European and APAC equity markets closed mixed, while all major US indices closed lower for a second consecutive day. US government bonds closed sharply lower after the FOMC meeting and benchmark European bonds closed slightly higher. European iTraxx indices closed slightly tighter across IG and high yield, while CDX-NAIG was flat and CDX-NAHY was wider on the day. The US dollar, copper, Brent, natural gas, gold, and silver closed higher, while WTI was flat on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- Major US equity indices closed lower; Russell 2000 -0.2%, Nasdaq -0.2%, S&P 500 -0.5%, and DJIA -0.8%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +8bps/1.58% yield and 30yr bonds +3bps/2.22% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/49bps and CDX-NAHY +4bps/281bps.
- The post-FOMC meeting statement triggered a the worst 15 minute performance of the day across the S&P 500 (-0.6%), CDX-NAHY (+2.3bps), and 10yr US govt bonds (+6.6bps), which was followed by the best 15 minute period starting at 2:50pm for those same markets as the press conference relieved some of the market's concerns over the Fed's view on inflation.
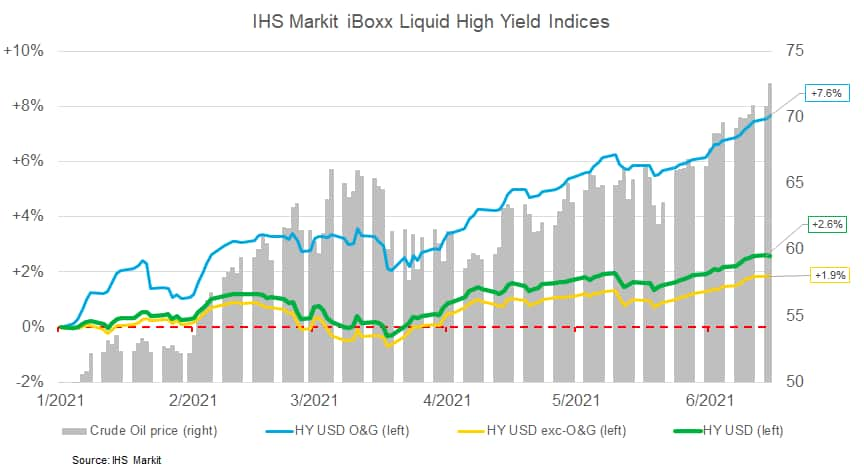
- The below chart shows daily 2021 WTI prices versus the IHS Markit iBoxx Liquid USD High Yield, IHS Markit iBoxx Liquid USD High Yield Oil & Gas, and IHS Markit iBoxx Liquid USD High Yield Excluding Oil & Gas indices. It clearly shows how the O&G index is significantly outperforming both indices at a +7.6% total return as of 15 June and is a key driver of US high yield's performance this year.
- DXY US dollar index closed +0.7%/91.13, with the entire rally occurring post-FOMC meeting.
- Gold closed +0.3%/$1,861 per troy oz, silver +0.4%/$27.81 per troy oz, and copper +1.2%/$4.39 per pound.
- Crude oil closed flat/$72.15 per barrel and natural gas closed +0.3%/$3.25 per mmbtu.
- China's National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration will soon release state stockpiles of metals including copper, aluminum and zinc, the agency said in a statement Wednesday. The metals will be sold in batches to fabricators and manufacturers, it said, without giving the volumes to be released. (Bloomberg)
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) concluded its scheduled two-day policy meeting this afternoon. There were no changes to policy setting and only one modest change to the characterization of recent developments pertaining to the near-term outlook. FOMC participants did revise their forecasts to show more GDP growth in 2021, a slightly larger decline in unemployment in 2022, and notably higher inflation primarily only in 2021. A majority of participants anticipate it will be appropriate to raise the target for the federal funds rate by 2023, with a sizeable minority expecting interest-rate lift-off in 2022. Interest rates on overnight reverse repurchase agreements and on banks' reserve balances were raised 5 basis points to 0.15% and 0.05%, respectively. These adjustments, which were taken following declines in some overnight money market interest rates to zero and even slightly below, are not viewed by policymakers as signifying a change in the stance of policy. (IHS Markit Economists Ken Matheny and Lawrence Nelson)
- A US district court in Louisiana lifted a pause on new oil and natural gas leases on federally managed lands and waters that President Joe Biden imposed via an executive order in January, calling it a violation of several federal laws. US District Judge Terry Doughty of the Western District of Louisiana issued a preliminary injunction 15 June against the pause contained in Biden's 27 January executive order on the climate crisis while the US Department of Interior (DOI) conducted a review of all new oil and gas leases to assess their contribution to GHGs. "The agencies could cancel or suspend a lease sale due to problems with that specific lease, but not as to eligible lands for no reason other than to do a comprehensive review pursuant to Executive Order 14008. Although there is certainly nothing wrong with performing a comprehensive review, there is a problem in ignoring acts of Congress while the review is being completed," Doughty wrote in a 44-page opinion. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Amena Saiyid)
- Construction of new housing in the past 20 years fell 5.5 million units short of long-term historical levels, according to a new National Association of Realtors report, which is calling for a "once-in-a-generation" policy response. U.S. builders added 1.225 million new housing units, on average, each year from 2001 to 2020, according to the report, which was prepared for NAR by Rosen Consulting Group LLC. That figure is down from an annual average of 1.5 million new units from 1968 to 2000. The 5.5 million-unit deficit includes about two million single-family homes, 1.1 million units in buildings with two to four units and 2.4 million units in buildings of at least five units, the report says. (WSJ)
- US single-family permits, a key number in the report, fell 1.6% (plus or minus 0.9%; statistically significant) to a 1.13 million rate in May. It is too early to make the call, but this category likely peaked in January. (IHS Markit Economist Patrick Newport)
- Multifamily permits fell 5.8% to a still-impressive 551,000 annual rate. The multifamily category has picked up in recent quarters. Multifamily permits reached a 34-year high in the first quarter, while multifamily starts scored their third highest reading in 33 years in the first quarter.
- Housing starts climbed 3.6% (plus or minus 10.3%, not statistically significant) to a 1.57 million annual rate in May; single-family starts rose 4.2% (plus or minus 9.2%, not statistically significant) to a 1.98 million rate; and multifamily starts edged up 2.4% to a solid 474,000 rate.
- The pace of new construction is still strong but is slowing. Builders are facing two major headwinds: higher material costs and material shortages.
- The good news is that the shortages and high material prices are temporary and some material prices, such as lumber prices, are falling back to earth. On top of this, builder margins are widening since the sales prices of new homes are increasing more than the costs of building the structures.
- The bad news is the quit rate in the construction industry is at a near record, so builders face higher labor costs on top of slowly unwinding higher material prices.
- The US index of import prices rose 1.1% month on month (m/m) in May following a 0.8% increase in April. The index's 12-month rate of increase continued to accelerate, coming in at 11.3%; however, this number is distorted by the 6.3% monthly drop in the index during May of the prior year. (IHS Markit Economist Gordon Greer)
- The index of nonfuel import prices increased 0.9% m/m in May, while its 12-month rate of increase was 6.0%.
- Fuel import prices rose 0.5% in May after an upwardly revised 1.6% increase in April. The cost of imported fuel was up 109.6% versus May in the prior year.
- Export prices jumped 2.2% m/m in May, and the 12-month rate of increase was 17.4%. Monthly changes for both agricultural and nonagricultural export prices were positive.
- According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the collection method for data in the May report was unchanged. The response rate for surveyed firms was 3.5 percentage points lower than in May 2020.
- FedEx and Nuro have signed a multi-year agreement to test an autonomous delivery pilot service in Houston (US). Under this partnership, Nuro's next-generation autonomous delivery vehicle will be deployed for FedEx's parcel logistics operations to test multi-stop and appointment-based deliveries. Rebecca Yeung, vice-president for advanced technology and innovation at FedEx, said, "FedEx was built on innovation, and it continues to be an integral part of our culture and business strategy. We are excited to collaborate with an industry leader like Nuro as we continue to explore the use of autonomous technologies within our operations." (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Pony.ai has launched fully autonomous vehicle testing on public roads in US cities of Fremont and Milpitas, California, according to a company statement. The company also plans to resume autonomous rideshare services to the public in Irvine using vehicles with a human safety driver. Its goal is to roll out the fully autonomous robotaxi service to the public in California in 2022. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- According to media reports, General Motors (GM) is planning to boost spending on electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous vehicles (AVs) to USD35 billion through to 2025. The additional spending is reported to include two new US battery plants and the speeding up of some of the automaker's EV investments. Reuters has reported that GM CEO Mary Barra is also planning to meet with US lawmakers to discuss about EVs and investments this week. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Cruise Automation president Dan Ammann has announced that the company is accessing a USD5 billion line of credit with General Motors (GM) Financial for the purpose of buying Cruise Origin vehicles once production starts. Ammann wrote that the line of credit will enable Cruise to "efficiently finance the expansion of our fleet as we scale up over the next few years. This bumps up Cruise's total war chest to over $10 billion as we enter commercialization." Ammann also confirmed that pre-production versions of the Cruise Origin have begun at GM's Pre-Production Operations center; the production vehicle will be assembled at Factory Zero (formerly the Detroit-Hamtramck plant) as development work between Cruise, GM and Honda continued despite the pandemic. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- General Motors (GM) and Wabtec Corporation have announced a non-binding memorandum of understanding (MoU) to collaborate on development and commercialization of GM's Ultium battery and HYDROTEC hydrogen fuel-cell systems for Wabtec freight locomotives; timing for deployment is not determined. According to a joint statement, Wabtec will bring expertise in energy management and systems optimization to develop a solution for heavy haul locomotives that takes full advantage of GM's advanced technologies. These technologies include the Ultium battery technology as well as GM's HYDROTEC fuel-cell cubes. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Startup solid-state battery maker Solid Power plans to go public through a merger with a special-purpose acquisition company (SPAC) called Decarbonization Plus Acquisition Corporation III. The deal is due to be closed in the fourth quarter. According to a press release from Solid Power, the company plans to be listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange and says the company will have a pro-forma enterprise value of about USD1.2 billion. On closure of the deal, assuming no redemptions by the SPAC's public stockholders, Solid Power says it will raise about USD650 million. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Lyft, in partnership with energy provider Peninsula Clean Energy, will launch an electric vehicle (EV) rental pilot program for ride-hailing drivers in San Francisco Bay Area (California, US). The pilot will provide about 100 EVs for use on the Lyft platform in the city's San Mateo County. To achieve this, Peninsula Clean Energy will offer USD500,000 in incentives to Lyft drivers to match the cost of renting an EV with a gasoline (petrol)-powered car. Lyft's Flexdrive unit, which works with local car dealerships to rent out vehicles, will operate the pilot program, reports Reuters. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Northwest Innovation Works-Kalama (NWIWK) announced 11 June it is abandoning its attempt to obtain approval from Washington state to build a methanol production and export facility at the Port of Kalama. "In light of the recent Washington Department of Ecology decision to deny the shoreline conditional use permit, the regulatory environment has become unclear and unpredictable. NWIWK is temporizing its development activities to assess the new regulatory and political landscape and determine an appropriate path forward," the company said in a press release. The termination of the 3.6 million mt/day methanol export facility, which was proposed in 2014, is the latest example in the US of a costly, high-profile fossil fuel project that has run into strong opposition from environmental groups who challenged both its GHG emissions and its economic value. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Kevin Adler)
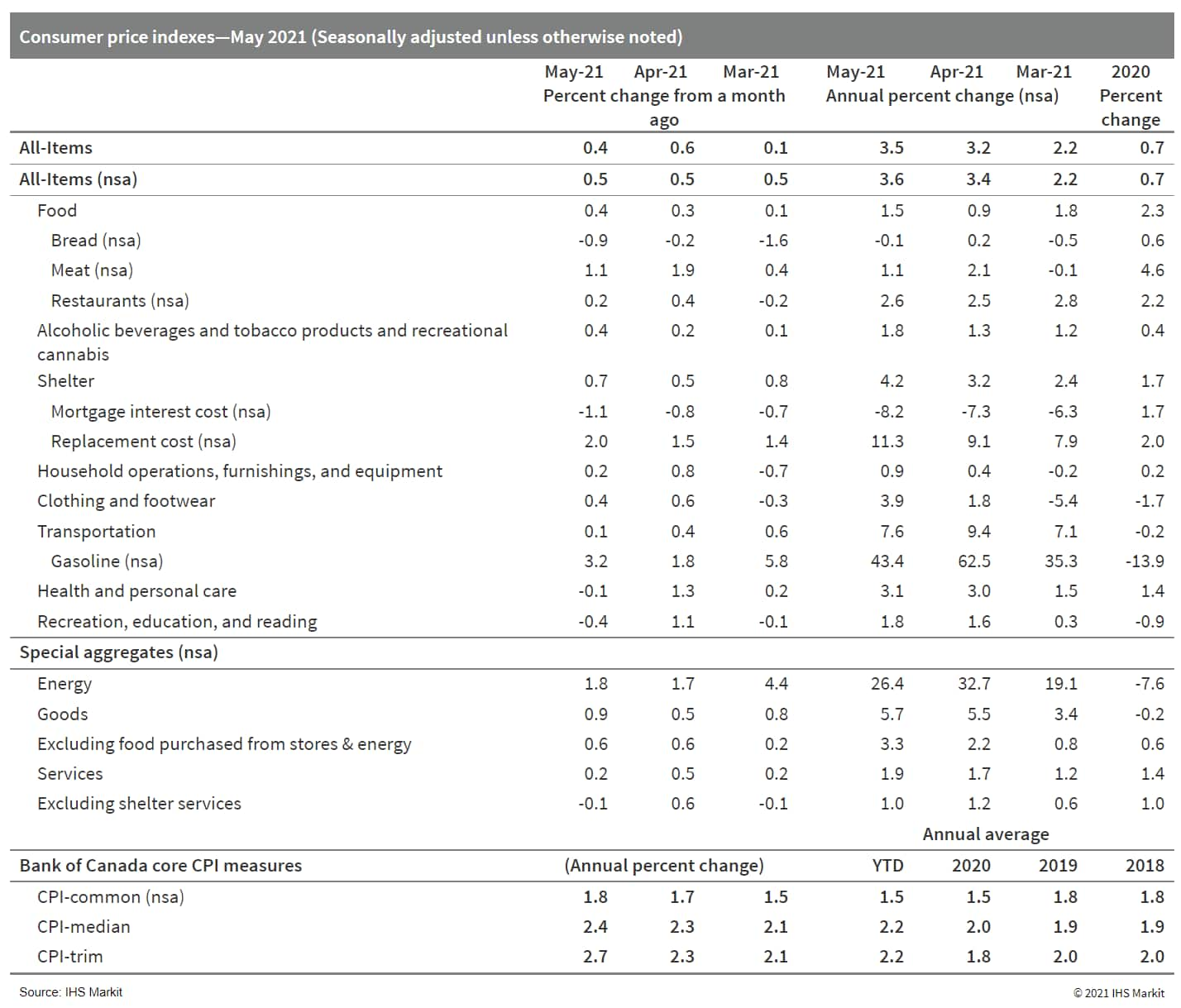
- Canada's consumer prices inflation advanced at a 0.4% month-on-month (m/m) rise on a seasonally adjusted basis (SA) and gained 0.5% m/m on a non-seasonally adjusted basis (NSA) again. (IHS Markit Economist Arlene Kish)
- Annual inflation rates quickened to 3.5% year on year (y/y) SA and 3.6% y/y NSA.
- The average of the core inflation rates was 2.3% y/y, with the consumer price index (CPI)-trim inflation rate advancing the fastest at 2.7% y/y.
- The stark difference in underlying inflation trends persisted in May with goods inflation outpacing services inflation. Low-base year-earlier price impacts from gasoline are still the biggest upward contributor to inflation pressures.
- Brazilian pigmeat exports generated USD1.08 billion in the first five months of 2021 - an increase of 23% y/y, according to data collated by the Brazilian Animal Protein Association (ABPA). In volume terms, shipments of fresh and processed pork increased by 18% y/y to 453,000 tons. China remains the leading export destination for Brazilian pork, taking 238,700 tons in the Jan-May period - a rise of 29% y/y. Brazilian pork has also gained ground in neighboring South American countries: Shipments to Chile reached 25,500 tons (+94%), while exports to Uruguay stood at 17,500 tons (+12%). A further 12,200 tons went to Argentina in the January-May period - up 63% y/y. For May alone, total exports were almost unchanged on last year at 102,000 tons, while export earnings increased 11% y/y to USD228 million. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Ana Andrade and Max Green)
- Peru's monthly output grew by 58.5% year on year (y/y) in April. This eye-popping result is mainly explained by the extremely low April 2020 comparison base, when monthly output reached a pandemic-era trough. (IHS Markit Economist Jeremy Smith)
- A targeted halt to economic activity during the Easter holiday in April led to a 0.8% decline compared with the previous month. In seasonally adjusted terms, output was around 5% below the January 2020 level.
- Although agriculture was the only sector to decline in y/y terms, sectoral recovery remains uneven. Activity in the mining sector and many service industries is still largely depressed compared with 2019.
- On the other hand, the construction sector continues to significantly outperform the rest of the economy: activity in March was nearly 22% higher than in January 2020. Fiscal stimulus has played a key role.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Major European equity indices closed mixed; France +0.2%, UK +0.2%, Italy +0.1%, Germany -0.1%, and Spain -0.3%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed higher; Germany/UK -2bps and France/Italy/Spain -1bp.
- iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/47bps and iTraxx-Xover -1bp/234bps.
- Brent crude closed +0.5%/$74.39 per barrel.
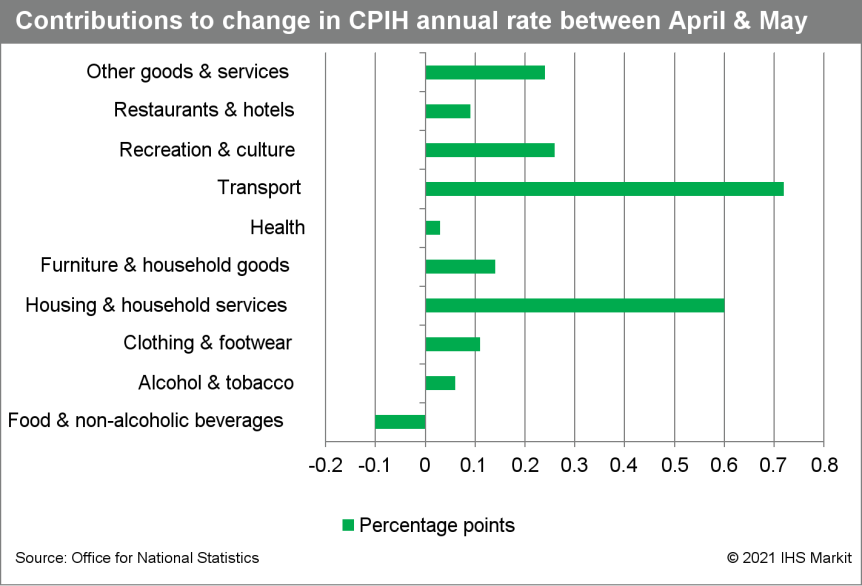
- The UK's Office for National Statistics (ONS) has reported that the United Kingdom's 12-month rate of consumer price index (CPI) inflation climbed to 2.1% in May from 1.5% in the previous month. (IHS Markit Economist Raj Badiani)
- Clothing prices increased by 2.3% y/y, the biggest gain since 2018, as retailers began to normalize their prices in the wake of customers returning to their reopened physical shops.
- All-services price inflation increased to 1.9% in May from 1.6% in April; for goods, it stood at 2.3%, up notably from 1.5% in April.
- Core inflation, excluding energy, food, alcoholic beverages, and tobacco prices, rose to 2.0% in May from 1.3% in April.
- The UK government and local authorities are said to be in talks with six businesses that could build large-scale EV battery manufacturing facilities in the country. Although the UK government has allocated a certain amount of funding to support battery manufacturing investment, the amount is relatively small. Nevertheless, such investment is important to making the UK a sustainable location for OEMs to build vehicles, given the shift towards EVs over the next decade or so. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Shell's Rhineland complex will become the first refinery in Germany to operate an electrolyzer plant in July, ushering in a new era for the country's dozen refineries as operators contemplate a strategic but uncertain transition from fossil fuel-derived grey to carbon-free green hydrogen. The plant, a 10-MW advanced polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolyzer, is on schedule to begin operating 2 July at the 140,000-b/d Wesseling refinery, part of the 325,000-b/d integrated Rheinland facility, according to a Royal Dutch Shell spokesperson. Shell is planning a tenfold increase in electrolyzer capacity and a complementary sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) plant at the site, both pending future funding from the EU and Germany. Notably, Shell's 10-MW Rhineland electrolyzer succeeded in securing €10 million ($12 million) funding from the EU through the Fuel Cell Hydrogen Joint Undertaking initiative and is set to model different scenarios for the commercial-scale production that continues to elude green hydrogen technology. Green hydrogen production at refineries is a slow burner riddled with challenges but promoted by incentives. As long as the political climate threatens to shake up its primary mode of operation, refineries could look toward green hydrogen plants as part of a revamped business model. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Cuckoo James)
- The BMW Group is looking to position itself as a leader in automotive quantum computing, with two announcements in one week on the subject. OEMs and suppliers are already looking at the way quantum computing can help their products in terms of navigation route optimization, R&D optimization, and material durability, while it can also be used in optimizing production processes. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- France has received clearance from the European Commission for its proposal to set up a "glyphosate exit" tax credit from 2021 for French farmers. This specific aid scheme, approved by the Senate in December, is already fully operational and will provide long-term support to farms that voluntarily renounce the herbicide, glyphosate, says the French Ministry of Agriculture. Introduced in article 140 of the country's finance law for 2021, the measure grants a tax credit of a lump sum of €2,500 ($3,052) for farms that stop using glyphosate in 2021. It applies to arable crops, arboriculture and viticulture sectors. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Policy's Sanjiv Rana)
- Tanzania's national budget for fiscal year (FY) 2021/22 (from 1 July 2021 to 30 June 2022) outlines spending commitments of TZS36.3 billion (USD15.6 billion) and revenue flows (including income from local government authorities) of TZS26 billion, leaving the fiscal deficit at an estimated 1.8% of GDP. The budget targets are based on GDP growth of 5.6% in 2021 and 6.2% by 2023. In the budget, headline inflation is expected to remain within the target range of 3-5%, while foreign reserve holdings are expected to remain above four months of import cover in FY 2021/22. (IHS Markit Economists William Farmer and Thea Fourie)
- Recurrent expenditure makes up 63.3% of total spending in the FY 2021/22 budget, of which wages and salaries (22.4% of total spending) and debt servicing costs (29.3% of total spending) make up the largest share.
- The remaining development budget forms part of the Five-Year National Development Plan, which stretches from FY 2021/22 to FY 2025/26. Although the Ministry of Works, Transport and Communications' budget is 20% lower in FY 2021/22 than in the year prior, priority projects under former president John Magufuli, who died in March, remain key priorities under new President Samia Suluhu Hassan. These include rail infrastructure (including the standard gauge railway line), power generation (including Julius Nyerere Hydro Power Project), and urban/rural water projects. The budget also makes available funding for the acquisition of pharmaceutical products, the 2022 national census, and student loans for free basic education.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; South Korea +0.6%, Australia +0.1%, India -0.5%, Japan -0.5%, Hong Kong -0.7%, and Mainland China -1.1%.
- Chinese smartphone maker Xiaomi plans to hire 20 engineers for autonomous driving technology development, to work in Beijing's Haidian district, reports the China Daily. The recruitment covers personnel familiar with hardware and software, and focuses on data platforms, car infrastructure, millimeter-wave algorithms, web platform research and development (R&D), embedded software, high-definition maps, sensors, and ultrasonic radar algorithms. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Baoneng New Energy Vehicle Group (Baoneng NEV), the NEV unit of Chinese property conglomerate Baoneng Group, will set up its headquarters in Guangzhou, reports Yicai Global. Baoneng Group and Guangzhou Development District signed an agreement yesterday (15 June) to set up its headquarters to integrate research and development (R&D) with manufacturing. As part of the strategic co-operation, state-owned companies in Guangzhou Development District will invest CNY12 billion (USD1.9 billion) in Baoneng NEV. The report added that Baoneng NEV will unveil a new premium electric vehicle brand in October this year, and the first model will be a sport utility vehicle (SUV). (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
- Japan's trade balance recorded a deficit of JPY187 billion (USD1.7 billion) on a non-seasonally adjusted basis in May for the first deficit in four months. The seasonally adjusted balance recorded a surplus of JPY43 billion, but this was down from JPY84 billion in the previous month. Exports surged by 49.6% year on year (y/y), recording the second-highest y/y growth since 1980, but the trade deficit reflected solid growth of imports, which accelerated to 27.9% y/y from a 12.8% y/y rise in the previous month. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- The substantial increase in exports was due partially to low base effects because of a plunge a year earlier caused by the global spread of lockdowns. The drivers were exports to the US (up 87.9% y/y) and the European Union (up 69.6% y/y), while exports to Asia remained solid at 32.5% y/y. Major contributors to the increase were exports of autos, auto parts, steel and iron, and non-ferrous metals. Increases in exports prices of steel and iron, non-ferrous metals, and some other products also helped to lift export growth. Despite y/y surges, seasonally adjusted export value held at the April level and was weaker than the trend in export volume of autos, suggesting negative effects of semiconductor shortages.
- The faster rise in imports largely reflected higher prices for energy and other commodities, as growth for import volume rose only moderately at 6.9% y/y. Major contributors to the increase were crude oil, petroleum products, and non-ferrous metal products, largely reflecting faster rises in import prices. Import of medical products (up 61.1% y/y) also contributed 3 percentage points to y/y growth of imports, reflecting rises in imports of COVID-19 vaccines from the European Union and the US.
- Japan's private machinery orders (excluding volatiles), a leading indicator for capital expenditure (capex), rose by 0.6% month on month (m/m) in April following a 3.7% m/m increase in March. The continued improvement reflected a 10.9% m/m rise in orders from manufacturing, although this was largely offset by an 11.0% m/m drop in orders from non-manufacturing (excluding volatiles). (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- Orders from overseas rebounded solidly, surging 46.2% m/m in April following a 53.9% m/m drop in March.
- The first increase in four months in orders from manufacturing largely reflected rebounds in orders from shipbuilding, non-ferrous metals, and general-purpose machinery. On the other hand, the weakness in orders from non-manufacturing was due largely to softening following solid rises in the previous month in orders from transportation and postal activities, information services, and other miscellaneous non-manufacturing groupings. Prolonged containment measures weighed on cash flow and suppressed demand for capital goods in the transportation sector and face-to-face services.
Posted 16 June 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.




