All major US and European equity indices closed higher, while APAC markets were mixed. US and benchmark European government bonds closed sharply lower. CDX-NA closed slightly wider across IG and high yield. The US dollar, natural gas, and oil closed higher, while gold, copper, and silver were lower on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- All major US equity indices closed higher, with DJIA +0.7% and S&P 500 +0.6% closing at new all-time highs; Russell 2000/Nasdaq +1.2%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +12bps/1.64% yield and 30yr bonds +13bps/2.03% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/50bps and CDX-NAHY +2bps/294bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed +0.6%/96.21.
- Gold closed -1.6%/$1,800 per troy oz, silver -2.3%/$22.81 per troy oz, and copper -0.9%/$4.42 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +1.2%/$76.08 per barrel and natural gas closed +3.4%/$3.68 per mmbtu.
- The seven-day average of daily reported Covid-19 cases in the U.S. reached a pandemic record 403,385 on Sunday, according to a Wall Street Journal analysis of Johns Hopkins University data. The fresh peak arrived even as most states paused reporting during the New Year's holiday weekend. Reporting delays will likely lead to spikes in reports of cases this week as states catch up. While COVID-19 tests remain in short supply in much of the U.S., COVID-19 testing was less robust last year, complicating comparisons between pandemic surges. Hospitalizations for confirmed or suspected COVID-19 reached a seven-day average of 97,855 on Monday, according to data posted by the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. That is up 41% in the past two weeks but below both the pandemic peak of 137,510 on Jan. 10, 2021, and the smaller peak of 102,967 on Sept. 4, 2021, during the Delta surge. (WSJ)
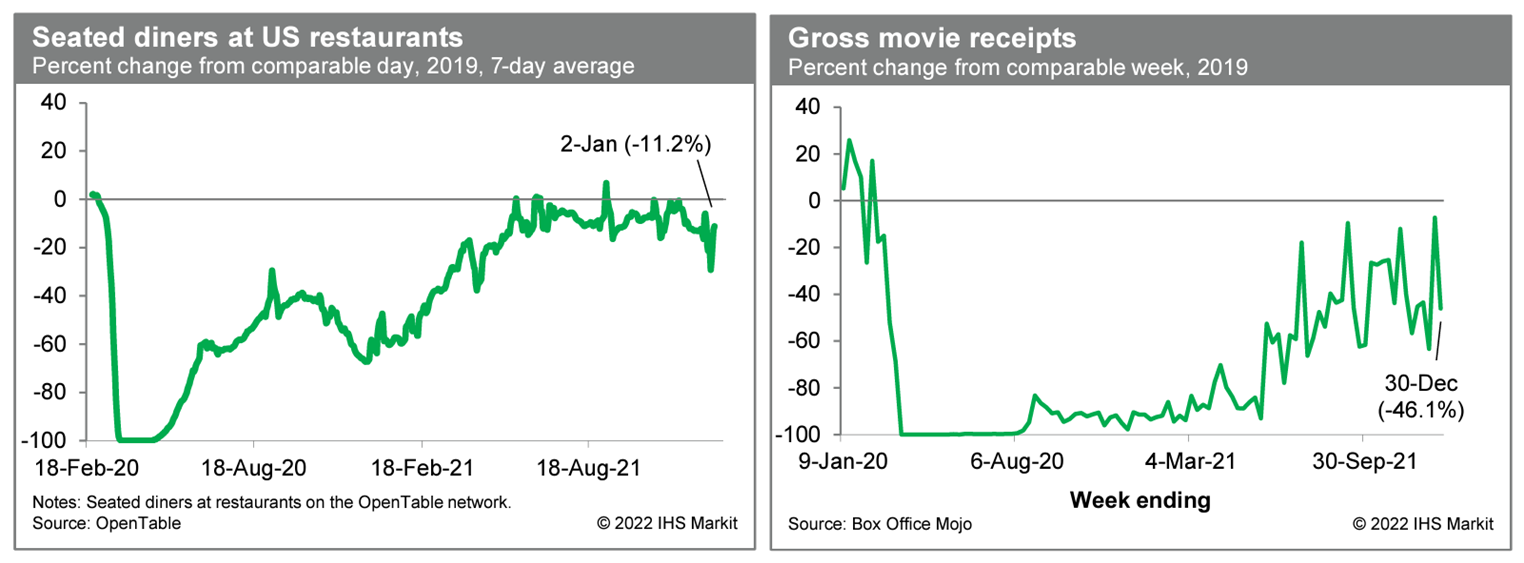
- Averaged over the last seven days, the count of US seated diners on the OpenTable platform was 11.2% below the comparable period in 2019. This indicator has been volatile over the last couple of weeks but is hinting at some renewed caution about dining out. The next week or so of readings on seated diners will clarify whether activity is indeed slowing materially. Meanwhile, box-office revenues fell last week to 46.1% below the comparable week in 2019. This was on the heels of solid revenues the prior week that were boosted by the release of Spider-Man: No Way Home. The return of revenues to roughly the prior trend indicates that the recovery in movie-theater activity remains far from complete. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- US total construction spending rose 0.4% in November, below expectations, but from levels of spending in September and October that were revised higher. Core construction spending also rose 0.4% in November following upward revisions to prior months. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- Firming costs and prices throughout the construction sector are boosting nominal construction spending generally. Furthermore, both total and core construction spending are benefitting from past (real) strength in the residential sector, although that source of strength is waning.
- Single-family housing permits peaked in January and have been generally moving lower since. While there were substantial gains over October and November, the level of single-family permits remained well below the January peak.
- This led to a slowing in the value of private residential construction put-in-place. Over the six months ending in November, private residential construction spending rose at a 9.0% average annual rate. This is down considerably from 24.4% average annualized growth over the prior six months.
- The recent jump in single-family permits will lead to renewed strength in residential structures spending, but this will be temporary, as permits are expected to turn lower beginning in December.
- Elsewhere in the construction report, private nonresidential structures rose 0.1% and public construction slipped 0.2% in November.
- Recent gains in private nonresidential construction have reflected strength in spending on commercial warehousing and manufacturing, two sectors that have benefited from recent very strong gains in demand for goods.
- The seasonally adjusted IHS Markit US Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI™) posted 57.7 in December, down from 58.3 in November but broadly in line with the earlier released 'flash' estimate of 57.8. The improvement in the health of the US manufacturing sector was the slowest in 2021 amid subdued output and new order growth. Ongoing efforts to build safety stocks and a severe deterioration in vendor performance, ordinarily signs of improving conditions, continued to lift the headline PMI, however. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
- An inability to source key inputs also weighed on new orders, which expanded at the softest rate for a year. Although some firms stated that demand was sustained at a strong pace, many suggested that customers were working through their stocks of goods before placing orders. The rise in foreign client demand was only marginal overall.
- Higher transportation and freight fees, alongside shortages of key items, led to a further marked increase in input costs during December. Although slowing to the softest for six months, the pace of increase remained among the quickest seen in the series history (since May 2007).
- Attorneys general from California, Minnesota, Iowa, Wyoming and a dozen other states are backing USDA's effort to combat consolidation in the meat industry, calling for aggressive action to restore "competition and integrity" to livestock markets. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Policy's JR Pegg)
- The state law enforcers contend weak enforcement of the Packers and Stockyards Act (P&SA) has contributed to consolidation in meat markets to the detriment of producers and consumers.
- Enacted in 1921, the P&SA was intended to ensure fairness in livestock and poultry markets, but critics say the law—and USDA's implementing regulations—have fallen short of that goal.
- "Structural changes in these markets, including increased concentration and changes in sales and marketing practices, have threatened producer viability, resulting in attrition, and reducing the number of producers participating in the livestock markets," the state attorneys general wrote in the December 22 letter to Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack. "We hope that with increased enforcement and government oversight, the purpose of the Packers and Stockyards Act can be fulfilled and return competition to these vital American markets."
- The letter echoes growing concern about the concentration of the beef, pork and poultry markets. The four largest beef packers controlled 25% of the market in the late 1970s, but now four firms─JBS, Tyson Foods, Cargill and National Beef─account for 85%. Similarly the top four pork packers now control 70% of the market up from 33% in 1976, and the four largest chicken processors' marketshare stands at 54%, up from 35% in 1986.
- On December 31, the New York State Office of Renewable Energy Siting sent a notice to Hecate Energy Cider Solar LLC that its application is deemed complete for a Siting Permit for the 500-MW (ac) Hecate Cider Solar Farm, to be located in the towns of Elba and Oakfield in Genesee County. (IHS Markit PointLogic's Barry Cassell)
- The application had been filed on June 4, 2021, and was amended and supplemented on September 3, 2021 and November 22, 2021. No later than sixty days following the date of this December 31 letter, the Office will publish on its website a draft siting permit for public comment or a statement of intent to deny the application.
- The project area is located to the north and west of the Village of Elba, and north of the Village of Oakfield. The northern portion of the project area is bisected by the New York Power Authority's (NYPA) 345-kV Dysinger-New Rochester transmission line and the Empire Gas Pipeline, which are located adjacent to each other and run east-west through the project area. The proposed project substation would interconnect to the NYPA transmission line in the center of the project area, west of Graham Road in the Town of Elba.
- In December 2021, Rock Creek Wind LLC applied with the Wyoming Industrial Siting Division for approval of an up-to-590-MW wind farm, to be located in Albany and Carbon counties, Wyoming. (IHS Markit PointLogic's Barry Cassell)
- The two phases of the project are called Rock Creek I and II. The project is planned to be up to 590 MW in total size, consisting of up to 111 wind turbines, depending on final turbine selection. It would include two project substations, and two 230-kV generation-tie lines; one to the Foote Creek Substation and the other to the Aeolus Substation.
- The Division and the state Industrial Siting Council, which would make the final decision on a permit for this project, will be taking public input on the application over the next few weeks.
- The 19-month construction schedule is anticipated to commence in April 2023 and be completed in December 2024.
- Rock Creek Wind is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Invenergy Wind Development North America LLC and an affiliate of Invenergy LLC, which is headquartered in Chicago.
- "The Project was selected for the PacifiCorp final shortlist for their 2019 [request for proposals (RFP)], and is currently negotiating the final details of the Build-Transfer contract," said the application. "As part of the contract, Rock Creek will develop and build the Project, but PacifiCorp (through its subsidiary Rocky Mountain Power) will operate the Project once it is completed."
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- All major European equity markets closed higher; Italy +1.4%, France +0.9%, Germany +0.9%, and Spain +0.5%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed lower; Spain +1bp, Italy +2bps, France +4bps, and Germany +6bps.
- Brent crude closed +1.5%/$78.98 per barrel.
- EU exports of sparkling wine to the rest of the world have fallen for the first time in ten years. On 31 December, the EU's statistical office Eurostat published its updated figures for sparkling wine and found that the bloc's exports dropped by 6% between 2019 and 2020, from 528 million liters to 494 million liters. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Policy's Pieter Devuyst)
- Eurostat explained that the COVID-19 pandemic significantly affected European wine trade after ten years of consecutive growth because many restaurants and bars were forced to close for a long period.
- Champagne was hit hardest by these lockdown measures, with EU sales of the French sparkling wine falling 20% in volume to 66 million liters from nearly 84 million liters the previous year, despite some pick-up in demand during the end-of-year holiday period. Producer group CIVC estimated earlier that their sales volume would drop by 18% and cause up to €1 billion in losses.
- Other types of sparkling wine were less affected by COVID-19 restrictions. Extra-EU sales of prosecco, by far the most exported EU sparkling wine, remained largely stable with 205 million liters compared to 207 million liters the year before. Cava, which is produced in Spain, even saw its exports increase by more than 10% to 58 million liters and replaced champagne as the second-most sold EU sparkling wine.
- Since 2010, the bloc's sparkling wine exports had consistently grown at an average rate of 8%, but CIVC now expects that COVID-19 will continue to weigh on demand for their products in the first half of 2022.
- Iran has exported 46,995 tons of pistachios in October-December 2021, 47% less y/y. Open mouth in-shells accounted for three quarters of the total, according to Tehran-based Green Diamond Tree in its latest market update. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jose Gutierrez)
- The main importers were the Far East, Russia and the EU, which took 36%, 19% and 17%, respectively.
- The 2021 crop totaled 135,000 toes (-44% y/y) with carry-over stocks at a minimum level of 5,000 tons, bringing the total supply to 140,000 tons. Sales totaled 57,000 tons in October-December 2021. Domestic consumption took 17% of the total shipments.
- This means the remaining 2021-22 supply totals 83,000 tons until the next harvest in Q3 2022.
- The combination of a disappointing crop and robust revenues may secure a firm market in H1 2022.
Asia-Pacific
- Most major APAC equity markets were still closed in observance of the New Year's holiday; India +1.6%, South Korea +0.4%, and Hong Kong -0.5%.
- India has deferred a proposed hike of its Goods and Services Tax (GST) on textiles to 12%, maintaining the status quo of 5% for now, India's Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman said in a press conference late last week. (IHS Markit Chemical Market Advisory Service's Chuan Ong)
- Its 7% GST rate increase for textiles was expected to kick-in January 1, 2022, before a policy U-turn following an emergency GST Council meeting on December 31 last year.
- The Finance Minister said that the Council decided to maintain the 5% rate on textiles, recognizing an existing rate inversion problem which will be rationalized after review, according to national broadsheet The Hindu.
- This review is expected to be completed in February, meaning that the existing textiles rates will remain at least through Q1 this year.
- India's GST Council had planned to correct an "inverted duty structure in footwear and textiles sector", it said in a press release following its 45th GST Council Meeting in September 2021.
- The inversion refers to uneven tax rates applied on synthetic or manmade fibers and its downstream sectors - current GST on manmade fiber is 18%, yarns from the same fibers 12%, while finished fabrics and textiles made from these raw materials are taxed at 5%.
- States in India including Gujarat, West Bengal, Delhi, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu had raised objections to the 12% GST hike, citing risks of job losses in the millions, factory closures in the hundreds of thousands, and foreign competition.
- India is a key producer of polyester, which is a synthetic fiber. The polyester sector is the biggest consumer of petrochemical feedstocks monoethylene glycol (MEG), purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and in turn its feedstock paraxylene (PX).
- Ginger harvests are in full swing in India and China and growers are expecting bumper crops due to growth in planted acreage, according to trading sources. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jose Gutierrez)
- This expansion has relied on record prices in 2020-21. However, prices are at low levels due to abundant supply. The 2021-22 global crop is expected to grow by 9% y/y to 3.26 million tons. In addition, Nigerian exporters are offering high discounts just before they ship the domestic crop in Q1 2022.
- Chinese sliced ginger was at $3,405/ton fob in December 2021 (-11.7% m/m and -32% y/y); Indian sliced ginger was at $1,865/ton (-9.7% m/m and -45% y/y).
- Prices are expected to stabilize in Q1 2022 as the global demand is gradually rising.

Posted 03 January 2022 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.


