All major European and most APAC equity markets closed higher, while the US was sharply lower. US government bonds were close to flat on the day and benchmark European government bonds closed mixed. European iTraxx and CDX-NA closed wider across both IG and high yield. Gold, silver, and copper closed higher on the day and oil was lower. All eyes will be on tomorrow's US Senate election runoffs in Georgia that will decide whether or not the Republican party will maintain their critical majority in the senate, as ceding those seats to the Democrats will enable president elect Biden to significantly expand the scope of new legislation aligned with his platform.
Americas
- US equity markets closed lower; S&P 500/Nasdaq/Russell 2000 -1.5% and DJIA -1.3%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed flat/0.92% yield and 30yr bonds +1bp/1.66%.
- CDX-NAIG +2bps/52bps and CDX-NAHY +11bps/304bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.1%/89.87.
- Gold closed +2.7%/$1,947 per ounce, silver +3.6%/$27.36 per ounce, and copper +0.9%/$3.55 per pound.
- Crude oil closed -1.9%/$47.62 per barrel.
- Georgia voters are hearing final arguments from two presidents on Monday, as Donald Trump and Joe Biden each make their cases ahead of high-stakes Senate runoff elections that will determine who controls the chamber and with it, Biden's agenda. The state's two seats are both up for grabs and if Republicans manage to keep just one of them, the party would have a narrow majority in the Senate, giving Majority Leader Mitch McConnell the power to block Biden's initiatives, nominees to his administration and the judiciary. If Democrats Jon Ossoff and Raphael Warnock can take both seats from Republican incumbents David Perdue and Kelly Loeffler, the Senate will be split 50-50, giving incoming Vice President Kamala Harris the tie-breaking vote. (Bloomberg)
- A health-care venture launched with great fanfare by three of the world's most prominent companies— Amazon.com Inc., Berkshire Hathaway Inc. and JPMorgan Chase and their chief executives is folding about three years after its founding. Haven's transformative ambitions proved too difficult to achieve, according to people familiar with the matter. Its shutdown attests to the challenges of making sweeping changes to the U.S. health-care system and of bringing innovations to hundreds of thousands of employees around the country working at different companies, the people said. (WSJ)
- The seasonally adjusted IHS Markit final U.S. Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI) posted 57.1 in December, up from 56.7 in November, to signal the steepest improvement in the health of the U.S. manufacturing sector for over six years. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
- The headline figure was also up from the earlier released 'flash' reading of 56.5. Production growth remained marked in December, despite the rate of expansion easing slightly from November's recent high. The pace of increase was the second-strongest since March 2015.
- Companies continued to link the rise to the release of pent-up demand, but some did temper this by stating that greater virus cases dampened output growth at the end of 2020.
- The rate of expansion in new orders softened in December, as some firms reported that supplier delays and reduced capacity due to additional COVID-19 restrictions had led to order cancellations. Nonetheless, the upturn was the second-sharpest since November 2018 and steep overall.
- Driving the headline figure higher, however, was a substantial deterioration in vendor performance. Supply chain disruptions escalated amid supplier shortages and transportation delays stemming from a lack of available drivers, and COVID-19 travel restrictions. Lead times lengthened to the greatest extent since data collection began in May 2007.
- Cost burdens were pushed higher. The rise in input prices was substantial and the fastest since April 2018, driven by raw material shortages and supplier price hikes.
- Supplier shortages also drove firms to boost efforts to stockpile inputs, as stocks of purchases fell only fractionally in December. Post-production inventories were depleted at the fastest pace since July, however, as firms sold from stock.
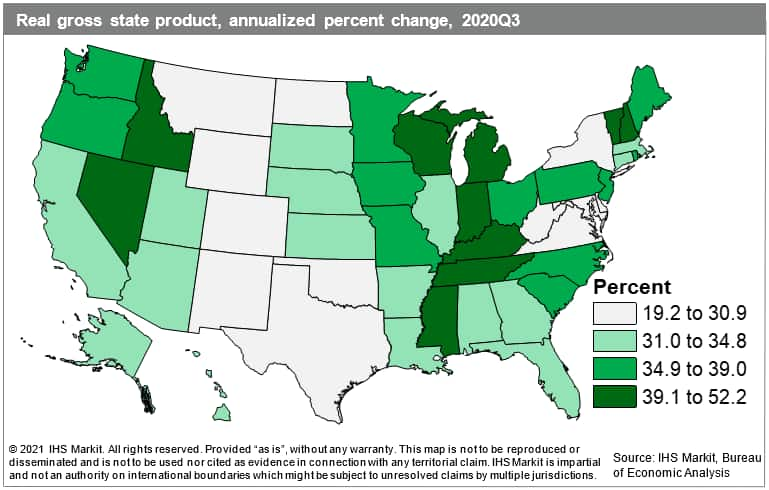
- The initial stages of the recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic began in every US state during the third quarter of 2020 as real gross state product (GSP) rebounded at double-digit annualized rates according to the latest data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). (IHS Markit Economist James Kelly)
- Following a 31.4% annualized decline in the second quarter when business restrictions and social distancing measures tied to the pandemic resulted in a rapid collapse in economic activity, the relaxation of some of those measures in the third quarter boosted total national economic output growth to an annualized pace of 33.4%. The start of a recovery in accommodation and food services coupled with strong gains in healthcare and durable goods manufacturing contributed to double-digit growth in all states.
- A further decline in output from the mining, quarrying, and oil and gas industry put a damper on expansions in energy-intensive states such as Wyoming and Oklahoma.
- The recovery in accommodation and food services output was most prominent in Nevada, the fastest-growing state in the third quarter. Despite this record-breaking surge in the hospitality sector, depressed travel and convention business in the Las Vegas area and rising caseloads and hospitalizations left the state trailing its pre-pandemic economy. Nevada's real GSP was roughly 4% below where it was in the fourth quarter of 2019, greater than the national gap of 3.4% and the ninth largest in the country.
- This incomplete recovery was echoed across the country as third-quarter gains did not fully make up for the contraction in the first and second quarters. Other fast-growing states in the third quarter, namely Tennessee and Idaho, were propelled by gains in healthcare output. The healthcare sector also supported overall growth throughout the West and parts of the Northeast. Manufacturers of durable goods around the Great Lakes benefited from a rebound in production, especially in Ohio, Illinois, Pennsylvania, and Michigan, the third-quickest-growing state.
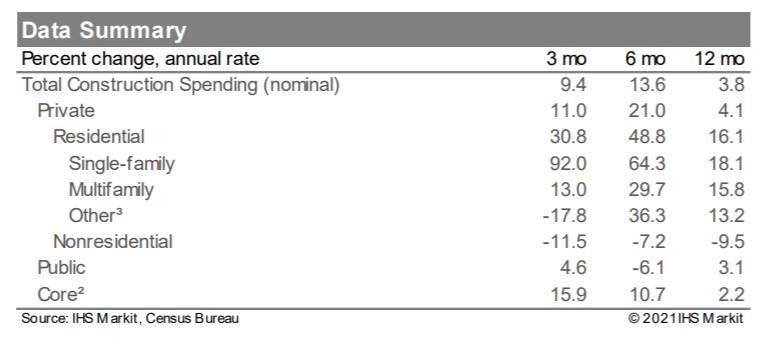
- Total US construction spending rose 0.9% in November, broadly in line with expectations. Prior months' spending levels were revised higher. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- Core construction spending, which directly enters our GDP tracking, rose 1.1% in November, close to what we had assumed. Prior months were revised higher.
- The construction sector continues to be driven higher by a robust residential sector. Private residential construction rose 2.7% in November to a level that far exceeds the pre-pandemic peak.
- Indeed, the level of spending in this sector has nearly reached the all-time high, a record that was set during the housing bubble of the mid-2000s.
- The residential sector is benefitting from historically low mortgage rates and some pent-up demand from when the US economy was "shutdown" last spring to stem the spread of the COVID-19 virus. As of last week, the contract rate on conventional 30-year fixed-rate mortgages was 2.67%.
- Private nonresidential construction spending, on the other hand, has been trending lower for about one year. Over this period, spending on manufacturing and power buildings has weakened enough to account for nearly one-half of the total decline.
- The trend in spending on office buildings has been weakening and is unlikely to improve if the trend towards working from home persists.
- State-and-local construction spending rose 0.1% in November but remains well below a peak reached last March. Tight state-and-local budgets will weigh on this sector for some time.
- Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer Tesla has posted initial figures for its global production and deliveries in the fourth quarter and full-year 2020, including 180,570 vehicles delivered and 179,757 vehicles produced in the fourth quarter. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Tesla's plant in Shanghai, China, was in operation throughout 2020, after initial production began at the facility in late 2019, and production of the Model Y started at Tesla's facility in California, United States, in January 2020. As a result, the fourth-quarter 2020 figures compare with 112,000 deliveries and 104,891 units produced in the fourth quarter of 2019.
- In full-year 2020, Tesla's production broke the 500,000-unit mark, with the company producing 509,737 units, while its deliveries were just shy of the 500,000-unit mark, at 499,550 units.
- Of the total figures, Tesla delivered a combined 57,039 units of the Model S and the Model X EVs and produced a combined 54,805 units of the two models. In 2020, the combined total of Model 3 and Model Y vehicles delivered was 454,932 units, and a combined 442,511 units of the two models were produced.
- Along with announcing its deliveries and production, Tesla confirmed that production of the Model Y has begun in Shanghai and deliveries are to begin "shortly".
- Tesla's initial report provides only a snapshot of its deliveries and production in the fourth quarter and the full-year 2020, and the company did not break down the figures by country or region. Further details will come when the company reports its fourth-quarter 2020 financial results.
- Peer-to-peer car-sharing company Turo is planning to go public this year following a strong 2020 performance, reports the Wall Street Journal (WSJ). The company posted its first-ever profitable quarter in 2020 and expects to turn a full-year profit in 2022. Turo CEO Andre Haddad said he is undecided whether to undertake a traditional initial public offering (IPO) or merge with a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC). Turo ended 2020 in a healthy financial position despite the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus pandemic. The company laid off one-third of its 330-person workforce and slashed marketing costs to shore up three years of cash. This year, Bloomberg reported that Turo and Getaround had secured US loans because of the economic effects of the pandemic on their transportation businesses. Turo's service is currently available in more than 5,500 cities in Canada, Germany, the UK, and the US. The company has over 450,000 vehicles listed, with more than 850 unique makes and models on its platform, and has a community of 14 million members globally. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Brazil's National Association of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (Associação Nacional dos Fabricantes de Veículos Automotores: Anfavea) indicates that light-vehicle registrations in the country were about 231,900 units in December, the best monthly result of 2020 but still meaning the full-year total was less than 2.0 million units, reports Automotive Business. According to the report, Anfavea will publish the full results for December 2020 on 8 January. The group expressed optimism over registrations in 2021, blaming the year-on-year (y/y) decrease in registrations in December on the holiday period as well as lower inventories of popular models. Anfavea stated that an average of 10,539 vehicles were registered on each of the 22 working days of December, compared with an average of 10,702 units per day in November. On the market in 2021, Anfavea president Eduardo Jurcevic reportedly said, "We believe that the market will grow, we still don't know how much… There is the challenge of cost, it is a relevant factor… It is not easy to make this projection, but the tone is optimistic." Jurcevic also reportedly said that Anfavea expects credit to grow 20% in 2021. The market situation in Brazil in 2020 was similar to that in other markets, including a deep trough in April and May, when the most restrictive COVID-19 lockdown measures were in place. At the end of November, year-to-date light-vehicle sales in Brazil were down 28.7% y/y. IHS Markit currently forecasts the Brazilian market will see light-vehicle sales improve to 2.36 million units in 2021, from less than 2.0 million units in 2020. A more detailed report on Brazilian light-vehicle sales, production, and exports will be published when the data are available. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Peruvian Congress on 30 December 2020 approved a law capping interest rates charged in the financial sector. The new law tasks the Central Reserve Bank of Peru (Banco Central de Reserva del Perú: BCRP) with setting a maximum interest rate for loans every six months. The law does not state a specific mechanism by which the BCR would set this rate, but it gives 60 days for the bank to publish internal rules to establish such arrangements. (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Alejandro Duran-Carrete)
- Peru's banking regulator, the Superintendence of Banks and Insurances (Superintendencia de Banca y Seguros: SBS), will be charged with the responsibility of enforcing and ensuring that the cap is being followed within the financial sector. The law also bans the imposition of fees on past-due loans.
- Proponents of the law have stated that it is intended to "protect citizens from usury". Revealing the ongoing confrontation between the government and the legislative power, Minister of Economy Waldo Mendoza has expressed his opposition to the bill. He warns that the law will limit financial inclusion, and has stated that the executive branch will appeal to the constitutional branch of the judiciary to block the law.
- If the new law is implemented and subsequent interest rate caps are set below market rates, banks would be likely to curtail lending to clients whenever they deem returns to be inadequate for the risks being taken. Contrary to its objectives of helping Peru's poorer citizens, the mechanism risks excluding those with weaker credit credentials from access to financial-sector borrowing.
- Affected customers would then be likely to seek recourse to black-market sources for funding, replicating the position in other Latin American (and other Emerging Market) countries that have imposed rate caps. Several Latin American legislatures have approved usury laws as populist measures over the last decade, despite warnings from central banks and regulatory bodies over their adverse impacts.
- Peruvian banks' profitability risks experiencing further downward pressure. During 2020, the Peruvian banking sector suffered from reduced financial margins and rising costs, resulting in a return on average assets (ROAA) of 1.0% in September 2020, way below the 2.3% registered in September 2019. The likely reduction in lending in response to the new cap would further damage financial margins in the sector and hinder the scope to regain prior margins once the COVID-19-virus pandemic is controlled.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- European equity markets closed higher; UK +1.7%, France +0.7%, Italy +0.4%, Spain +0.3%, and Germany +0.1%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy +1bp, Spain -1bp, France/UK -2bps, and Germany -3bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +1bp/49bps and iTraxx-Xover +7bps/250bps.
- Brent crude closed -1.4%/$51.09 per barrel.
- Ineos has completed the $5-billion acquisition of BP's worldwide aromatics and acetyls businesses, comprising 15 manufacturing sites and 10 joint ventures (JVs). The businesses will be known as Ineos Acetyls and Ineos Aromatics. Ineos announced the acquisition in June last year. The deal includes five manufacturing sites in the Americas, two in Europe, and eight in Asia, as well as the 10 JV site locations, and will extend Ineos's portfolio and geographic reach, it says. The purchase "is a logical development of our existing petrochemicals business, extending our interest in acetyls and adding a world-leading aromatics business supporting the global polyester industry," says Ineos chairman Jim Ratcliffe. The acquisition provides "good scope for expansion and integration with our existing business," he says. The acquired aromatics business is a world leader in purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and para-xylene (p-xylene) production and technology, with six manufacturing sites, according to Ineos. The business supplies the global polyester business, including polyester fiber, film, and polyethylene terephthalate packaging. It also licenses PTA production technology to other producers worldwide. The acetyls business produces acetic acid and a range of derivatives from nine manufacturing sites, supplying sectors such as the food, pharmaceuticals, paints, adhesives, and packaging industries, Ineos says. Ineos Styrolution, the wholly-owned styrenics subsidiary of Ineos, is the formal acquirer of BP's businesses. In 2019, BP's petrochemicals business made 9.7 million metric tons of products, according to BP. The businesses included in the transaction together employ more than 1,700 worldwide. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- The Volkswagen (VW) passenger car brand has pledged to significantly ramp up the number of electric vehicle (EV) charging points at its German sites, according to a company statement. The brand is going to install 750 new points at its 10 plants and corporate sites in Germany, adding to the 1,200 that are already installed. Many of the new points will be high-power charging stations with power of up to 300 kW/hour, which represents the state of the art in terms of fast charging at the present time. A large share are publicly accessible and can also be used by EV drivers who do not work for VW. The biggest charging park, with approximately 500 charging points, is located in Wolfsburg. More parks have been installed in Hanover, Brunswick, Salzgitter, Kassel, Emden, Osnabrück, Zwickau, Chemnitz, and Dresden. Thomas Ulbrich, Member of the Board of Management of the Volkswagen Brand responsible for E-mobility, said, "As announced, 2020 marked the start of Volkswagen's major electric offensive. We successfully launched the ID.3, and are already following that up with the next model, the ID.4. Volkswagen is also making an important contribution to the urgently needed expansion of the charging infrastructure. We need significantly more charging points in Germany and Europe if electric vehicles are to establish themselves quickly. For that reason, all players from the fields of politics and industry must continue their efforts in the coming year." Having around 2,000 charging points at VW plant and corporate locations will be necessary so the cars manufactured can be charged to be driven to storage prior to shipping, and workers and the public can use the points as well. While it is a good move for VW to make these points accessible to the general public, it is unlikely that most BEV owners will be prepared to drive to their local VW factory to charge their vehicle. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- The French passenger car market has fallen by over one-quarter during 2020 according to the latest data published by the French Automobile Manufacturers' Committee (Comité des Constructeurs Français d'Automobiles: CCFA) as COVID-19 virus measures caused swings in registrations. During the year, registration volumes have dropped by 25.5% year on year (y/y) to 1,650,118 units. Demand was also weak in December, when passenger car registrations dropped by 11.8% y/y to 186,323 units. When taking in to account the additional working day during that month - 22 days versus 21 days in December 2019 - the rate of decline is an even steeper 15.8% y/y. Given the severe drop suffered by the wider passenger car market during 2020, domestic OEMs have been unsurprisingly weaker. Groupe PSA led the way in terms of volumes with 530,606 units, and this was a decline of 25.1% y/y. Peugeot was its leading brand but its registrations fell by 20.5% y/y to 301,935 units, while Citroën fell 30.8% y/y to 162,688 units. Furthermore, Opel tumbled by 34.5% y/y to 43,801 units, as DS Automobiles slipped by 17.4% y/y to 22,182 units. There is a degree of uncertainty about how 2021 will pan out, given that the COVID-19 virus remains a threat, particularly given the emergence of a new, more infectious, strain, although the roll-out of vaccines should help matters. For now, IHS Markit expects that passenger car registrations will increase by 10% y/y to around 1.8 million units, putting it well below the 2-million-unit mark that the market recorded between 2016 and 2019. We do not expect this level to be surpassed over the course of the decade. In the LCV category, those with a GVW of over 6 tons should rise by less than 5% y/y to over 415,000 units, but again we do not expect previous levels to be hit during the decade. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Austria's labor market indicators are deteriorating again now due to the fresh constraints on economic activity caused by the recent lockdown restrictions imposed by the government to regain control over COVID-19 infections. A sustained economic rebound will require widespread vaccination to have been completed by around mid-2021 and a subsequent labor market improvement should therefore not be expected before late 2021. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- According to the Austrian Labour Market Service (AMS), there were 459,682 unemployed people in Austria at end-December 2020, up 69,000 from November and up 110,000 (31.4%) versus December 2019. The gap with the unemployment rate a year earlier had peaked at 5.4 percentage points at the height of the initial lockdown in April before narrowing temporarily to 1.7 points in October, but December's rate at 11.0% is now 2.5 points higher than in December 2019. The closure of hotels and restaurants and large parts of the retail sector and the educational system has had a major impact, and ski resorts also were not allowed to open before 24 December (and then only to domestic tourists). Only the fact that manufacturing sector operations could continue has prevented a return to the conditions observed during March and April 2020.
- The unemployment rate on a harmonized, seasonally adjusted basis as calculated according to European Union and thus International Labour Organization (ILO) criteria, is still only available until October 2020. At that time, it remained steady at 5.4%, with September being revised down from 5.5% originally. This compares to an interim peak of 5.9% in June, caused by ramifications of the March-April lockdown, and a cyclical low point of 4.3% in November-December 2019. The annual gap in October is 1.0 percentage points, remaining considerably smaller than the gap of its national counterpart in October (1.7 points). The ILO data are survey-based and therefore are much less volatile in reaction to changes in economic activity than the national numbers that reflect registrations for unemployment benefits.
- Vacancies, which still had exceeded their year-ago level until February, were down 22.7% y/y in December (absolute level: 50,610). The recovery tendency observed until October has reversed during the last two months, as signaled by deepening year-on-year (y/y) declines.
- Finally, dependent employment declined by 53,000 (or 1.4%) y/y in December, representing relative stabilization following the October-November deterioration that corrected for the interim recovery phase between April (-200,000, or -5.0%, y/y) and September (-35,000, or -0.9%, y/y).
- The dip by 53,000 in combination with the unemployment increase of 110,000 means the labor force has increased by 57,000 y/y (or 1.4%). This compares to September's modest increase of only 0.7% y/y and a peak in April 2020 at 2.0% y/y.
- Note that quarterly data for seasonally adjusted employment had already swung abruptly from 0.3% q/q in the fourth quarter of 2019 to -0.4% q/q in the first quarter of 2020, but this has been followed by even greater volatility during the two latest quarters - a plunge by 4.0% q/q in the second quarter and a partial rebound by 3.0% q/q in the third. The employment levels of 2019 will hardly be restored before late 2022 or even 2023.
- The corrective improvement in the Austrian labor market between May and October, profiting from a loosening of COVID-19-related lockdown measures, has been partly unwound again in late 2020. This deteriorating tendency should continue during the first half of 2021 owing to the negative knock-on effects of the fresh lockdown that is due to last at least until 18 January.
- Even if some loosening occurs at that point, employment related to large public gatherings or people potentially being in close contact to one another, such as spectator sports, festivals, fairs, cinemas, or theatres, will remain sub-normal until mid-2021 in any case. Labor market conditions will improve lastingly only once widespread vaccination has been achieved. Company insolvencies and thus unemployment will increase once more for the next 6-9 months.
- IHS Markit currently expects a recession of -6.8% in 2020 and an only partial rebound by 3.6% in 2021.
- Switzerland's manufacturing PMI and KOF Economic Barometer data for December surprised positively once more, seemingly ignoring deteriorating COVID-19 related developments across Europe (including Switzerland). Swiss authorities' reticence with respect to tightening administrative restrictions on economic activity can explain this at least in part. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- In December, the purchasing managers' index (PMI) for the manufacturing sector (seasonally adjusted) - compiled by the association for Procurement and Supply Management procure.ch and published by Credit Suisse - unexpectedly extended its November rebound, increasing from 55.2 to a 27-month high of 58.0 that markedly exceeds its long-term average of 53.7.
- Even the PMI counterpart for the service sector, which had fallen sharply during October-November, recovered modestly from 48.0 to 49.2 in December. This latest level remains in (sub-50) contraction territory, however. The components for new orders (50.0) and current business (53.0) provided most of the upward impetus.
- A closer look at the manufacturing sector reveals that December's fresh improvement owed to weighted contributions from four of the five components (output, supplier delivery times, employment, and stocks of purchases) that were roughly equal in size. Only new orders, which had spiked sharply in November, unwound about half of that in December and thus exerted a restraining influence. A caveat applies to the rising index for supplier delivery times, as this is possibly helped by renewed supply chain disruptions and thus does not necessarily reflect higher demand.
- Overall, the recent underperformance of the headline manufacturing PMI index versus its German counterpart during June-October has been broadly erased again by December. Furthermore, December's Swiss PMI level of 58.0 represents widening outperformance versus the eurozone average (55.2, up by only 1.4 points from November).
- Meanwhile, the KOF Barometer, which is a broad-based indicator reflecting sentiment in all areas of the economy, also edged up from November's 103.7 to 104.3 in December. This indicator had corrected during October-November from September's 10-year high of 110.0. The latest level, remaining above its long-term (2009-18) average of 100.0, remains quite encouraging for the near-term outlook in view of the burden linked to the expanding second wave of COVID-19 infections across Europe during the fourth quarter of 2020.
- Switzerland's latest leading indicators reflect a better near-term outlook than might have been expected in view of the renewed spike in COVID-19 infections since October and the associated tightening of administrative restrictions on economic activity. That being said, the Swiss authorities have been relatively reticent in this regard, for instance refraining from closing down skiing resorts as observed in most other countries sharing the Alps. As before, manufacturing is performing much better than services, but even the latter managed to recover slightly in December after its October-November setback.
- We currently estimate that GDP will have contracted by a relatively mild 3.2% in 2020, to be followed by a rebound of 3.3% in 2021.
- Aker Solutions has secured a contract from Aker Carbon Capture for engineering, procurement and management assistance to realize the CO2 capture plant at Norcem's cement factory in Brevik, Norway. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Helge Qvam)
- The project will start in January 2021 and work will be completed in 2024. The contract has a value of about USD70 million (NOK 500 million).
- The plant will become the world's first large-scale capture plant at a cement producer, capturing some 400,000 metric tons of CO2 annually.
- Aker Carbon Capture is the main contractor for engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) and will apply its proprietary and patented technology for carbon capture. The company is responsible for the delivery to Norcem HeidelbergCement of a complete new facility for capture, intermittent storage and offloading of CO2, with integrated waste-heat recovery. Aker Solutions' scope includes engineering, procurement and management assistance (EPMa) for the new installation.
- Aker Solutions expects around 100 employees will be involved in delivering these services. The project includes deliveries from the company's offices in Fornebu and Mumbai, with most of the work being performed in Norway.
- The development in Brevik is part of the Norwegian government's Longship demonstration project to realize the full value chain for carbon capture and storage. Longship also includes the development of new installations for permanent storage in the seabed off the west coast of Norway. On December 17, 2020, Aker Solutions announced contracts of about NOK 1.3 billion for delivering the CO2 receiving facilities Northern Lights, as well as subsea equipment for injecting captured CO2 into a reservoir for permanent storage. The CO2 captured in Brevik will be transported to the Northern Lights project for permanent storage.
- Realizing Northern Lights means that multiple companies across northern Europe now have a real opportunity to remove their CO2 emissions and transform their industries into sustainable businesses.
- The contract will be booked as order intake in the fourth quarter of 2020 in the Renewables and Field Development segment.
Asia-Pacific
- Most APAC equity markets closed higher except for Japan -0.7%; South Korea +2.5%, Australia +1.5%, Mainland China +0.9%, Hong Kong +0.9%, and India +0.6%.
- Mainland China retightens banks' lending to the real estate sectors in an effort to prevent systemic financial risk, according to a new bank loan management mechanism issued jointly by the People's Bank of China (PBOC) and the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Committee (CBIRC) on 31 December 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- Based on the new rules, all domestic banks' outstanding property loans as well as outstanding mortgages as proportion of total loans should both be capped under a five-tiered system. For mainland China's big four state-owned banks, the rail will be capped at 40% and 32.5%, respectively. For second-tier banks, including state-owned policy banks and 12 joint-stock holding commercial banks, the two ratios are 27.5% and 20%, respectively. For smaller city and rural commercial banks as well as small village banks, the two ratios are even lower. To be noted, loans for renting are excluded from the new rules.
- The new rules took effect 1 January 2021. Regulators said the requirements could be adjusted depending on a region's economic performance. Banks that do not meet the requirements will be granted an unspecified grace period from two to five years.
- The new rules followed a series of measures to curb overlending to the property sector, which was seen as driving the price bubble and adding to financial risk. Regulators released a 'three red lines' directive in August 2020, setting caps on the amount property developers could borrow, which has led to a decline of the debt-to-equity ratio across mainland Chinese-listed property companies.
- As the new rules are targeting the ratio of property loans, the scale of overall loans may not be impacted. Meanwhile, considering that large banks contribute over 80% of the asset increase in the banking sector, while the caps for large banks are relatively higher, the overall impact of the new rules on the banking sector could be limited.
- Mainland China issued the first foreign investment negative list specifically for Hainan free trade port (FTP) on 31 December 2020. The 27-item list was jointly released by the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and the Ministry of Commerce (MOC). Effective 1 February 2021, Hainan's negative list further relaxed market access restrictions for foreign investors compared with the nationwide list. (IHS Markit Economist Lei Yi)
- Notable changes fall in sectors including telecommunication and education. Restrictions on foreign investment in online data processing and online transaction processing businesses will be removed. Enterprises registered and operating in Hainan FTP shall be permitted to set up internet data centers and carry out content distribution businesses targeting clients in Hainan FTP and overseas. In terms of education, overseas top universities and vocational colleges specializing in science, engineering, agriculture, and medicine will be allowed to establish institutions in Hainan independently.
- Additionally, Hainan's list lifted the 50% cap on foreign ownership for passenger carmakers, which was originally scheduled for 2022 nationwide. Investment restrictions in mining was also dropped; and foreign investors will be able to participate in social research, with an upper ownership limit setting at 33%.
- The newly unveiled Hainan-specific negative list further improves the region's attractiveness for foreign investment, building on a set of preferential policies which have been rolled out since mid-2020. According to the local commerce department, in the first three quarters of 2020, Hainan added 540 foreign enterprises, up by 130% year on year (y/y); foreign investment utilized during the same period reached USD528 million, surging by 93.1% y/y.
- China has further reduced subsidies on new energy vehicles (NEVs) to promote the healthy development of the industry, according to a statement posted on the official website of the Ministry of Finance on 31 December 2020. From 1 January 2021, the ministry has reduced subsidies on NEVs in public transportation by 10% compared with the level of 2020. Subsidies on other NEVs have been reduced by 20%. Local government authorities are allowed to provide subsidies for new energy buses to speed up the adoption of zero-emission buses in cities. The Ministry of Finance's statement is aligned with what was announced earlier in the year regarding China's plan to phase out subsidies on NEVs by 2022. Because of demand contractions in the NEV market during 2019 and the outbreak of the COVID-19 virus outbreak, Chinese authorities did not make significant subsidy cuts in 2020. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Great Wall Motor (GWM) has launched the "331 Strategy" under its "Coffee Intelligence" program as it aims to be a leading intelligent driving tech developer. The Coffee Intelligence program encompasses six redundancy systems for vehicle perception, controller, braking, framework, power source, and steering. GWM also announced that it aims to achieve Level 3 automated vehicle operation with redundancy throughout a vehicle in 2021. GWM's car will be equipped with LiDAR and with NOH (Navigation On Highwaypilot) capability in 2021. In addition, GWM has signed agreements with Qualcomm and Huawei to co-operate on in-vehicle smart chips and high computing power smart driving computing platforms. GWM will integrate Qualcomm's Snapdragon Ride autonomous vehicle (AV) platform into the intelligent driving system of its premium models to be rolled out in 2022. Huawei will provide its MDC-based high computing power intelligent driving computing platform to GWM required for intelligent driving. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Xpeng Motors is to deploy Livox's LiDAR sensor in its new 2021 production model. For this collaboration, Livox is to customize its Horiz LiDAR sensor to meet automotive-grade requirements, delivering cost efficiency and reliability for production models, says the company. Livox has enhanced the detection range of its Horiz sensor to 150 meters and has included a new "ultra FPS" (Frames Per Second) LiDAR technology concept. In addition, the customized Horiz sensor's ROI (Region Of Interest) point cloud density has increased to 144 lines and horizontal FOV (Field Of View) has expanded to 120 degrees. The integration of the LiDAR sensor into Xpeng's autonomous vehicle (AV) system, called XPILOT, will further enhance the system's safety, as well as the ability to cover a comprehensive range of driving scenarios. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Valeo, a major French component supplier, is testing Level 4 autonomous vehicle (AV) technology in Japan, reports Nikkei Asian Review. The trials are conducted on a 6.7-km circuit on urban street to test its AV system's dependability and to identify potential risks. The system uses a combination of three-dimensional maps and information gathered from communications between the vehicle and traffic lights. These demonstrations are aimed at assessing the reliability of its automated driving prototype that uses its "SCALA" LiDAR laser scanner for use in Level 4 cars. The prototype deploys a second-generation SCALA in the front part of the car, three first-generation SCALAs each in the front and rear parts of the vehicle and a camera integrated in the windshield. The suite of sensors allows the system to detect static or moving obstacles and anticipate events. LiDAR sensors are necessary for AVs as they measure distance via pulses of laser light and generate 3D maps of the world around them. Unlike cameras, LiDAR sensor can detect shadows and are not blinded by bright sunlight. The biggest hurdle for mass adoption of LiDAR is its high cost, and companies around the world are racing to develop sophisticated but low-cost LiDAR technologies. Major component suppliers including Denso and Continental are also planning to roll out mass production of LiDAR laser scanners. Recently, Mobileye announced plans to develop its own LiDAR sensors to bring down costs for AV systems for consumer cars. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Japan is witnessing very cold temperatures which have significantly increased electricity demand in the region for heating purposes. For the passing week-53, Japanese electricity demand stood at 97GW, up 8GW y/y. Electricity prices in the Japanese wholesale market (JPEX) for the day-ahead contract (on 4 January 2021) hit a record high level of Yen 62.41/kWh versus the previous all-time high of Yen 26.16/ kWh witnessed on 24 July 2018. As per IHS Coal, Metals and Mining database, Newcastle 6000NAR fob coal prices for week-53 stood at $81.13/t, up 27% y/y. North Asian LNG spot prices have also skyrocketed and were all set to cross the $18/MMBtu mark. Due to strong anticipated heating demand from the Far East, there was a significant increase in thermal coal shipments from Australia to Japan which helped December 2020 to close above the 35mt mark despite ongoing negligible buying from China (Mainland). As per IHS Markit Commodities at Sea, Australian coal shipments during December 2020 stood at 35.9mt, down 7% y/y. In terms of coal grade, thermal and metallurgical shipments stood at 20.5mt (down 1% y/y) and 15.4mt (down 15% y/y), respectively. In terms of destinations, Australian shipments during December 2020 to China (Mainland) continued to decline and stood at just 0.3mt (down 97% y/y). Shipments to Japan, India, South Korea, and Taiwan stood at 12mt (up 27% y/y), 7.1mt (up 30%), 5.8mt (down 8%), and 2.4mt (up 10%), respectively. (IHS Markit Maritime and Trade's Pranay Shukla)
- Beverages containing fruit juice are subject to a 12% GST (general sales tax) in India: those that do not are now taxed at 40%. Under the GST structure, taxes are levied under 5, 12, 18 and 28 per cent levels. On top of the highest tax bracket, a second tax is levied on luxury, 'sin' and 'demerit' goods, and the proceeds from the same are used to compensate states for any revenue loss. In August, regional beverage companies were placed under scrutiny for paying lower taxes despite not adding fruit juice to their beverages. These companies were subsequently investigated. Already badly affected by the pandemic crippling their businesses, the beverage companies decided to avoid substantial penalties for evading GST. Foreign beverage giants were urged in 2014 to add fruit to carbonated soft drinks to boost sourcing from Indian farmers. The announcement resulted in both multinational and local beverage firms launching such beverages subject to lower GST. However, adding a fruit component incurred extra production costs that were beyond the means of many small manufacturers. Critics of the GST says that it will benefit large players such as Coke and PepsiCo in India's USD1.9 billion soft drinks industry. The Indian Beverage Association (IBA), which represents the non-alcoholic beverage industry and major industry players such as Coca-Cola India, Pepsico India Holdings, Dabur India, Red Bull India, Tetra Pak India, Pearl Drinks, Bengal Beverages and others, has calculated that the industry will contract in 2020 by about one-third, in financial terms, following the effects of the pandemic on its sales. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Neil Murray)
Posted 04 January 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.


