, which rank first and second by population, made the biggest contributions to that total as their own tallies hit records of 22,485 and 13,308, respectively. Hospitalizations also hit records in Alabama, Arkansas, Arizona, Georgia, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina and Tennessee. (FT)
- For all of December, requests for driving directions on Apple Maps were roughly 4% above 13 January 2020. Over the last five years (2015-19), average vehicle miles traveled in December were about 11% above that of January, so the Apple data could suggest reduced internal mobility this December. Meanwhile, the Weekly Economic Index (WEI), from researchers affiliated with the New York Federal Reserve, stood at -1.2 last week. Averaged over the fourth quarter, the WEI was -2.7, a reading consistent with our latest forecast of a 2.7% decline in real GDP over the four quarters of 2020. Furthermore, last week's WEI, if maintained over the balance of the first quarter, would be consistent with our forecast of a 0.9% decline in real GDP over the four quarters ending in the first quarter of this year. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Joel Prakken)

- With an estimated sales pace of 16.2-16.4 million units seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) at time of publishing, December auto demand improved from the previous month's result. The December result will help push the fourth-quarter average pace of sales above a level of 16.0 million units. While still below pre-COVID-19 levels, it would be a vast improvement from the 11.3-million-unit reading in the second quarter. A deeper dig into the demand details shows that retail sales volumes have matched or exceeded year-earlier levels since September, reflecting that auto demand by the public has returned to "normal" levels and that those consumers who are willing, ready, and able to purchase a new vehicle continue to do so. It is fleet sales, especially to the daily rental channel, that remain hindered. While the pace of the recovery for auto sales flattened out after September 2020, IHS Markit expects continued growth in auto demand levels in 2021, supported by sustained economic developments from vaccinations and economic stimulus. IHS Markit projects US sales volume to reach 16 million units in 2021, up an estimated 10% from the projected 2020 level of approximately 14.5 million units. The pace of sales is anticipated to be stronger in the second half of the year, following the expected widespread availability of the vaccine by summer. Stock management will continue to be an important variable moving through the immediate forecast horizon, but the all-out vehicle production schedules now should help improve the situation as we progress through 2021. Month-end December inventory levels as reported by AutoData at time of publishing were estimated to have declined from the previous month. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Hopson)
- Ascend Performance Materials (Houston, Texas) has acquired Eurostar Engineering Plastics (Fosse, France), a compounder with a broad portfolio of flame-retardant (FR) engineered plastics and expertise in halogen-free formulations. Terms of the deal were not disclosed. The company also says it is very close to obtaining FDA and EPA approval to make COVID-19-related claims for its Acteev Protect antimicrobial fabric technology. Ascend, a fully integrated producer of nylon-6,6, acquired two other European businesses, Poliblend and Esseti Plast GD, from D'Ottavio Group in February 2020. That deal brought a manufacturing facility in Mozzate, Italy; Esseti Plast's masterbatch portfolio; and Poliblend's portfolio of engineering plastics, which included virgin and recycled grades of nylon-6 and nylon-6,6, polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), and polyoxymethylene (POM or polyacetal). In June 2020, Ascend acquired the assets of NCM (Changshu) Co. and Tehe Engineering Plastic (Suzhou) Co. located in Changshu Yushan High-tech Industrial Park near Shanghai. Ascend intends to expand the compounding assets at the site and to establish a global research and development center. Ascend launched the Acteev Protect antimicrobial technology, which embeds zinc oxide within the polymer lattice of nylon-6,6, in June. Ascend originally developed Acteev to control odor in fabrics by inhibiting bacterial growth, but over 350 third-party studies have shown it is also highly effective against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. The company has been working with FDA and EPA since the second quarter of 2020, and it expects the agencies to approve the use of Acteev in masks and other applications to protect against SARS-CoV-2 during the first quarter of 2021. Ascend has already produced millions of pounds of Acteev nylon-6,6, a portion of which the company used to make over 600,000 masks. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- Magna and Fisker are adding the development of advanced driver assist systems (ADAS) to their vehicle partnership, supporting the planned launch of the Fisker Ocean in 2022. According to a statement released by Magna, the two will "work together to develop industry-unique ADAS features and a suite of software packages powered by a scalable domain controller architecture." The system will use cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and what Magna says is a first-to-market digital imaging radar technology. That technology, developed with a Texas startup called Uhnder and called ICON RADAR, is the first digital imaging single-chip radar solution for autos. The announcement follows an announcement in October 2020 that Magna will build the Fisker Ocean at its facility in Europe in 2022, using Magna's electric vehicle (EV) architecture and Fisker's platform that was finalized in December 2020. For Magna, this is about building opportunities for business with other new OEMs, and Kotagiri said the Magna is in talks with other companies, although he declined to name them. The evolution keeps Magna relevant and at the leading edge of technology for its Power & Vision (powertrain, electronics, mirrors, lighting, and mechactronics) division as well as its Complete Vehicles business, which grew 11% in 2019 to account for USD6.7 billion of the company's USD38.4 billion in net sales. Magna's Power & Vision division, which includes powertrain and electronics, recorded revenue of USD11.3 billion in 2019. The Fisker project should enable Magna to integrate work from both divisions. Fisker gets to market more quickly and with less direct capital investment. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- LiDAR sensor manufacturer Aeva Inc has raised USD200 million in private investment from Hong Kong SAR hedge fund Sylebra Capital ahead of its public listing through a reverse merger. In November 2020, Aeva announced that it will go public through a merger agreement with InterPrivate Acquisition Corp, a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC), with a post-deal market valuation of USD2.1 billion. The new investment from Sylebra will bring Aeva's total raised capital to more than USD560 million, reports Automotive News. Dan Gibson, Sylebra's Hong Kong-based chief investment officer, said, "The company is a leader in frequency modulated continuous wave technology, which we believe is where the market is headed, not just for auto, but also for consumer, industrial and commercial applications. We are buying at price points that are very attractive versus the long-term opportunity and the firm is backed by strong and experienced management." Aeva is a California-based startup founded in 2016 by former Apple engineers Soroush Salehian and Mina Rezk. Aeva provides a unique LiDAR solution that can measure distance as well as instant velocity without losing range. The company has said that its newest LiDAR product, called the Aeries, which has a 120-degree field-of-view, will cost less than USD500 when manufactured in high volume. Last year, Porsche, part of the Volkswagen (VW) Group, invested in Aeva. Aeva has signed a sensor-system deal with Audi subsidiary Autonomous Intelligent Driving (AID) and ZF Friedrichshafen. Aeva is one of the five LiDAR manufacturers that have announced to go public through SPAC mergers; the others being Velodyne Lidar, Luminar, Innoviz, and Ouster. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Brazil is strengthening its position as the top exporter of chicken meat to South Africa as key competitors in Europe face bans following outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian flu (HPAI). Newly released figures show that Brazil supplied more than 60% of the chicken meat imported by South Africa in November 2020. Imports from the South American country amounted to 24,358 tons in November, up 3% on the same month last year. In contrast, no chicken meat at all was imported from Poland due to a ban imposed following avian flu outbreaks earlier this year. Poland was previously the largest EU supplier to South Africa, providing the country with about 4,000 tons a month in 2019. Until now, some other European countries have been helping fill the gap in Polish supplies, with Ireland, Denmark, Netherlands and Spain all shipping significantly more chicken meat to South Africa in the first eleven months of this year. The spread of avian flu to many of these countries means they too will be banned by South Africa - a country that normally reacts to outbreaks by banning imports on a national rather than regional basis. A ban on imports of Danish poultry meat has already been confirmed in a 25 November notification to the World Trade Organization. Data from the EU's Disease Notification System shows that ten EU countries have been hit by HPAI outbreaks since November. These include Poland, UK, Denmark, Ireland, France, Germany, Croatia, Sweden and the Netherlands. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Max Green)

- The Central Bank of Chile (Banco Central de Chile: BCC) reported the first annual advance in the country's economic activity indicator during November 2020. In seasonally adjusted terms, the index recovered by 1.1% month on month (m/m) in November 2020 following the October 2020 contraction. (IHS Markit Economist Claudia Wehbe)
- According to the BCC, the monthly economic activity indicator - a proxy for GDP - advanced by 0.3% year on year (y/y) in November 2020, the first annual advance in Chile's economic activity indicator following persistent contraction during March-October 2020 because of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-virus pandemic.
- The result was driven by a 15.3% y/y gain in commerce, which more than offset contractions in services (-2.3% y/y) and goods production, mainly driven by a 3.6% y/y contraction in construction. Mining activity contracted by 1.1% y/y. Non-mining activity recovered by 0.4% y/y, while manufacturing advanced by 1.6% y/y.
- Seasonally adjusted mining activity lost 2.0% while non-mining gained 1.4% compared with October's results. The overall 1.1% monthly gain was driven by gains in services (1.9% m/m) and goods production (1.0% m/m) that more than offset a 1.3% m/m decline in commerce. Results are likely to be revised due to challenges in collecting data during the pandemic.
- Chile's modest economic performance was still dampened by mobility restrictions and partial closures because of the pandemic. IHS Markit currently forecasts real GDP to advance by approximately 6.2% in 2021; we do not project the economy to be back to its end-2019 levels until 2022.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Most European equity markets closed lower, except for UK +0.6%; Germany -0.6%, Italy -0.5%, France -0.4%, and Spain -0.1%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; UK +4bps, Germany +3bps, France/Italy +2bps, and Spain -1bp.
- iTraxx-Europe closed flat/49bps and iTraxx-Europe closed +5bps/255bps.
- Brent crude closed +4.9%/$53.60 per barrel.
- After several delays, Hornsea Project Three has finally received its consent from the United Kingdom Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS). Ørsted had initially submitted the development consent order (DCO) application in May 2018. However following the subsequent consultation and examination period, the decision deadline was repeatedly delayed from October 2019, up to 31 December 2020. It is understood that the delays were the result of the potential adverse effects of the project on the environment around the Flamborough and Filey Coast Special Protection Area, including the nesting sites of kittiwakes. Ørsted has stated that they have worked closely with key stakeholders to develop a robust compensation plan to address this. Hornsea Project is a 2.4 GW offshore wind farm to be located 120 kilometers off the north Norfolk Coast. The project will comprise up to 300 turbines. Ørsted completed its 1.2 GW Hornsea One project in January 2020, and recently started construction, in October 2020, the 1.4 GW Hornsea Two project, slated for completion in 2022. When completed, Hornsea Three will be the biggest global offshore wind farm project. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
- German retail sales did not show the expected correction in November, instead adding another 1.7% m/m that has pushed the annual comparison to almost 10% y/y in nominal terms. Although much of this reflects one-off catch-up and substitution effects linked to the pandemic, plus support from July's VAT cut that expired at the end of 2020, consumers are not holding back on spending as long as shops are open. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- According to Federal Statistical Office (FSO) data, real retail sales excluding cars increased by a solid 1.9% month on month (m/m, seasonally and calendar adjusted) in November, adding to October's 2.6% m/m. Price-adjusted November retail sales thus exceeded their June levels (just before the VAT cut) by 5.2% and November 2019 levels by 8.7%.
- Calendar-unadjusted year-on-year (y/y) rates were dampened by a missing shopping day but still posted 5.6% in real terms and 6.5% in nominal terms. This compares to average growth of 3.2% and 3.7%, respectively, in 2019, and even lower long-term trend growth of 0.6% and 1.3%.
- Recent above-trend retail sales are attributable to three factors: the temporary VAT cut (July-December 2020), catch-up effects due to the enforced inability to make purchases during the March-April lockdown, and substitution effects with respect to income that cannot be used for services which - for public health reasons - are either not available at all or only with restricted capacity, e.g. restaurants. Furthermore, with a greater share than usual spent indoors, people want to improve their living conditions at home and turn to DIY and household equipment.
- Major categories of the price-adjusted y/y data for November (total 5.6% y/y, details see table below) show a much stronger increase for non-food sales (8.5%) than for food sales (0.8%). Among the former, 'internet and mail orders' remain far ahead of the rest at 31.8% y/y, followed by 'furniture/household goods/DIY' (15.4%) and sales in 'specialty stores such as for toys, books, bicycles' (3.7%). The other major groups of goods all posted declines, specifically -0.8% y/y for pharmaceutical/cosmetic goods, -6.1% y/y for sales at general department stores, and -20.0% y/y for textiles/shoes.
- As before, a clear distinction needs to be made between retail sales alone and consumer demand in general, given the above-mentioned catching-up, substitution, and tax effects. Many services in the recreation and entertainment sector will remain underutilized until widespread vaccination has been completed, which is unlikely before mid-2021. Until that time, consumers will spend an above-average share of their income on retail goods, compared to long-term trends.
- Meanwhile, the latest GfK consumer confidence survey conducted during December (overall index slipping from -6.7 to -7.3, still well up from April's lockdown low of -23.1 but clearly below pre-pandemic levels around 9.5) reveals dampening influences from households' assessment of their personal financial situation in the next 12 months and a rising propensity to save. On the other hand, consumers' willingness to make major purchases posted a significant rebound, and consumers' assessment of the economic outlook - while not linked directly to the GfK headline index - also recovered to some extent following declines during October-November.
- Seasonally adjusted German unemployment declined by 37,000 month on month (m/m) in December 2020, similar to developments during October-November 2020. This is the sixth successive monthly drop following a cumulative surge by 671,000 during the second quarter of 2020. By comparison, the cumulative decline during July-December was 164,000, and the unemployment level at the end of December 2020 was 2.776 million. The latter remains well above the March 2020 cyclical low of 2.269 million but is also far from the interim high of 2.940 in June 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- Separately, the Federal Employment Agency has calculated that unemployment as a result of the COVID-19 virus was -39,000 in December 2020, which matches the average monthly dampening effect during September-November 2020 and follows a neutral effect during July-August 2020. In contrast, the COVID-19 virus impact in the second quarter of 2020 contributed 638,000 cumulatively. The net boost to unemployment since April 2020 that can be linked directly to the pandemic is 481,000, down from the June 2020 peak of 638,000. The German unemployment rate, which had increased from 5.0% in March 2020 (close to 40-year lows) to 6.4% during June-July 2020, stayed at 6.1% in December 2020.
- Seasonally adjusted underemployment (as opposed to unemployment), which had deviated in both directions during 2019 owing to fluctuations in the number of people receiving some form of (non-insurance related) government support - which affects the underemployment data but not official unemployment - declined by modestly less than headline unemployment in December 2020, posting -28,000 m/m. The employment agency points out that statistical under coverage of the number of people benefitting from public support measures - in turn related to COVID-19 virus contact impediments and preoccupation with administering short-time work applications - is at least partly responsible for recent declines. The official number for these measures (-10.9% y/y in December 2020, following -10.6% in November 2020) indicates an ongoing sideways tendency of late.
- The December 2020 additional decline in unemployment is somewhat misleading because the strict lockdown imposed in mid-December 2020, leading to the closure of non-essential shops and most services, is not yet reflected in the data (the measurement date was 10 December 2020). Improvements since mid-2020 have been driven by natural corrections from the second-quarter-2020 slump owing to the March-April 2020 lockdown, in line with the subsequent loosening of restrictions.
- Passenger car registrations in Ireland declined by 24.6% year on year (y/y) during 2020 because of the COVID-19 virus outbreak. According to the latest data released by the Society of the Irish Motor Industry (SIMI) and published by beepbeep.ie, passenger car demand dropped from 117,109 units in 2019 to just 88,324 units. Leading the market this year was the Volkswagen (VW) brand which fell by 20.9% y/y to 10,691 units, while Toyota in second slipped by 17.3% y/y to 10,021 units and Hyundai contracted by 26% y/y to 8,180 units. However, registrations in December leapt from 224 units to 601 units. Registrations in Ireland's light commercial vehicle (LCV) market retreated by 14.2% y/y to 21,732 units in 2020, but leapt by 72% y/y in December to 301 units. Ireland's medium and heavy commercial vehicle (MHCV) category also recorded a fall in registrations for 2020 of 22.3% y/y to 2,066 units, with December bringing a drop of 40.8% y/y to 29 units. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- The Italian passenger car market has fallen by 27.9% year on year (y/y) during 2020 as a result of the disruption caused by the COVID-19 virus pandemic. According to the latest data published by the National Association of Foreign Vehicle Makers' Representatives (Unione Nazionale Rappresentanti Autoveicoli Esteri: UNRAE), registrations have fallen from 1,916,949 units in 2019 to 1,381,496 units. The market's performance in December helped little with the country suffering a contraction of 15% y/y to 119,454 units. In Italy, the government introduced a range of incentives intended to help lift the market, the most successful being those which came as part of the 'Decreto Agosto'. This has helped to moderate the impact on private registrations, where registrations have dropped 'only' 19.1% y/y during 2020. This compares to the short-term rental category, which tumbled by 54.3% y/y on the collapse in the tourism sector, a 44.4% y/y retreat in company car registrations, while long-term rentals have declined by 24.5% y/y. Furthermore, the market could well be continuing to see registrations of vehicles made thanks to this scheme as private registrations slipped only 0.5% y/y in December. With the introduction of new incentives as part of the Italian government's latest budget, UNRAE is more positive with regards the new year. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Vestas has acquired a 25 percent minority stake in greenfield renewable energy fund manager Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP) for a total consideration of EUR 500 million, with EUR 180 million as upfront payment, and EUR 320 million as potential earn out. Proceeds of the transaction will be committed as re-investments into CIP, and new funds to accelerate growth and innovation. Central to the latter part will be CIP's creation and co-investment into a new Energy Transition Fund, to be launched in the first half of 2021.The fund will focus on leading-edge technologies in the field of decarbonization, such as Power-to-X. CIP currently manages EUR 14 billion of assets and has stated its ambition to grow this rapidly to EUR 75 to 100 billion by 2030. Vestas will be represented at the CIP Holding Board but will however not influence the selection of wind turbine vendors and services, or participate in negotiating competitive market terms. CIP will continue to lead project origination, and project and investment structuring. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
- Offshore wind heavyweights Iberdrola, EDP Renewables and ENGIE have recently struck deals in Poland to gain access to the market there. Ocean Winds, the equal joint-venture company of EDP Renewables and ENGIE, signed a major cooperation agreement with Polish utility TAURON. Under the terms of agreement, TAURON will acquire half the share in Ocean Winds' portfolio. In return, Ocean Winds will receive half the shares of TAURON's Baltic Sea wind farm projects. Spanish offshore wind company Iberdrola also struck a deal in Poland to acquire a 50% stake in Sea Wind. Sea Wind has seven projects in early development with a potential capacity of up to 7.3 GW. Prior to the transaction, Iberdrola had an offshore wind project pipeline of around 20 GW. Iberdrola has stated its intention to geographically diversify its business into markets with favorable investment conditions, such as Poland, and has recently gained access to markets such as Japan and Sweden. The company's key focus however remains in the North Sea, Baltic Sea, and the United States. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
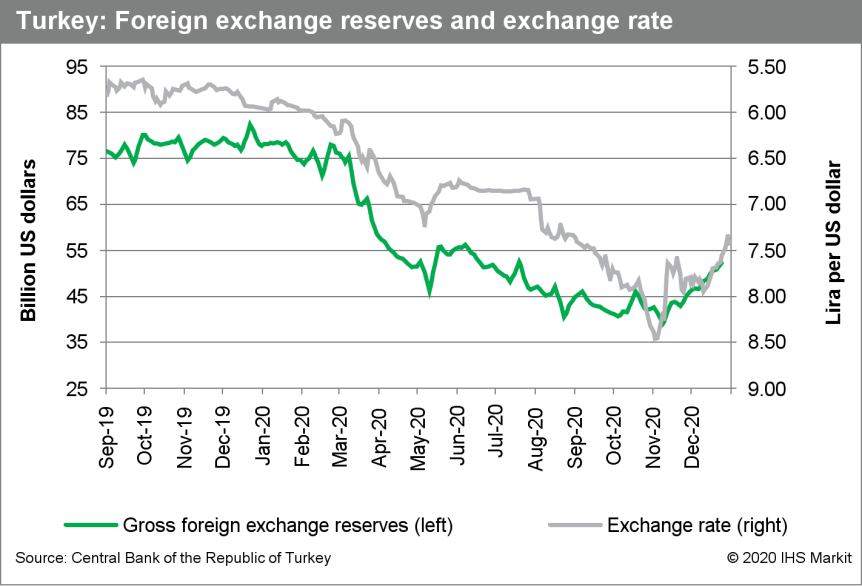
- Annual inflation reached 14.6% at end-2020 in Turkey, accelerating over the final quarter of the year. For 2020 as a whole, inflation averaged 12.3%, fueled by one of the sharpest depreciating currencies in the world. The central bank governor has vowed to keep borrowing costs high to tackle inflation, which may be even worse than officially reported. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew Birch)
- The Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey (TCMB) reported that the annual rate of consumer price inflation accelerated to 14.6% as of end-2020. Inflation accelerated sharply during the final quarter of the year, up from 11.8% as of September 2020, but remained below the end-2019 rate of 15.2%.
- With annual inflation hovering around 11.5% to 12.5% throughout most of the first three quarters of the year, average annual inflation in 2020 was lower than end-year inflation, at 12.3%. Average annual inflation was also lower than it had been in 2019 (15.2%) as well as in 2018 (16.3%).
- Although inflation did decelerate compared with the previous two years, it nonetheless continues to far surpass the TCMB's inflation target of 5%. End-year inflation also accelerated well above the last TCMB inflation forecast of 12.1%, which was made at the end of October.
- Over the course of 2020, food and transportation prices contributed the most to the rise of overall consumer prices. Prices of the former soared by 20.6% in 2020 and the latter's prices jumped by 21.1%. Of all the expenditure categories making up the total consumer price index, only clothing and footwear prices fell, by 0.3% in 2020.
- Although annual inflation was elevated, several indicators suggest that actual prices may have grown even faster and that the data is being manipulated by the Turkish Statistical Institute. An independent institution headed by academics from several Turkish universities, ENAGrup, reportedly estimated that prices actually grew by 36.7% in 2020.
- A faltering of merchandise exports and the continued rise of imports caused Turkey's trade deficit to surge in November 2020. The trade gap for the year as a whole is on track to widen by more than USD20 billion compared with 2019. The widening of the trade gap has contributed to the rise in external debt. The trade deficit will retreat in 2021 but remain large. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew Birch)
- The Turkish Statistical Institute has reported that the country posted a merchandise trade deficit of USD5.0 billion in November 2020, up by more than USD3 billion from a year earlier. The year-on-year (y/y) widening was significant throughout 2020, with the trade gap through the first 11 months of the year reaching USD45.3 billion, up by USD20.5 billion from the same period of 2019.
- Although the new central bank governor began tightening monetary policy in November, demand for imports remained high. That month, imports surged by 15.9% y/y. Expansionary economic policies through the first part of 2020 continued to have an effect on imports, fueling a 41.4% y/y surge in consumption goods imports in November and a 32.6% y/y jump in capital goods imports.
- Meanwhile, exports faltered in November, with the resumption of COVID-19-virus lockdowns undermining demand from Turkey's key export market, the European Union. Shipments to the EU slipped by 1.4% y/y in November.
- The Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey (TCMB) also reported that as of end-September 2020, Turkey's external debt had climbed to USD435.1 billion, up by more than USD11 billion over just the course of the third quarter. Total debt accounted for 71% of estimated 2020 GDP as of end-September, a surge forward compared with the end of 2019, when total external debt accounted for just 57% of GDP that year. The TCMB has been a prime contributor to the rise of debt over the course of 2020, adding nearly USD13 billion in external debt since the end of 2019, a reflection of its huge expansion of forward swaps to build foreign-currency reserves.
- The surge in the merchandise trade deficit will combine with a sharp deterioration in the services balance to send Turkey's current-account deficit to nearly 5% of GDP in 2020 as a whole. IHS Markit anticipates that the trade and current-account deficits will narrow once again in 2021, although they will continue to be large. Both are expected to remain at around 4% of GDP for 2021 as a whole.
- We anticipate that the much tighter economic policies being pursued by the TCMB to rein in inflation will begin to have more of a dampening effect on imports in the first half of 2021.
- The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC)'s higher social spending needs push up the 2021 budget's estimate without clarity on expenditure cuts, increasing the risk of a higher anticipated fiscal deficit in 2021. (IHS Markit Economist Alisa Strobel)
- The finance bill for the 2021 fiscal year was tabled on 30 October 2020 in the National Assembly of the DRC. Prime Minister Sylvestre Ilunga Ilunkamba presented the first draft budget for 2021 on 13 November 2020 in the National Assembly with an estimated budget targeted at USD6.9 billion.
- However, the National Assembly revised upwards the targeted budget for 2021 from USD6.9 billion to USD7.1 billion in December 2020. Overall, the national budget for 2021 suggests a USD1.4 billion increase in funds compared with 2020's national budget. The increase is set to reflect the higher spending needs on social expenditure. After its adoption by the National Assembly, the 2021 finance bill must be sent to the Senate for a second reading, before its promulgation by the president of the Republic, Félix Tshisekedi.
- The prime minister in November 2020 highlighted that the main projects to be funded by the 2021 national budget include the security sector's reform program, the creation and deployment of the revenue chain, the healthcare system's development program, the construction and rehabilitation of schools, an urban development program, as well as the fight against erosion. Rural electrification development and road infrastructure works as well as exploitation and geological research for the certification of mineral reserves are also among the main projects to be funded for 2021.
- With a focus of 10% of the allocated budget to the healthcare sector to address the COVID-19-virus pandemic, 10% to rural agricultural development, and 20% to education, there remains some element of uncertainty as to how effective expenditure cuts will be to offset the higher costs, particularly as public-sector wage cuts still remain controversial.
- Furthermore, the anticipated larger-than-previously-scheduled national budget of USD7.9 billion and challenging revenue generation are expected to widen the fiscal account in 2021, suggesting the need for a more prudent fiscal policy stance ahead, while monetary policy is expected to remain accommodative as long as headline inflation remains below the target.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Nikkei -0.4%, Australia flat, India +0.5%, Hong Kong +0.6%, Mainland China +0.7%, and South Korea +1.6%.
- Dongfeng Motor has partnered with Aurora Mobile to strengthen artificial intelligence (AI)-based smart mobility services. This partnership will enable Dongfeng Motor's one-stop mobility service platform, DFGO, to enhance operational and service efficiency and optimize user experience. Aurora Mobile will use its AI-based push notification services and machine learning-based operational analysis capabilities to enable DFGO to gain insights into user needs and improve user experience. DFGO currently offers services including online ride-hailing, premium car hailing, timeshare car leasing, taxi-hailing, used-car transaction services and electric vehicle (EV) charging. In future, DFGO plans to upgrade its products and technologies by connecting its platform with urban transportation systems and expanding its service coverage to bike sharing, bus services, hitch riding and intercity vehicle services. Last year, Dongfeng partnered with Chinese technology company Tencent to jointly deploy smart mobility services. It has also partnered with FAW Group and Chongqing Changan to form a venture named T3 Mobile Travel Services to establish a ride-sharing platform. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Chinese exporters see the shortage of reefer containers and the rising sea-freight rates continuing in the first week of 2021. This problem may well stay until H2 2021. Some exporters seem pessimistic when talking to IHS Markit. The sea freight rate to the UK for a 40-ft. reefer container has climbed to USD11,000 per ton. A Chinese frozen vegetable exporter said that: "We are now sending the scheduled goods with orders placed in Q4 2020. We are making a loss for each order. But we still have to continue the shipments as we wanted to fulfil the contracts to maintain long-term relationships with our European clients." Another local source told IHS Markit that: "Freight rates to Japan remain stable; rate increases to the Middle East are not as high as to Europe." According to the Shanghai Containerized Freight Index, rates for West Japan were USD244/FEU on 31 December 2020, unchanged from 25 December. Rates to south-east Asia showed a marginal increase of USD23 to USD933 on 31 December. Sino-Europe railway's refrigerated availability remains tight in the new year. The UK port congestion has an impact on Chinese exports. Terry Zhang the sales manager of Shandong Harvest Agriculture Co Ltd, told IHS Markit that: "The port congestion in the UK has somewhat deterred exporters from sending goods. Fresh ginger is at risk of deteriorating due to the delayed unloading." (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Hope Lee)
- China Huadian Corporation's first offshore wind project, with a generation capacity of 300 MW, has come online. The Fuqing Haitan Strait offshore wind project is located offshore the northeast part of Longgao peninsula in Fuqing county, and consists of 22 MingYang MySE7.0-158 turbines rated to 7 MW each. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
- Ørsted is divesting 50% of its stake in its 605 MW Greater Changhua 1 Offshore Wind Farm to a consortium comprising Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec (CDPQ), and Taiwanese private equity fund Cathay PE. As part of the agreement, Ørsted will continue construction under a full-scope EPC contract, and provide long-term operations and maintenance services. The total sales price, inclusive of the 50% ownership stake and the investors' commitment to fund 50% of the payments under the EPC contract, is valued at TWD 75 billion (USD 2.68 billion). The sale is subject to regulatory approval from the Taiwanese authorities. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
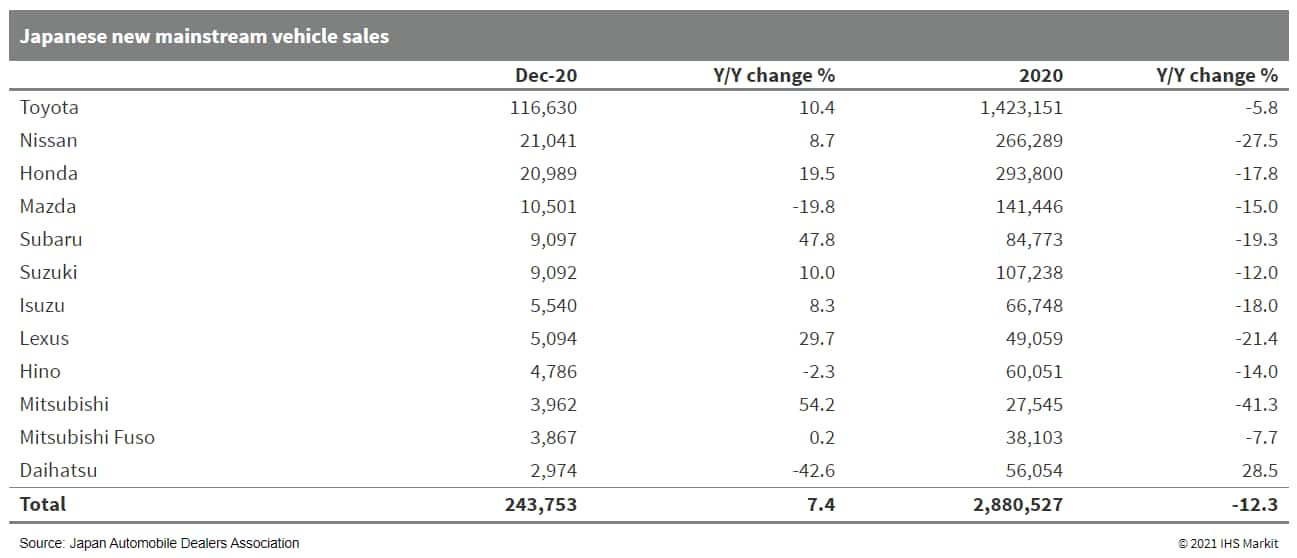
- Japanese sales of mainstream registered vehicles increased by 7.4% year on year (y/y) during December 2020 to 243,753 units, according to data released by the Japan Automobile Dealers Association (JADA) today (5 January). This figure excludes mini-vehicles, thus covering all vehicles with engines greater than 660cc including both passenger vehicles and commercial vehicles (CVs), sold in Japan. Of this total, sales of passenger and compact cars grew by 8.2% y/y to 210,696 units in December 2020, while truck sales were up by 4% y/y to 32,442 units. Bus sales were down by 37.4% y/y to 615 units. In the full year 2020, sales of mainstream registered vehicles were down by 12.3% y/y to over 2.8 million units. Sales of passenger and compact cars declined by 12.2% y/y to 2.47 million units, truck sales were down by 12.7% y/y to 392.361 units, and bus sales were down by 31.3% y/y to 9,334 units. Japanese new vehicle sales posted yet another month of consecutive growth in the domestic vehicle market in December 2020 owing to the recovery trend in the macroeconomic environment through the COVID-19 virus pandemic. The rise in sales last month can also be partly attributed to the low base of comparison from 2019 as customers trimmed their spending following the 1 October 2019 consumption tax rise. Nevertheless, the growth in the last few months was not sufficient to offset the declines in the first three quarters of the calendar year as full-year volumes were down by over 12%. Even with the government easing guidelines for public gatherings, as well as travel and dining promotional campaigns with subsidies, weak employment conditions and uncertainties over the pandemic with possible flare-ups will keep consumers cautious, and thus remain key downside risks. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
- Preliminary data from the General Statistics Office showed that Vietnam's GDP expanded by 4.48% year on year (y/y) during the fourth quarter of 2020, up from a revised 2.69% y/y in the third quarter. Vietnam's GDP managed to expand by 2.91% y/y in 2020, one of the strongest growth rates in the world. (IHS Markit Economist Jola Pasku)
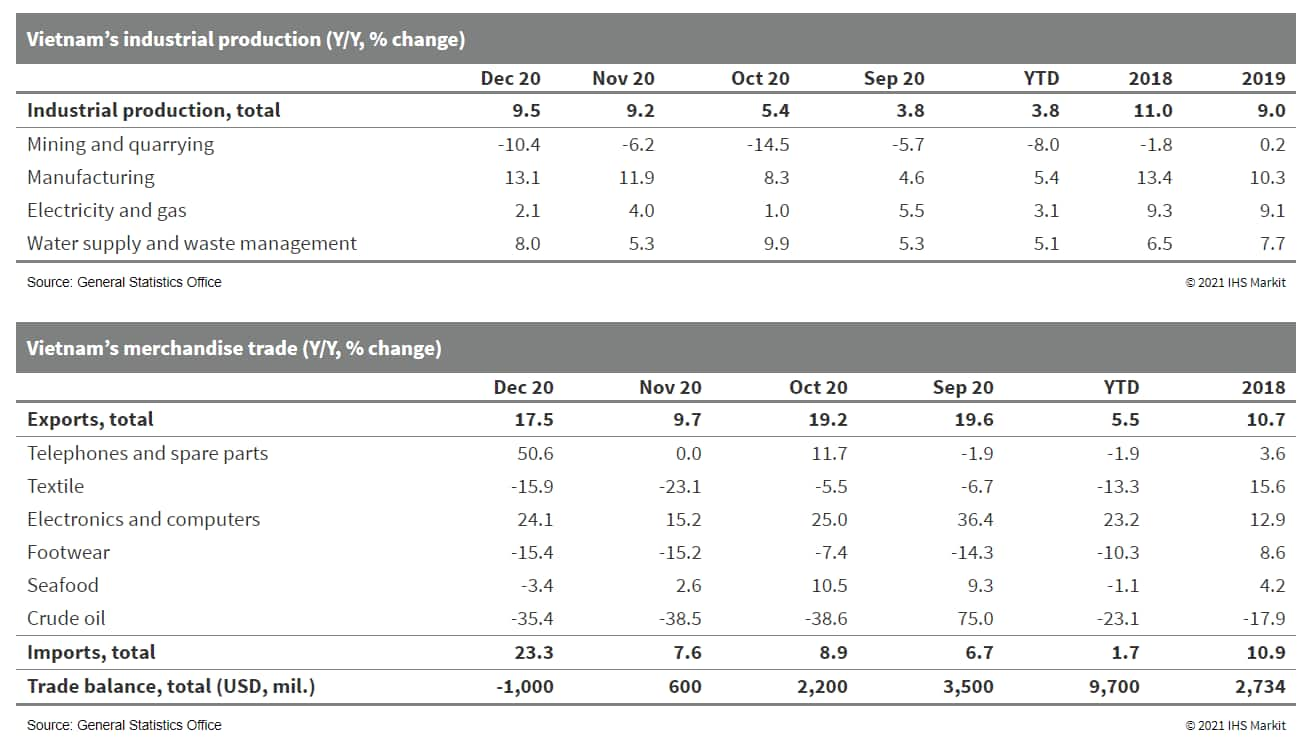
- On the supply side, the industry and construction sector led in terms of growth, rising 3.98% y/y and contributing 53% to overall growth. Agriculture came in second (up 2.68%), followed by the services sector (up 2.34%).
- The services sector posted the lowest growth reading in over nine years amid COVID-19 pandemic-related disruptions. The ongoing travel ban on tourist arrivals has disrupted Vietnam's tourism and associated services, which account for 40% of total revenue in the services sector.
- Full-year high-frequency data showed that exports also played an important role in supporting the economic recovery. Vietnam's exports are estimated to have risen by 5.5% y/y to USD271.0 billion for 2020, while imports grew 1.7% y/y to USD262.1 billion, resulting in a trade surplus of USD9.7 billion.
- Despite the COVID-19-induced blow to the demand and supply sides in 2020, Vietnam has weathered the crisis well. The country's economy proved resilient and continued to grow at a time when those of regional peers contracted.
- The major driver behind this resilience stems from the government's success in controlling the spread of the virus, with very limited cases of community transmission. The government's aggressive containment measures in the form of outright travel bans, heavy testing, direct and indirect contact tracing, mandatory quarantines, and domestic lockdowns facilitated a return to normalcy ahead of many regional neighbors.
- The government ramped up spending on large-scale infrastructure projects such as roads and bridges in an effort to offset the COVID-19-related shock during the year. Public investment rose to a nine-year high in the first 11 months of the year (up 34%).
- The pandemic disrupted supply chains and highlighted the risks associated with over-reliance on China to many global manufacturers, which prompted a fresh wave of investment to neighboring Vietnam. The relocation helped propel Vietnam's manufacturing sector, which grew by 5.8% during 2020, and enabled the country to have one of the strongest growth rates in the world.
- Southeast Asian ride-hailing and food delivery firm Grab's net revenue grew 70% year on year (y/y) in 2020, President Ming Maa said in a newsletter. In addition, the company has recovered to above pre-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus pandemic levels and has achieved segment breakeven for ride-hailing in all its operating markets. The company has reduced EBITDA spending by approximately 80% over the last year, reports The Straits Times. Ming Maa also said that Grab's food delivery business is expected to achieve breakeven by the end of 2021. Grab is focusing on expanding its range of services, from transport to food delivery and payments, and is making aggressive efforts to expand. In 2020, Grab added nearly 600,000 new merchants onto its platform. Grab's app has been downloaded on 166 million devices and it processes more than 6 million ride orders per day. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Indonesia's ride-hailing and payments giant Gojek is in advanced merger talks with local e-commerce company PT Tokopedia, reports Bloomberg. The companies have "signed a detailed term sheet to conduct due diligence of each other's business". According to the report, the merged entity will have a combined valuation of about USD18 billion and has plans to go public in Indonesia and the United States. The merged company will offer businesses ranging from ride-hailing and payments to online shopping and delivery. Gojek and Tokopedia started conducting discussions for a potential merger in 2018, but the deal did not materialize. Negotiations between the companies gained attention in November 2020 after months-long merger talks between Gojek and rival Grab reached an impasse. Common investors of Gojek and PT Tokopedia include Temasek Holdings, Sequoia Capital, and Google. The combined entity will create a powerhouse dominating the Indonesian market, one of the world's fastest-growing internet economies. This deal is likely to face less regulatory opposition than Gojek's merger with Grab as the latter would have hampered competition in ride-hailing, delivery, and digital payments in Southeast Asia. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
Posted 05 January 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.





