All major US and APAC equity indices closed lower, while European markets were mixed. US government bonds closed mixed with the curve slightly flatter on the day, while all benchmark European bonds closed lower. European iTraxx closed slightly tighter across IG and high yield, CDX-NAIG closed flat, and CDX-NAHY was wider on the day. Oil, natural gas, silver, and gold closed higher, the US dollar was flat, and copper was lower on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- All major US equity indices closed lower; S&P 500 -1.0%, Nasdaq -1.2%, DJIA -1.4%, and Russell 2000 -1.5%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +2bps/1.94% yield and flat/2.24% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/69bps and CDX-NAHY +5bps/375bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed flat/96.03.
- Gold closed +0.4%/$1,907 per troy oz, silver +1.3%/$24.31 per troy oz, and copper -0.2%/$4.51 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +1.9%/$91.91 per barrel and natural gas closed +1.5%/$4.50 per mmbtu.
- The Russian ruble strengthened against the dollar on Tuesday, gaining steam after President Biden unveiled a new package of sanctions. The U.S. dollar bought about 78 rubles late Tuesday, compared with around 80 earlier in the day. The market reaction could indicate that traders felt the package was less aggressive than it could have been. (WSJ)
- Rising from an 18-month low of 51.1 in January to 56.0 in February, the seasonally adjusted IHS Markit Flash US Composite PMI Output Index indicated a substantial expansion in private sector output that outpaced the long-run series average. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
- February data highlighted a sharp and accelerated increase in new business among private sector companies that was the fastest in seven months. Firms mentioned that sales were boosted by the retreat of the pandemic, improved underlying demand, expanded client bases, aggressive marketing campaigns and new partnerships. Customers reportedly made additional purchases to avoid future price hikes. Quicker increases in sales were evident among both manufacturers and service providers.
- Inflationary pressures across the private sector intensified in February, with the rate of input price inflation quickening from January's ten-month low. Panelists continued to indicate higher raw material, transportation and wage costs. Global shortages of raw materials and lingering supply-chain disruptions were again cited, albeit less so than in prior months.
- Prices charged for goods and services in the US rose at a record pace in February as companies continued to share additional cost burdens with their clients. Manufacturers signaled a sharper increase in selling prices than service providers, though the latter reported a record rise.
- At 56.7 in February, up from 51.2 in January, the seasonally adjusted IHS Markit Flash US Services PMI™ Business Activity Index highlighted a substantial and accelerated upturn in output.
- The IHS Markit Flash US Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI™)1 rose from 55.5 in January to 57.5 in February, signaling a stronger improvement in business conditions across the sector.
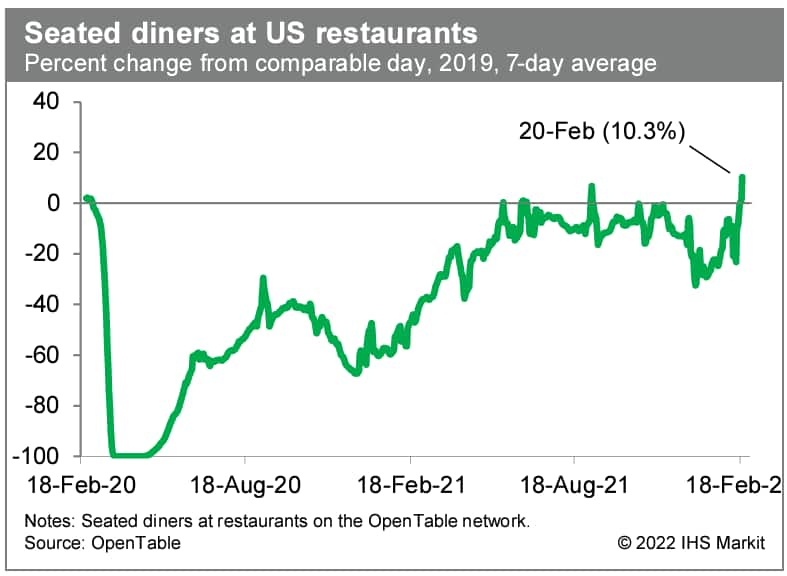
- Averaged over the last seven days, the count of seated diners on the OpenTable platform was 10.3% above the comparable period in 2019. This was the strongest reading so far in the recovery and a sign that diners are becoming more sanguine about risks of exposure to COVID-19. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- The US Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index edged down 0.6 point to 110.5 (1985=100) in February, the second consecutive monthly decline. (IHS Markit Economists Akshat Goel and William Magee)
- The overall index was pulled lower by a weakening in expectations; the present situation index firmed.
- The expectations index is based on the short-term outlook for income, business, and labor-market conditions. The share of survey respondents who expect their income to increase was 15.7% this month, down from 16.2% in the prior survey.
- Similar declines were recorded for the shares of respondents who expect business conditions to improve and who expect more jobs to be available.
- Furthermore, the share of consumers who reported they were planning to purchase big-ticket items over the next six months (homes, cars, major appliances, and vacations) fell.
- While up in total, consumer attitudes about the present situation—general business conditions and job availability—were mixed.
- In a broad historical context, consumer assessments of labor-market conditions are favorable. The net percentage of respondents noting that jobs were "plentiful" (versus "hard to get") remained elevated at 42.0, well above averages prior to the pandemic.
- Turning back to the overall index, levels in recent months remained below averages prior to the pandemic but above lows in the early months of the pandemic.
- The cut-off date for this month's survey was 16 February, prior to recent escalation of tensions surrounding Russia and Ukraine.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Major European equity markets closed lower; UK/Spain +0.1%, France/Italy flat, and Germany -0.3%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed lower; France/Italy +2bps, Germany +4bps, UK +7bps, and Spain +9bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/71bps and iTraxx-Xover -3bps/348bps.
- Brent crude closed +1.5%/$96.84 per barrel.
- On 21 February, Ursula von der Leyen, President of the European Commission, and Charles Michel, President of the European Council, which represents the 27 European Union (EU) member states, issued a joint statement in opposition to Russia's President Vladimir Putin's formal recognition of Ukraine's breakaway entities Donetsk People's Republic (DPR) and Luhansk People's Republic (LPR) as independent states and stated that the EU would impose "sanctions against those involved" in the "illegal act". (IHS Markit Country Risk's Petya Barzilska, Jan Gerhard, Dijedon Imeri, Alex Kokcharov, Blanka Kolenikova, Bibianna Norek, and John Raines)
- Immediate EU sanctions are likely to target individuals and companies involved in the decision to recognise DPR and LPR, opening the option for sanctions' expansion. The Commission confirmed on 22 February that the proposed sanctions are targeted and entail "those involved in yesterday's decision", as well as banks funding Russian military and other operations in DPR and LPR and trade from the two breakaway regions.
- The imposition of EU sanctions requires unanimous support from all EU member states, delaying their implementation probably by a few weeks. The Council of the EU is likely to first make a political decision on the sanction list, while the legal decision will probably be approved in coming weeks. EU member states are reportedly still divided around the trigger events to impose sanctions on Russia and around the severity of the immediate and follow-up sanctions against Russia in the case of an incursion into Ukraine outside the Donbas conflict zone, concluding in new Russian territorial gains.
- The UK government is likely to initially focus on targeted sanctions affecting Russian individuals and businesses. UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson stated that UK sanctions "will hit Russia very hard" and announced on 22 February that the United Kingdom plans to sanction five Russian banks and three individuals who have been on the US sanctions list since 2018.
- On 21 February, the US announced sanctions against DPR and LPR, meaning that no US firms or entities can invest or engage in financial or business transactions with entities from those areas or "any person determined to operate in those areas". The US did not explicitly increase sanctions against Russia itself, despite pleas from US Republican lawmakers, who continue to pressure the White House to increase sanctions on Russia and the Nord Stream 2 pipeline immediately.
- In the event of a full invasion leading to new Russian territorial gains, the US is likely to implement additional sanctions. These include targeted sanctions against high-worth Russian individuals with perceived close ties to the Kremlin; the prevention of several large Russian banks from conducting US dollar transactions; use of the Foreign Direct Product Rule, which would prohibit the exportation to Russia of items created using US technology, software, or goods, involving integrated circuits and chips (much like the previous sanctions on Huawei); and the prevention of purchases of Russian state-owned-entity debt in secondary markets. The banking sanctions would likely freeze any sanctioned banks' USD-denominated assets domestically and internationally.
- Lotus is said to be considering an initial public offering (IPO) for its China-based arm that is developing its electric vehicle (EV) portfolio. James Andrew, a spokesperson for the company, was quoted by Bloomberg News as saying that its Lotus Tech unit is eyeing a listing in the UK, US or China. He added that the company is yet to determine the size of the issue and valuation, and that a decision has yet to be made. The automaker is reportedly gauging investor appetite for a possible listing of Lotus. Bloomberg News reported that last week that Lotus's new electric sport utility vehicle (SUV), currently codenamed Type 132, was shown to the financial community and its dealers in London (UK). The Financial Times (FT) said that this event was held over two days, and followed similar events in Guangzhou, Shanghai and Beijing (all China) last year. The decision to undertake an IPO at this point is likely to be aimed at raising funds to support its expansion plans, similar to the approach that its key investor Zhejiang Geely Holdings has taken with Volvo Cars, which completed its own IPO in the fourth quarter of 2021. Its Polestar business will also undertake its own listing on the US-based Nasdaq exchange via a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC). (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Established leaders in Europe's steel industry such as Sweden's SSAB and Germany-based ThyssenKrupp Steel, as well as Swedish startup H2 Green Steel, made major announcements in the last few weeks about their paths towards low-carbon and net-zero production. In the near term, steelmakers across Europe are committing billions of euros to installing new low-carbon manufacturing technology and closing high-emissions blast furnaces. By the end of the decade, they may be running furnaces with no-carbon green hydrogen and capturing carbon from process units. A combination of these technologies will be needed to control emissions from an industry that, according to IHS Markit, contributes 9% of Europe's annual man-made GHG emissions, or about 3.6 gigatons of CO2. (IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Kevin Adler)
- On the demand side, steelmakers are lining up customers among automakers, builders, and wind farm developers. The ability to make "green" steel may prove to be a weapon against higher-carbon imports from China, Russia, South Korea, and Turkey, according to a report delivered to the European Parliament in December.
- Managing these challenges is critical not only for the industry's survival but also for the economy of Europe, according to paper from the European Parliament's Committee on Industry, Research and Energy (ITRE). Europe's steel producers accounted for 7.6% of global production in 2020, or 139.3 million metric tons (mt), according to ITRE, down about 10% from the prior year due to COVID-19. The industry contributed €132 billion ($150 billion) in gross added value to the EU economy, ITRE said in a paper "Moving towards zero-emission steel," published in December.
- "Since the steel industry is capital and energy intensive, any required investment into decarbonization technologies will impact the profitability of EU steelmakers that already operate in highly competitive global markets. Thus, a major challenge for the EU steel industry will be to remain competitive vis-à-vis players based in regions where carbon regulations and costs are non-existent or limited," ITRE said.
- However, the region has shifted from being a net exporter in 2011 to a net importer by 2020, said ITRE, sending out 17.7 million mt of steel but importing 21.1 million mt.
- The extended recovery of Germany's Ifo business confidence in February, now also supported by better current conditions, will very likely be rolled back in March given escalating military developments in Ukraine during the last 24 hours. The expected setback should be driven by the manufacturing sector as supply chains receive a fresh jolt, whereas consumer-facing services will continue to benefit from diminishing pandemic-related restrictions, cushioning the likely drop in overall business confidence. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- February's headline Ifo index, which reflects business confidence in industry, services, trade, and construction combined, extended January's rebound and climbed from 96.0 (revised up from 95.7) to 98.9. This recoups the losses sustained during the fourth quarter of 2021 and exceeds both its pre-pandemic level of February 2020 (96.2) and the long-term average of 97.1. The Ifo Institute said, "The German economy is betting on an end to the coronavirus crisis", but added that "the escalation of the crisis engulfing Ukraine remains a risk factor".
- Unlike in January, when only business expectations improved, companies' assessment of their current business conditions equally contributed to February's 2.9-point increase of the headline index. Expectations rose from 95.8 to 99.2, while current conditions improved from 96.2 to 98.6. This means that both measures are now above their long-term averages of 97.5 and 96.7, respectively.
- February's sectoral breakdown reveals that the wholesale sector enjoyed the largest rebound, followed by services and the retail sector. Business confidence in the manufacturing sector, which had started its recovery in December 2021 already, increased moderately further, while construction sector confidence improved only marginally. The latter was due to worsening expectations, the only component in the February survey to do so. In contrast, improvements in the service, wholesale, and retail sectors were driven to a greater degree by expectations than by current conditions.
- Falck Renewable and BlueFloat Energy, through their development company Nora Ventu, are in consultation with local communities on two floating wind projects planned in Italy. The 795 MW Nora Energia 1 will be located off the south-west of the Sardinian coast, and the 600 MW Nora Energia 2 will be located off the south-east. Both windfarms will feature 15 MW offshore wind turbines. The next step after local consultation would be to kick off the authorization process, starting with the preliminary consultation and environmental impact study. Together with three other projects planned in the country, the partners have around 4.5 GW of floating wind capacity in their sights. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
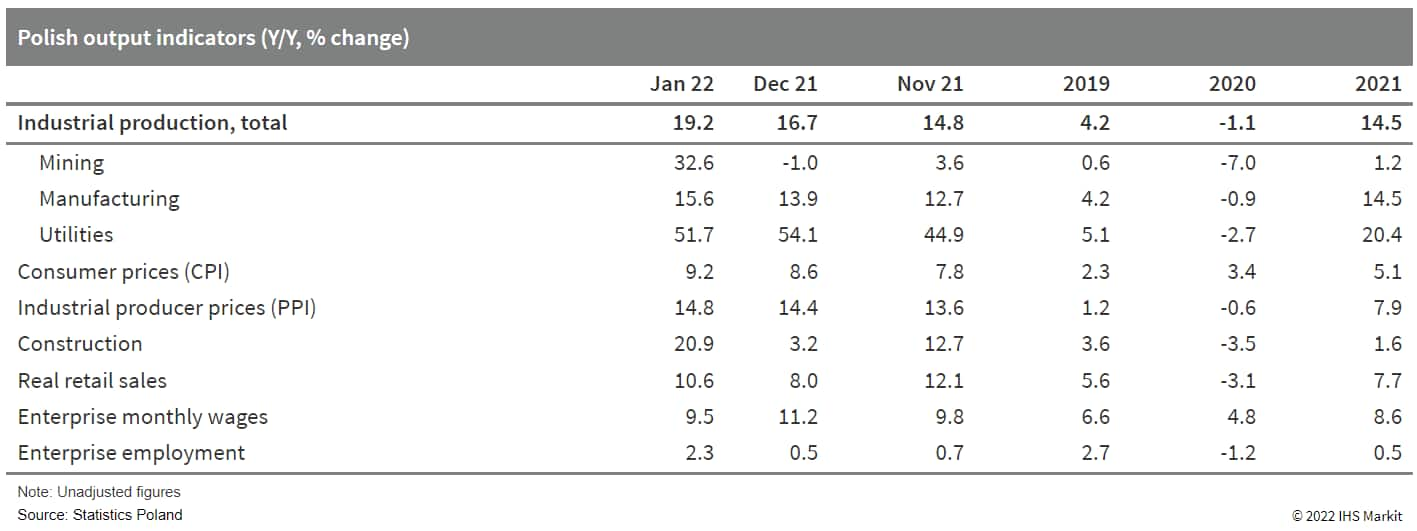
- Poland has recorded a robust start to 2022 as industrial production, retail sales, and construction surged strongly in two-digit territory in January, while labor market conditions remain very tight, intensifying pressures on wages and raising concerns about the levelling up of the wage-price spiral. (IHS Markit Economist Michal Plochec)
- The latest release from Statistics Poland reveals that in January, unadjusted industrial production (IP) surged by 19.2% year on year (y/y), driven by strong internal and external demand.
- Manufacturing output grew by 15.6% y/y. The highest growth was in energy production, which grew by 39.2% y/y, and intermediate goods, which increased by 19.0% y/y. Also, manufacturing of durable consumer goods recorded solid growth of 15.9% y/y.
- Surging natural gas prices prompted a broader switch to a comparatively cheaper coal-based electricity production, owing to which mining increased by 32.6% y/y in the first month of 2022.
- In separate release, in real terms retail trade was reported to spike by 10.6% y/y in January. The increase in nominal terms amounted to 20.0% y/y, on the back of raging inflation. The strongest growth was observed in sales of clothing and footwear, which surged by 97.7% y/y, although the magnitude of the growth largely stemmed from very low base effects (as shopping centers were closed in January 2021 owing to the pandemic). Contrarily, car sales shrunk by 13.5% y/y in the first month of the year.
- Also, construction activity recorded a spectacular rebound, as at the onset of New Year it surged by 20.9% y/y, after growing by 3.2% y/y in the last month of 2021.
- The labor market remains very tight, as wages and salaries in the enterprise sector continue to grow around two-digit territory, increasing by 9.5% y/y in January, after growing by 11.2% y/y in December 2021.
- Audi South Africa, in partnership with GridCars, a South Africa-based manufacturer of electric vehicle (EV) charging points and management systems, has made an investment (undisclosed amount) to install ultra-fast charging stations across the country at publicly accessible sites, reports Cape Business News. As part of the partnership, Audi will invest to set up 70 new 150-kW direct current (DC) charge connectors across 33 sites. The charging station setup will offer charging facility to all EV consumers, regardless of vehicle ownership. Winstone Jordaan, managing director at GridCars, said, "GridCars, established in 2009, operates and manages the most extensive network of public charging stations across the country and the partnership and additional investment with Audi not only expands the network, but allows it to be upgraded with additional ultra-fast charging opportunities is a first for our country, for all EV drivers, regardless of brand or vehicle model. The possibilities for EV adoption in South Africa are already positive and through this partnership with Audi South Africa, we are hoping to further progress the EV journey and tackle the challenges around charging, range and accessibility." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
Asia-Pacific
- Major APAC equity markets closed lower; Australia -1.0%, India -0.7%, Mainland China -1.0%, South Korea -1.4%, Japan -1.7%, and Hong Kong -2.7%.
- The Chinese central government has issued tax relief and fiscal compensation policies as well as policies prohibiting excessive COVID-19 control measures to help boost the service sector, shifting to a more "precise" approach to pandemic control. (IHS Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- Mainland China has issued polices to help its fragile services sector better cope with the economic fallout from pandemic, according to a 10-page policy paper released jointly by the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) together with 13 other government departments on 18 February.
- The policy paper states that local governments are not allowed to seal off cities and districts or suspend public transport without permission from the State Council. Businesses services including restaurants, supermarkets, cinemas, and scenic spots should not be closed. Moreover, the policy paper stipulates pandemic relief measures for catering, retail, tourism, transport and aviation, including financial support for medium and small businesses and tax reliefs for transportation.
- According to authorities, the latest support policies are aimed at prohibiting excessive COVID-19 prevention and control measures, but officials also added that "sitting back and relaxing" in the face of a virus outbreak would not be allowed.
- Chinese electric vehicle (EV) startup Hozon New Energy Automobile has secured CNY2 billion (USD315.4 million) in a third round of series D funding, reports automotive industry news source Gasgoo. Main investors in the startup's latest round of funding include the Chinese CRRC Corporation-owned fund and Shenzhen Capital Group Co Ltd. According to the report, the entire D round of funding will value Hozon at over CNY25 billion. The Chinese EV firm is also working with Morgan Stanley and UBS Group AG on its planned initial public offering (IPO), which could take place as soon as this year. Hozon is seeking to raise about USD500 million ahead of the IPO at a valuation of about USD7 billion. In October 2021, Hozon announced that it had raised CNY4 billion in its D1 funding round, led by the Chinese internet safety giant 360 Security. Meanwhile, according to data from the China Passenger Car Association, Hozon's sales totaled 69,674 units in 2021, up 361% year on year (y/y). The startup is seeing rising demand from private EV buyers for the Neta V and U. Sales of the Neta V, a subcompact model, soared 212% y/y to 6,482 units in January to become Hozon's best-selling model. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
- Hongqi, the premium brand under FAW Group, intends to deepen its collaboration with Chinese battery-swapping station operator Aulton to expand the battery-swapping network in Changchun. The two teamed up last year when Hongqi rolled out its first model with swappable batteries, the E-QM5, in Changchun. Under the partnership, Aulton provides swappable batteries to the E-QM5 vehicles at its battery-swapping station in the city. The two companies are said to work together to wider the application of battery swap technologies in electric vehicles in Changchun and other cities. According to Gasgoo, Aulton plans to build 120 battery-swapping stations in Changchun in three phases, accommodating the needs of 8,000 new energy vehicles (NEVs). The Changchun network will then become the largest battery-swapping network in the severe cold weather area in China. According to the China Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Promotion Alliance (EVCIPA), there are 1,386 battery-swapping stations in China as of the end of January. NIO is the largest operator of such facilities, with more than 860 battery-swapping stations in operation across the country, while Aulton has the second largest battery-swapping network thanks to the company's co-operation with BAIC Motor Group and FAW Group. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Chinese electric vehicle (EV) maker Xpeng has reportedly formed a subsidiary which will focus on autonomous technology to develop robotaxis. The new firm, called Guangzhou Pengxu Autonomous Driving Technology Co. Ltd., has a registered capital of CNY10 million (USD1.6 million) and is 100% held by Xpeng. The new company's business scope includes artificial intelligence software development, data processing and storage, natural science research and experimental development, technology development, and technology consulting, reports CnEVPost. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Southeast Asian fast-food chains had to ratio French fries sales as disruption to supply-chain slowed deliveries of the products from the US and Europe. After a rationing operated by McDonald Japan following flooding at Canada's Vancouver port, more recently KFC Singapore has announced that it will replace side orders of fries with potato waffles. McDonald's outlets in Malaysia and Indonesia halted sales of large-size portions of fries late last month. Fast food chains, which rely heavenly on imported potatoes, explained that the pandemic has put a strain on supply chain and distribution networks. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Cristina Nanni)
- Labor shortage, lower crop yields and overseas ports congestion have all contributed to exacerbate the drop in supplies. At the same time, goods entering Asian ports are also facing longer-than-usual delays.
- Demand for frozen French fries has started to recover and seems to be on a growth in Asia with volumes being above pre-pandemic levels.
- In January-December 2021, Singapore imported 32,300 tons of frozen French fries of which 68% supplies by the US, 9% from Belgium and 8% from the Netherlands. Volumes imported are the highest of the last 10 years and 22% higher than in 2020.
- Malaysia imported 88,000 tons of frozen fries in 2021, 12% more than in 2020 and above the 75,000 tons recorded in 2019. The US, Belgium and the Netherlands are again the largest suppliers with shares of 43.7%, 22% and 15%, respectively.
- In the same period, frozen French fries shipments to Indonesia hit 80,000 tons against 63,000 tons in 2020 and 69,000 tons in 2019. In this case, Belgium is the largest supplier (52% of the total), followed by the US (19%) and the Netherlands (15%).
- Conglomerates and startups are gaining a foothold in the Indonesian green transportation industry by manufacturing and procuring electric vehicles (EVs) for their operations, reports The Jakarta Post. PT Vektr Mobiliti Indonesia (VKTR) became the latest company to enter the market, announcing that it would develop electric buses in conjunction with local carrosserie manufacturer Tri Sakti and Chinese EV manufacturer BYD Auto. "With this partnership, we are officially opening the first e-bus manufacturing facility in Indonesia," said Anindya Novyan Bakrie, president, director, and CEO of Bakrie and Brothers (BNBR). VKTR is a spin-off of PT Bakrie Autoparts, an automotive component subsidiary of BNBR, a conglomerate with interests in mining, construction, agriculture, manufacturing, trading, and other industries. VKTR was founded with the goal of focusing on transportation electrification, beginning with the heavy mobility EV segment. Meanwhile, VKTR president director Gilarsi Setijono announced that the company would deliver 30 e-buses to Transjakarta's feeder bus fleet this week. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Other conglomerates in the automotive distribution segment, such as Indika Group, PT Astra International, and Salim Group, have also entered the Indonesian EV market. Indika Energy, Indika's coal mining arm, formed PT Electra Mobilitas Indonesia (EMI) last year to create electric motorbikes and the ecosystem that goes with them, including energy storage systems (ESS), battery-swapping stations, and EV research and development facilities. Indika Energy has also signed an USD8-billion investment agreement with Taiwanese firms and the Indonesia Battery Corporation to create Indonesia's EV ecosystem.
- Salim Group, which holds a majority stake in PT Nissan Motor Distributor through its automotive subsidiary PT Indomobil Sukses Internasional (IMAS), has been selling the Nissan Leaf EV since August 2021.
- Astra International introduced EVs in 2009 with the launch of the Toyota Prius through PT Toyota Astra Motor. Start-ups that rely significantly on motorcycles have also entered the EV industry.
- Ride-hailing service Grab and e-commerce platform Lazada have started using electric bikes in their delivery fleets. The report also highlights that ride-hailing firm Gojek also established a joint venture (JV), Electrum, with PT TBS Energi Utama to develop an end-to-end EV ecosystem.
- These developments are in line with the Indonesian government's aim to make the country an electrified vehicle hub for Asia and beyond, with the target of starting production of such vehicles this year. The government also aims for electrified vehicles to account for 20% of the country's total car production by 2025 and intends to produce 600,000 BEVs by 2030

Posted 22 February 2022 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.




