All major European equity indices closed higher, while the US and APAC were mixed. US government bonds closed lower, while most European benchmark bonds were slightly higher. European iTraxx and CDX-NA closed modestly tighter across IG and high yield. Copper and the US dollar closed lower, gold was flat, and oil, natural gas, and silver closed higher on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- Major US equity indices closed mixed; Russell 2000 +1.1%, DJIA +0.1%, S&P 500 -0.1%, and Nasdaq -0.1%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +3bps/1.61% yield and 30yr bonds +3bps 2.29% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed -1bp/50bps and CDX-NAHY -2bps/285bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.2%/89.83.
- Gold closed flat/$1,905 per troy oz, silver +0.3%/$28.10 per troy oz, and copper -0.5%/$4.65 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +2.1%/$67.72 per barrel and natural gas closed +4.0%/$3.10 per mmbtu, with Crude oil closing at the highest price in over three years.
- The seasonally adjusted IHS Markit U.S. Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) posted 62.1 in May, up from 60.5 in April and from the earlier release 'flash' estimate of 61.5. The increase in business activity signaled among U.S. manufacturers was among the strongest in the 14-year series history. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
- New orders increased at the fastest pace on record in May, as both domestic and foreign client demand ticked higher.
- New export order growth quickened, and was the sharpest since the first month of data collection in May 2007.
- US monthly GDP rose 0.1% in April, following a 2.6% increase in March. The increase in April reflected positive contributions from net exports, nonresidential fixed investment, and the portion of monthly GDP not covered by the monthly source data, which were nearly offset by negative contributions from inventory investment and personal consumption expenditures. The level of monthly GDP in April was only 0.2% below the February 2020 level (the pre-pandemic peak). We estimate GDP surpassed the pre-pandemic peak in May 2021. (IHS Markit US Macroeconomic Team)
- US total construction spending rose 0.2% in April, a smaller increase than both the Bloomberg expectation and the IHS Markit assumption, but from a level in March that was revised higher. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- Core construction spending rose 0.3% in April, just shy of our estimate, but following upward revisions to both February and March.
- Including the upward revisions, data through April point to a firming trend in construction activity, albeit at a somewhat softer pace than was in place late last year. News reports suggest anecdotally that spot labor and materials shortages as well as permitting delays could create a headwind for construction activity in coming months.
- Private residential construction rose 1.0% in April, following an upwardly revised 2.6% in March. Since reaching a trough in May 2020, private residential construction has risen a stunning 35.2%. The residential sector has benefited from low mortgage rates, a migration to less densely populated suburban areas, limited inventories of homes for sale, and some release of pent-up demand.
- Private nonresidential construction spending declined 0.5% in April, but from a level in March that was revised materially higher. Nonetheless, private nonresidential construction has been on a downward trend for a little over one year. State-and-local construction spending, meanwhile, declined 0.2% in April, the fourth consecutive monthly decline.
- Farmers in California's Central Valley Project will get none of their water allocations in 2021, according to the US Bureau of Reclamation. Growers received only 5% of their contracted water supply, due to severe drought in February, mirroring the 2015 season when farmers had to let 500,000 acres lie fallow due to lack of water. Central Valley Project irrigates 5.0 million acres when it has enough water. The California Department of Water Resources reported that 2021 may be one of the driest recorded years, with soil already dry and snow melted. As such, reservoirs that were already less than half full would not be replenished, meaning the new year would open with a deficit. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jose Gutierrez)
- Renewable diesel fuel is gaining investment support in the US and Canada, as the drive to reduce carbon emissions from trucks and other diesel uses is stimulating development of the fuel. Renewable diesel is a type of biodiesel produced through various processes such as hydrotreating, gasification, pyrolysis, and other biochemical and thermochemical technologies. Because renewable diesel is chemically similar to crude-based diesel, the renewable fuel can either blend with it at any ratio or substitute for it fully. Renewable diesel differs from biodiesel, which is produced via trans-esterification, and is typically blended at a 5-20% ratio with fossil-derived diesel fuel. The big driver for renewable diesel to date is California's Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS), which provides blenders with credits for the use of low-carbon biofuels. California LCFS credits were recently assessed at $193.50/mt by OPIS, an IHS Markit price reporting agency. In dollars-per-gallon terms, a $200 LCFS credit is worth approximately $1.60/gal for renewable diesel and $1.76/gal for biodiesel diesel, according to Stillwater Associates. (These figures vary in the LCFS system depending on the carbon intensity "pathway" to produce the fuel, with lower-carbon pathways generating more credits and thus making a gallon of biofuel more valuable.) For comparison, the OPIS fuel tracking service puts spot diesel prices at $2.00-$2.05/gal currently in major wholesale markets, depending on location. In addition to California's program, Oregon has its own LCFS, and Washington State is in the process of implementing a similar program. Other states, including New York, New Mexico, and Minnesota are contemplating adopting similar programs. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Jeffrey Barber and Jordan Godwin)
- Tesla has enabled monitoring capability of the vehicle with the in-car camera in the autopilot mode with a software update, reports Tech Crunch. According to the source, citing Tesla, the "cabin camera above the rearview mirror can now detect and alert driver inattentiveness while Autopilot is engaged". According to the automaker, the system will not be able to save or transit information unless data sharing is enabled by the user. Until now, Tesla was not using the camera, which comes pre-installed in its vehicles, and instead relied on sensors in the steering wheel that measured torque, requiring the driver to keep their hands on the wheel. This system was reportedly not fool proof and was easy to trick into thinking that the driver's hands are on the steering wheel. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
- Battery electric vehicle (BEV) startup Rivian is planning to go public by the end of 2021 and has selected underwriters for the initial public offering (IPO), according to a report by Bloomberg citing unnamed people familiar with the matter. The automaker is reported to be working with Goldman Sachs Group Inc., JPMorgan Chase & Co., and Morgan Stanley and is expected to seek a value of USD70 billion when it goes public. However, the final decision has not been made and details of its potential listing may change, according to the report. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
- As expected, Canadian real GDP growth was slightly higher than Statistics Canada's initial estimate. Real GDP output increased for 11 consecutive months, recovering to 1.1% below the pre-pandemic level in February 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Chul-Woo Hong)
- Following a 0.4% decrease in February, goods-producing output solidly rebounded in March. The gain was led mainly by strong construction growth and a solid rebound in mining and oil and gas extraction output. Reflecting March's record-high housing starts level, real residential building construction strongly jumped for four successive months, now reaching 19.7% above the pre-pandemic level.
- Output growth in service-producing industries solidly accelerated in the previous month as output jumped in 14 of 15 major industries. The largest advance was the accommodation and food services, up 5.0% m/m as accommodation services surged 11.0% m/m, mostly because of the mandatory quarantine measures at a government-authorized hotel for all air travelers. The 3.7% m/m jump in retail trade followed as the second-largest advance thanks to eased restrictions.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- All major European equity indices closed higher; Germany +1.0%, UK +0.8%, France +0.7%, Italy +0.6%, and Spain +0.5%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Germany/France/Italy/Spain -1bp and UK +3bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/49bps and iTraxx-Xover -2bps/244bps.
- Brent crude closed +1.3%/$70.25 per barrel.
- After scrapping their May meeting and with the spring unwinding of production cuts now well underway, the OPEC+ group met today to review its production strategy over the coming months, a task which it dispatched laconically, with the meeting lasting less than half an hour and most key issues including Iran's return side-stepped. With prices moving above $70/bbl for Brent, two months left in the agreed unwinding schedule and the demand recovery in the Atlantic Basin starting to take shape, the group has the flexibility to kick the can down the road without risking derailing the price recovery. (IHS Markit Energy Advisory's Roger Diwan, Karim Fawaz, Ian Stewart, Edward Moe, and Sean Karst)
- Despite Saudi Energy minister Abdulaziz bin Salman's penchant for market surprises this year, he mostly passed up the opportunity to firm up market expectations for continued tight market management beyond July. While the path of production through July was unlikely to deviate materially from the current trajectory, the minister only briefly addressed the few questions in the press conference pertaining to the return of Iran, solely reiterating the group's intent to continue to carefully manage the market.
- Iran talks have progressed significantly since the last OPEC+ meeting in early April and the clearing of the Iranian presidential election field from prominent reformists lessen the likelihood of the election outcomes becoming a sticking point in terms of timing. While the recent IAEA report confirming excess enrichment from JCPOA levels does provide a reminder that there will still be bumps in the road, the increase was largely telegraphed since last year by Iranian leadership and its eventual disposal a central element of the negotiations.
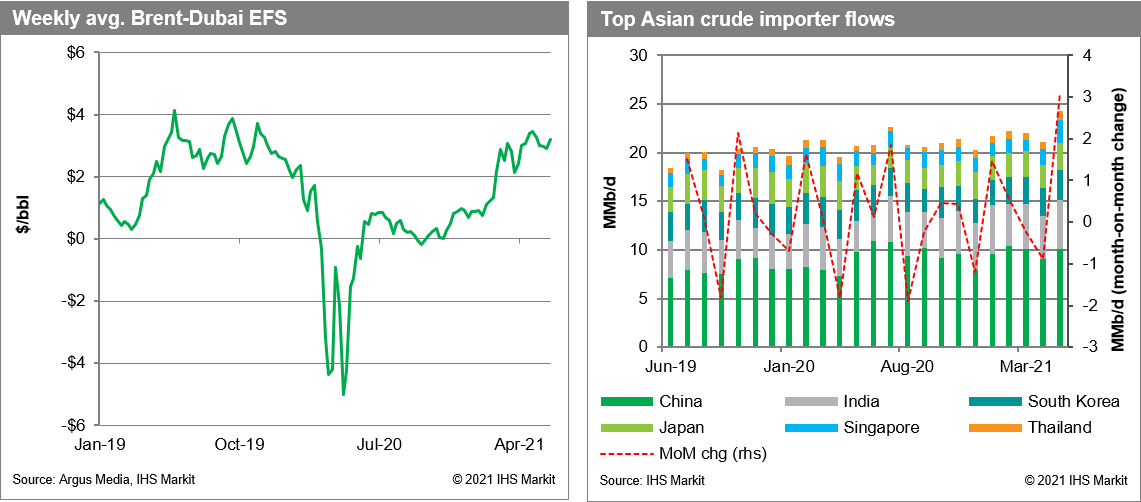
- IHS Markit estimates show total shipments to key markets bouncing 3 MMb/d last month for a multi-month fresh high of 24.23 MMb/d, in a sign of both recovering demand and increased OPEC+ shipments taking shape. The return of more capacity will keep runs moving up in June, slightly offset by the ongoing crisis in India, and new outbreaks in Malaysia and Guangzhou, China. The return of Asian demand, peppered with risk of more COVID-19 lockdowns, also accommodated an incremental 1.1 MMb/d of oil from the Mideast over the same time, easing the path for the wider OPEC+ group's efforts to add 600,000 b/d in May and plans for another 700,000 b/d in June.
- UK-based connected-car data startup Wejo has announced plans of going public through a reverse merger deal with Virtuoso Acquisition Corp, a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC). The deal implies an equity value of the combined entity at USD1.1 billion, according to a company statement. The combined company will get proceeds of USD330 million from the deal, which includes USD230 million of cash from the SPAC. It also raised USD100 million of financing through a private investment in public equity (PIPE) with participants including Palantir Technologies Inc. and General Motors (GM). The merger deal with Virtuoso is expected to close in the second half of the year. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- After over 20 years of absence, US food giant Kraft Heinz has announced it will invest GBP140 million (USD198 million) into a processing facility near Wigan, the largest investment in UK manufacturing since Brexit. The Kitt Green plant, already Europe's largest food manufacturing site, will restart production of ketchup, mayonnaise, and salad cream brands, discontinued in 1999, in Britain. Besides the iconic sauces, the Kitt Green site will continue processing its 1.3 billion of cans of beans, soup and pasta. Heinz's investment in the next four years will be directed towards updating manufacturing equipment and technology at the plant in order to reduce non-renewable resource use, produce fully recyclable items and help cut its CO2 emissions. In 2020, the UK imported over 180,000 tons of ketchup, about 2% more than in 2019 despite the pandemic, the largest volume recorded on the global market. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Cristina Nanni)
- The IHS Markit headline PMI broke new records for a third month in a row during May to rise to a new high of 63.1. The surging manufacturing sector adds to signs that the eurozone economy is rebounding strongly in the second quarter, especially as the upturn in May was accompanied by signs from the flash PMI of the service sector also showing renewed signs of life. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
- Production growth would have been even stronger in May had it not been for record supply delays. Supply difficulties and widespread shortages of inputs are constraining output and leaving firms unable to meet demand to a degree not previously witnessed by the survey.
- With new orders growing faster than output, the production shortfall relative to demand signaled in May was the largest for 12 years.
- Backlogs of uncompleted work (orders received by manufacturers but not yet started or completed) have consequently accumulated at a record pace.
- High sales volumes are consequently depleting warehouse stocks, resulting in a new order to inventory ratio far in excess of anything previously recorded by the survey.
- While forward-looking indicators bode well for production and employment gains to persist into coming months as firms seek to catch up with demand, the flip-side is higher prices. The combination of strong demand and deteriorating supply is pushing up prices to a degree unparalleled over the past 24 years.

- Germany's Federal Statistical Office (FSO) has reported, based on data from various regional states, that the country's national consumer price index (CPI) increased by 0.5% month on month (m/m) in May, well above the 0.2% m/m average for this month in recent years. This boosted annual inflation from April's 2.0% to 2.5% y/y. The EU-harmonised CPI measure posted an as-expected 0.3% m/m - its y/y rate thus only increasing from 2.1% to 2.4% y/y. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- Energy prices were only partially responsible for the renewed acceleration of inflation, with their 0.4% m/m increase in NRW raising the y/y rate from 8.4% to 10.4%. This was partly offset by cheaper food, as its annual rate softened from 1.3% to 0.8%.
- Critically, however, the partial opening up of services in the recreation and culture area led to a major inflation increase in this category from 1.1% to 3.7%, driven by package tour prices leaping from -3.1% to 7.4% y/y.
- Furthermore, pent-up consumer demand is having an effect among durable goods, as inflation for furniture and household goods rose from 0.8% to 1.8% and inflation for clothing and shoes rose from -1.0% to 0.1% y/y.
- Seasonally adjusted German unemployment declined by 15,000 month on month (m/m) in May, which remains compatible with a sideways rather than a downward trend for now. At latest count, only about 30% of the initial, pandemic-related surge recorded in the second quarter of 2020 has been unwound so far. The end-May unemployment level of 2.739 million compares with the March 2020 cyclical low of 2.269 million and an interim high of 2.935 million in June 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- The Labor Agency calculates a cumulative COVID-19-related effect on unemployment of 453,000 by May 2021, down from 509,000 in April and a peak of 638,000 in June 2020. This represents a comparison with a hypothetical continuation of the pre-pandemic trend if the pandemic had never occurred.
- Germany's (national) unemployment rate has remained at 6.0% in May, which compares to its 40-year low of 5.0% in March 2020 and an interim high of 6.4% in June and July 2020.
- Turkish GDP grew by 1.7% quarter on quarter (q/q) in the first quarter of 2021, according to seasonally and calendar adjusted data from the Turkish Statistical Institute (TurkStat). After dropping by 11.0% q/q in the second quarter of 2020 due to the intensification of the COVID-19 virus pandemic last year, the economy has strongly recovered in the three quarters since. GDP in the first quarter of 2021 was up by 7.3% from its pre-pandemic size. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew Birch)
- Turkey will ban the import of multiple categories of plastic waste from 3 July. Nearly one-quarter of plastic waste exported by EU countries, approximately 31.7 million tonnes, went to Turkey in 2020, which is 20 times more than in 2016, following China's ban of plastic waste imports in 2017. Its prohibition, initially announced on 20 May, follows a Greenpeace investigation claiming that most of the plastic waste imported from EU member states to be recycled in Turkey is instead being dumped illegally and burned. The new restrictions prohibit Turkish imports of polyethylene, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE), which is used to produce plastic milk bottles and containers for shampoos and detergents, and low-density polyethylene (LDPE), which is used to produce soft plastic films and bags. In the future, Turkey will only accept polypropylene plastics (PET), which include recyclable water bottles and soft drink bottles. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Emre Caliskan and Jan Gerhard)
- Mozambique's real GDP edged up by 6.6% quarter on quarter (q/q) and 0.1% y/y during the first quarter of 2021. (IHS Markit Economist Thea Fourie)
- The agriculture and fishing sector combined with the services sector, including government services, were the biggest contributor to the modest annual growth rebound, contributing 1.1 percentage point and 1.7 percentage points to the overall annual GDP growth performance respectively.
- Other sectors in the Mozambican economy showed less resilience, the Mozambique Statistical Services (INE) reported. Mining production contracted by 18.9% y/y followed by hotels and restaurants - a proxy for tourism - down by 15.1% y/y, and transport and communication, down by 9.6% y/y.
- Other sectors which recorded negative annual growth during the first quarter include the construction sector (down by 8.4% y/y), manufacturing production (down by 2.3% y/y) and electricity and water (down by 2.2% y/y).
- Wholesale and retail trade - a proxy for household spending on goods - fell by 0.2% y/y during the first quarter of 2021.
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)'s authorities reimposed on 26 May a ban on the export of copper and cobalt concentrates, while allowing companies in possession of waivers to continue exporting. The DRC announced a ban on the export of unprocessed copper and cobalt in 2013, but since then implementation has been postponed repeatedly, primarily due to a continuing shortage of power and smelting infrastructure. In August 2020, the DRC's Ministry of Mines announced that it would waive the export ban on copper concentrate for an undetermined period, as well as introduce an indefinite waiver from the export ban on cobalt hydroxides and carbonates. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Jordan Anderson)
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Hong Kong +1.1%, South Korea +0.6%, Mainland China +0.3%, India flat, Japan -0.2%, and Australia -0.3%.
- China's official manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) declined for the second consecutive month by 0.1 point in May, but at 51.0 it remains in expansionary territory and above the 2020 and 2019 May readings. Variations in performance were noted across sub-indices, with the imbalance between demand and supply recovery persisting. Demand continued to weaken as the new orders sub-index fell by 0.7 point to 51.3 and new export index fell by 2.1 points to contraction territory. Supported by strength in the upstream ferrous-metals production and the downstream general-purpose equipment sectors, the output sub-index rose by 0.5 point to 52.7. Thanks to the soaring commodity price inflation, prices of purchased materials and producer prices further rose. Surging inflation and weakened downstream demand further weakened the manufacturing outlook as the employment and the expectations sub-index declined further. (IHS Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- By firm scale, the PMI of small firms dropped by 2 points to contraction territory, leading the decline in the headline manufacturing PMI, while large and medium-sized firms reported faster expansion versus April levels.
- China's non-manufacturing Business Activity Index rose by 0.3 point to 55.2 in May, entirely driven by faster growth in the construction segment. However, despite the May holiday driving up retail, catering, and entertainment consumption, the services Business Activity Index edged down owing to slower expansion in household services, water transportation and capital market services.
- The People's Bank of China (PBoC) announced on 31 May that the foreign-exchange (FX) reserve requirement ratio (RRR) will rise from 5% to 7% from 15 June. This is the first rise since 2007, when the FX RRR was raised from 4% to 5%. According to Global Times, this is equivalent to reducing FX liquidity by USD20 billion (CNY127.4 billion). (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Angus Lam)
- Chinese electric vehicle (EV) startup Li Auto is aiming to have a total of more than 200 direct retail stores by the end of the year and for its monthly sales to exceed 10,000 units in September, reports Gasgoo, citing a statement from company's founder and chairman, Li Xiang. According to the report, the automaker recently launched eight direct-sale retail shops in China, which are located in Ningbo, Chongqing, Wuhan, Tianjin, Ganzhou, Qinhuangdao, Zhengzhou, and Tai'an. As of 30 April, Li Auto has 73 retail stores covering 53 cities and 143 servicing centers and authorized body and paint shops operating in 105 cities. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
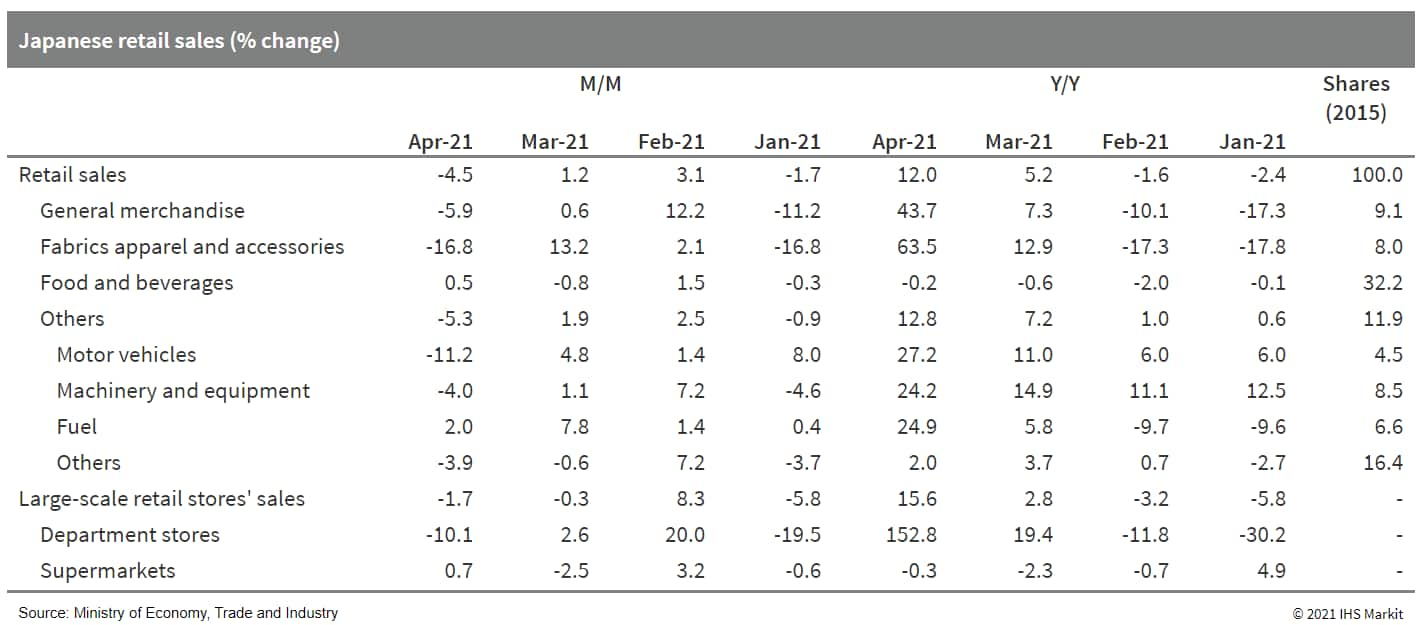
- Japan's retail sales fell by 4.5% month on month (m/m) in April. The largest m/m drop since April 2020 largely reflected the negative impact of the reintroduction of states of emergency and pre-emergency containment measures in several prefectures. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- Major factors behind the decline were drops in sales of fabric, apparel/accessories, motor vehicles, and sales by other miscellaneous retailers. Although foot traffic has not dropped significantly, limits on operating hours and requests for the temporary closure of larger stores (excluding necessities) by local governments affected a broad range of retail sales.
- In line with uncertainties over COVID-19 virus variants and the extension and expansion of areas under state emergency, the consumer confidence index continued to fall, moving down 0.6 point to 34.1 in May. This weakness largely reflected a 1.4-point drop in employment. That said, the index remained above the level that it reached under the previous state of emergency in the first quarter of 2021.
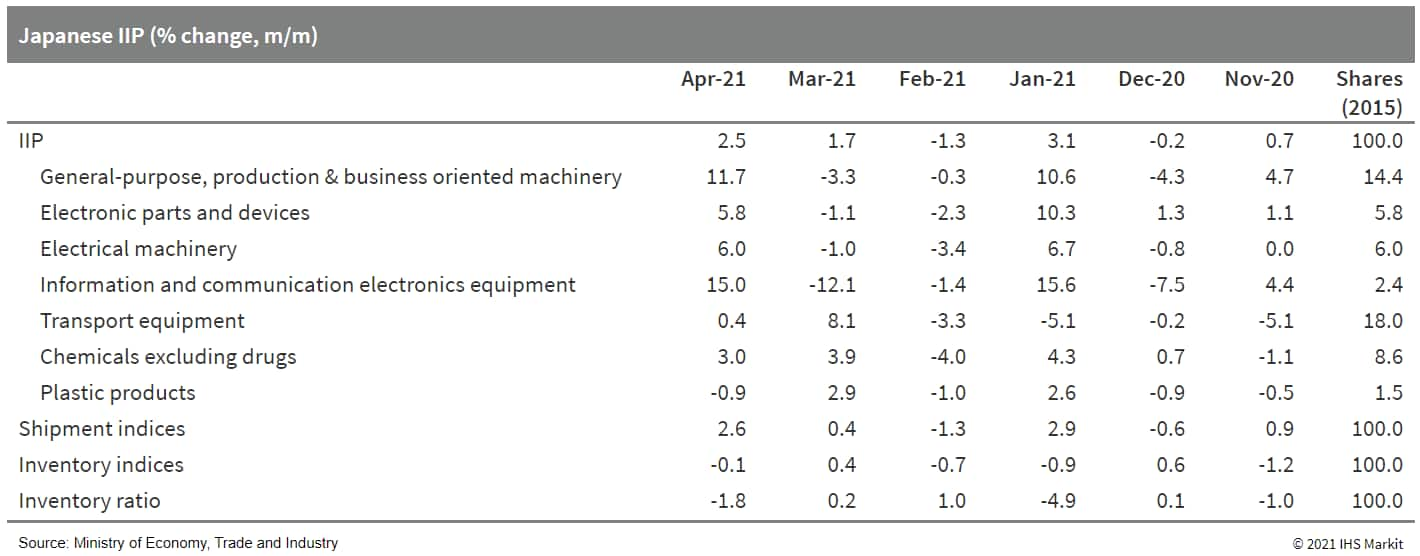
- Japan's index of industrial production (IIP) rose by 2.5% month on month (m/m) in April following a 1.7% m/m rise in March, reaching its highest level since September 2019. Manufacturers' shipments (up 2.6% m/m) outpaced production, leading to declines in inventories (down 0.1% m/m) and the index of inventory ratio (down 1.8 m/m). (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- According to financial statements for the first quarter of 2021, sales for all of Japan's industrial sectors, excluding finance and insurance, rose by 0.6% quarter on quarter (q/q) for the third consecutive quarter of increase. Year-on-year (y/y) figures continued to decline, but narrowed to 3.0%. The continued q/q growth was thanks to a 3.4% q/q rise in sales of manufacturing, reflecting solid external demand. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- Sales in non-manufacturing fell by 0.5% q/q, in line with the negative effects of containment measures. The y/y improvement in sales reflected increases in sales in transport equipment, production/general-purpose and business-oriented machinery, and production/transmission and distribution of electricity, offsetting declines in sales in a broad range of industry groupings.
- Ordinary profits also rose by 5.6% q/q, and y/y figures rose for the first time in nine quarters with a 26.0% jump thanks largely to growth of 12.5% q/q and 63.2% y/y in manufacturing. The solid y/y rise in ordinary profits for manufacturing was driven by increases in transportation equipment, petroleum and coal products, production and business-oriented machinery, and some other industry groupings.
- A 10.9% y/y increase in ordinary profits in the non-manufacturing sector largely reflected improved profits for services, wholesale, and information and communication services, offsetting continued declines in accommodations and eating/drinking places, transport and postal services, and production/transmission and distribution of electricity. Although sales remained weak, lower payroll costs and declines in cost of sales helped lift ordinary profits.
- While fixed investment including software in manufacturing increased by 0.5% q/q (the first rise in six quarters), a 0.9 q/q decline in non-manufacturing widened the y/y contraction for all industries from 4.8% in the previous quarter to 7.8%.
- Renesas Electronics announced in a release today (1 June) that a full recovery in output at its fire-damaged Naka semiconductor plant in Japan will be delayed to mid-June, as it needs time to get manufacturing equipment replaced and operational. Output capacity had recovered to about 88% of pre-fire levels by the end of May. The company said that the procurement of manufacturing equipment damaged by the fire has been completed for all necessary equipment to return to pre-fire production capacity. The last equipment, the CMP equipment, was delivered on 27 May and the start-up is scheduled by mid-June, which will bring the production capacity to pre-fire levels. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
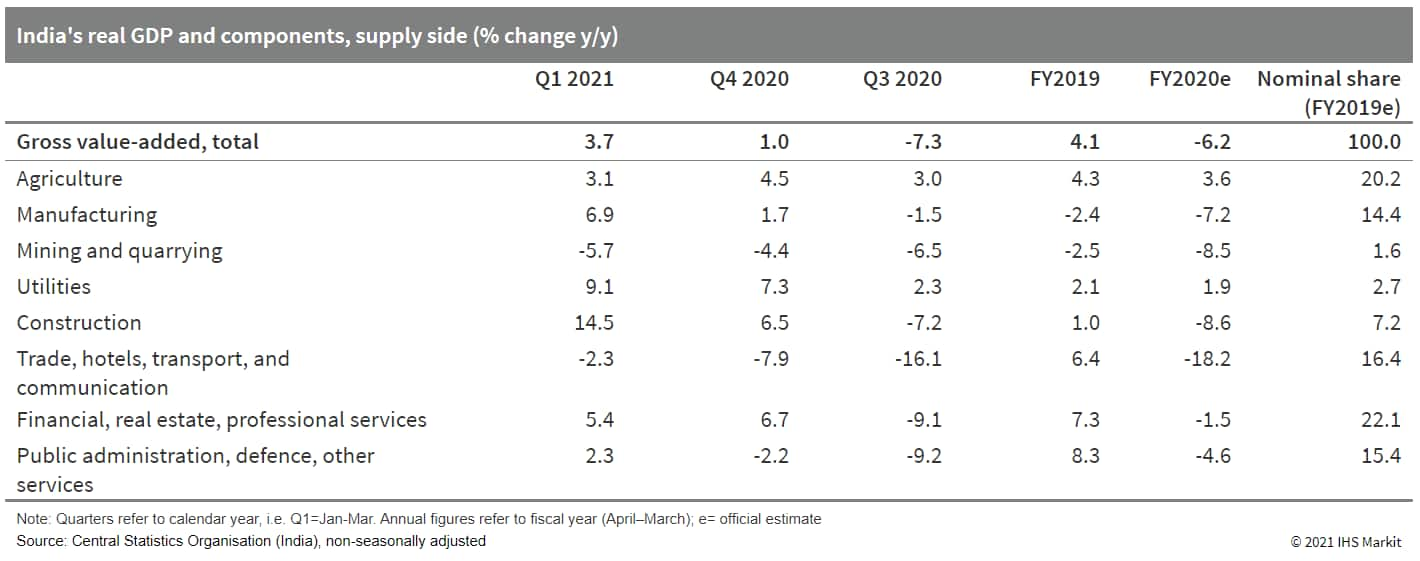
- India's real GDP grew by 1.6% year on year (y/y) during the March quarter - the last quarter of Indian fiscal year (FY) 2020 - suggesting that the country's economic recovery was well under way before the second wave of the COVID-19 virus pandemic. This narrowed the full-year contraction to 7.3% from our forecast of 8.2%. However, with the pandemic-affected June-quarter GDP likely to show near double-digit sequential contraction, the full FY 2021 growth forecast stands at 7.7%, with growth mainly reflecting the weak base of the 2020 lockdown. (IHS Markit Economist Hanna Luchnikava-Schorsch)
- The recovery in domestic demand was mainly driven by a sharp boost to public consumption, which grew 28.3% y/y, as the government ramped up spending as part of its fiscal stimulus to alleviate the impact of the pandemic. Following a freeze on multiple government projects during the lockdown, government expenditure has picked up progressively since November 2020 and more than doubled in January-March 2021 compared with the same period in 2020, particularly after the government announced additional front-loaded spending as part of its Union Budget for FY 2021 in February.
- Private consumption also started to recover, returning to growth of 2.7% y/y during the March 2021 quarter following three quarters of contraction.
- Fixed investment grew by a robust 10.9% y/y, boosted by the rise in public capex spending. Although there is no breakdown available to assess the strength of private investment, the latest available estimates of industry capacity utilization indicate some - albeit only modest - recovery in private capital expenditure.
- The Google-backed delivery and e-commerce company Dunzo Digital (India) is leading a consortium of companies to pilot a drone delivery system for medicines in India. According to India's Business Standard, the "Medicine from the Sky Project", is being conducted by the Med-Air consortium, led by Dunzo Digital and encompassing various industry experts, with the aim of providing medical supply delivery services to districts in the Indian state of Telangana. The drone delivery project, which has been launched by the state government of Telangana and the World Economic Forum, will initially focus on the delivery of COVID-19 products, in an effort to improve access to healthcare during the pandemic. The pilot project will conduct experimental Below Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) drone delivery flights with a focus on "an end-to-end ecosystem for drone-based logistic transportation" and it will "utilize the existing logistics network of the state", according to the source. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Sacha Baggili)
- Thai-based oil and gas conglomerate PTT Plc and Taiwan's Foxconn have signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to manufacture electric vehicles (EVs) and components in Thailand, reports Reuters. Under the partnership, an "open platform" that provides both hardware and software services will be available to automakers in the country, although no details of the size of investment and production plans were revealed. The platform in Thailand will build on the Foxconn-led industry alliance, MIH, a network that the company said would offer manufacturers a cost-effective solution to make EVs. "This cooperation with PTT and the Thai government to realise the vision of sustainable development of the EV industry, demonstrates that the MIH ecosystem is growing," said Foxconn chairman Liu Young-way. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- The Malaysian government has not allowed vehicle manufacturing, assembly and sales operations under the movement control order (MCO) 3.0, which will be in effect from 1-14 June. However, car workshops, spare parts businesses, and tire shops can operate. Several OEMs present in the country have announced that operations at their plants and dealer showrooms will cease temporarily during the aforementioned period. They plan to resume operations from 15 June upon approval from the government. Separately, the Malaysian government has decided to extend the 100% sales tax exemption on locally assembled completely knocked down (CKD) passenger vehicle models and the 50% exemption on fully imported completely built-up (CBU) passenger vehicle models until 31 December 2021, reports the Malay Mail. The sales tax exemption, which has been running since 15 June 2020, was scheduled to come to an end on 30 June 2021. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
Posted 01 June 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.






