Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
BLOG — Jul 01, 2021

By Chris Fenske
All major US and European equity indices closed higher, while APAC markets were lower. US government bonds closed higher and benchmark European bonds closed mixed. European iTraxx closed slightly tighter across IG and high yield, while CDX was close to flat on the day. The US dollar, oil, natural gas, and oil closed higher, while silver and copper were lower on the day. All eyes will be focused on tomorrow's (Friday) US non-farm payroll report ahead of the US Independence Day holiday weekend.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
1. Most major US equity indices closed higher and the S&P 500 +0.5% closed at another record high; Russell 2000 +0.8%, DJIA +0.4%, and Nasdaq +0.1%.
2. 10yr US govt bonds closed -1bp/1.46% yield and 30yr bonds -3bps/2.06% yield.
3. CDX-NAIG flat/48bps and CDX-NAHY -1bp/273bps.
4. DXY US dollar index closed +0.2%/92.6.
5. Gold closed +0.3%/$1,777 per troy oz, silver -0.4%/$26.10 per troy oz, and copper -1.2%/$4.24 per pound.
6. Crude oil closed +2.4%/$75.23 per barrel and natural gas closed +0.3%/$3.66 per mmbtu.
7. The world's leading economies have signed up to a plan to force multinational companies to pay a global minimum corporate tax rate of at least 15% following intense negotiations in Paris at the OECD. The historic agreement among 130 countries will ensure the largest companies, including Big Tech, pay at least $100 billion a year more in taxes, with more of that money going to the countries where they do most of their business. (FT)
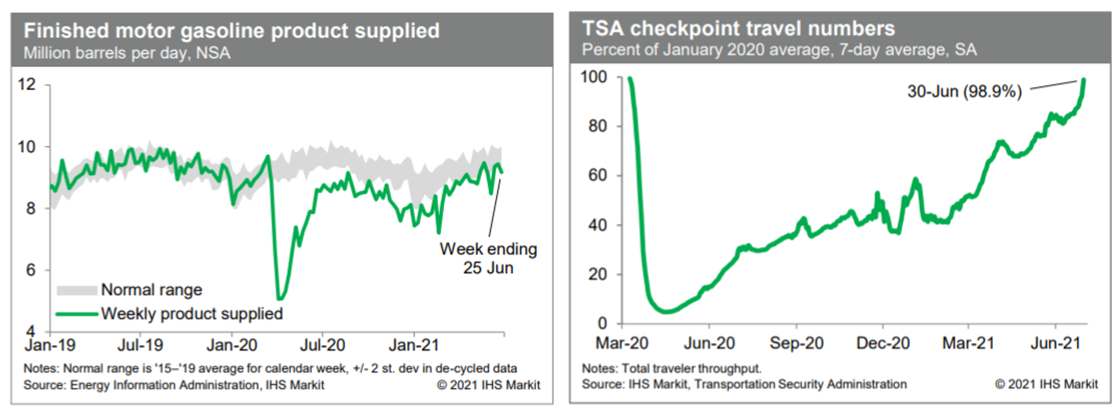
8. Consumption of gasoline declined last week but remained within the lower end of a range that we view to be normal for this time of year. This points to a nearly full recovery in internal mobility. Meanwhile, averaged over the seven days ending yesterday (30 June), passenger throughput at US airports (adjusted for seasonal variation) was 98.9% of the January 2020 average, marking (essentially) a full recovery in air travel. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Joel Prakken)
9. US seasonally adjusted (SA) initial claims for unemployment insurance fell by 51,000 to 364,000 in the week ended 26 June, its lowest level since the week ended 14 March 2020. The number of workers seeking unemployment benefits is falling as companies are struggling to fill job openings and thus are hesitant to lay off existing employees. (IHS Markit Economist Akshat Goel)
a. Seasonally adjusted continuing claims (in regular state programs) rose by 56,000 to 3,469,000 in the week ended 19 June. The insured unemployment rate was unchanged at 2.5%.
b. In the week ended 12 June, continuing claims for Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC) fell by 12,117 to 5,261,991.
c. There were 115,267 unadjusted initial claims for Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) in the week ended 26 June. In the week ended 12 June, continuing claims for PUA dropped by 15,231 to 5,935,630.
d. The disincentive effect of emergency and extended federal unemployment benefits has come under scrutiny following employment reports for April and May that were below expectations. As a result, 25 states (at last count) have announced that they will opt out of these programs prior to the scheduled termination on 6 September.
e. In the week ended 12 June, the unadjusted total of continuing claims for benefits in all programs fell by 180,890 to 14,659,791.
10. US employers announced 20,476 planned layoffs in June, according to Challenger, Gray & Christmas—down 16.7% from May's 24,586. June's total is the lowest monthly reading since June 2000 and is 88% lower than the June 2020 reading, when the pandemic was still the main factor influencing job-cut decisions. (IHS Markit Economist Juan Turcios)
a. For the year to date (YTD), 212,661 job cuts have been announced, down 87% from the 1,585,047 job cuts announced over the same period in 2020. Over the second quarter, employers announced 67,975 job cuts, which was the lowest quarterly reading since the second quarter of 1997.
b. So far this year employers have cited COVID-19 as a reason for 7,797 planned job cuts. Employers have cited other reasons including market conditions (48,047), demand downturn (39,444), restructuring (38,151), closing (34,278), and acquisition/merger (9,425) more frequently than COVID-19 as causes of job-cut announcements this year.
c. Job hiring plans are also down from the pandemic highs of last year. So far in 2021, employers have announced plans to add 551,789 jobs, down 58.7% from the 1,336,115 announced through the same time last year. The robust hiring announcements last year reflected a surge in hiring in grocers, delivery apps, food chains, and warehouses as employers dealt with a pandemic-driven increase in demand for online shopping.
d. Aerospace/defense has announced 32,930 job cuts so far this year, the highest number of any industry. The entertainment/leisure sector has announced 11,944 job cuts YTD, down a whopping 98.2% from the same point last year. This sector was pummeled by the pandemic and announced the highest number of jobs cut last year. This is another indicator of the diminished role of COVID-19 on job-cut decisions.
e. Rounding out the five sectors that have announced the most job cuts this year are telecommunications (24,824), services (17,977), energy (16,291), and retail (14,049).
11. Total US construction spending declined 0.3% in May, in contrast to expectations for an increase. Revisions to prior months reveal a softening trend. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
a. Core construction spending slipped 0.2% in May following upward revisions to the level of core spending in prior months. In response, we lowered our estimate of second-quarter GDP growth by 0.1 percentage point to 8.0%.
b. Over the three months ending in May, total construction spending rose at a 3.2% annual rate, below the 8.0% rate of increase over the six months ending in May. The slowdown largely reflects deceleration in single-family structures and private nonresidential structures.
c. The slowdown in total (and core) construction spending follows a period of rapid growth fueled largely by strength in residential construction spending. Low mortgage rates, intra-region migration (from urban to suburban areas), and the release of some pent-up demand has been bolstering residential construction activity.
d. We believe new single-family permits and starts have peaked. If this is correct, single-family value put-in-place is near a peak. With unfavorable conditions for private nonresidential structures (including the effects of working from home and online sales) and an uncertain outlook for public spending (given the political uncertainty surrounding the passage of a new infrastructure bill), the outlook for total construction spending is soft.
12. Three US offshore wind projects received positive news on 30 June, marking new milestones in the industry's rapid and recent march towards expanded commercial application. The New Jersey Board of Public Utilities (NJBPU) voted to award two offshore wind projects with a total combined capacity of 2,658 MW, which it said marks the largest single procurement of offshore wind in the US. On the same day, the US Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) issued a Notice of Intent to proceed with an environmental impact study for one part of the Vineyard Wind Project off the coast of Massachusetts. The pace of activity in the US has picked up under the Biden administration, which has set a goal of 30,000 MW of offshore wind installations by 2030. In response, BOEM and its parent agency, the Department of Interior, announced in June new offshore wind lease sales in New Jersey and New York, and another in the Gulf of Mexico Outer Continental Shelf. BOEM started the process in May of assessing two areas off California's coast as well. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Kevin Adler)
13. Canada's transport ministry issued a "mandatory target" for all light-duty vehicle sales to be zero-emission vehicles by 2035, advancing a prior target date of 2040. The target date of 2035, along with being more aggressive as the country is emboldened by similar statements in other countries, complies with Canada's goal of achieving net zero emissions by 2050. According to Transport Canada, the 2035 target helps Canada achieve net zero emissions by 2050 because light-duty vehicles are typically in service for about 15 years, thus potentially enabling nearly 100% of Canada's light-vehicle parc to be zero-emission vehicles by 2050. Canada's annual light-vehicle sales are forecasted to be 2.0 million units per year in 2027 and remain there through at least 2033. Canada accounts for about 2% of global light-vehicle sales. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
14. Having already attained pre-COVID-19 virus pandemic levels late last year, the Paraguayan economy grew 0.6% year on year (y/y) in the first quarter of 2021. In seasonally adjusted terms, real GDP expanded 0.8% compared to the fourth quarter of 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Jeremy Smith)
a. From a demand-side perspective, fixed investment single-handedly drove the first-quarter expansion. This principally reflects the strength of construction, which was easily the best-performing sector with 14.2% y/y growth.
b. Private consumption continued its gradual recovery but still contracted 0.3% y/y, as a spike in COVID-19 infections dampened consumer confidence and spending on high-contact services such as transportation, hotels, and restaurants.
c. Net exports were the most significant drag on growth owing to export weakness. Tourism-related service exports remained heavily depressed, and relatedly, the border re-export trade with Brazil has yet to fully rebound. Soybean volumes have also fallen relative to last year's record harvest.
d. In addition, the Paraná River is at the lowest depth in decades, affecting hydroelectric output and exports. Excluding the agricultural sector and the output of Paraguay's binational hydroelectric dams, which are both heavily influenced by climate conditions, output grew 2.8%.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
1. All major European equity indices closed higher; Spain/UK +1.3%, Italy/France +0.7%, and Germany +0.5%.
2. 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy/Spain -2bps, France flat, and Germany/UK +1bp.
3. iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/46bps and iTraxx-Xover -3bps/229bps.
4. The IHS Markit's eurozone manufacturing PMI broke new records for a fourth
straight month in a row during June, rising to a new high of 63.4. The recent growth spurt in manufacturing is therefore the strongest recorded for at least 24 years. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
a. Both output and new orders rose at some of the fastest rates ever seen by the survey as demand surged following the opening up of economies from COVID-19 lockdowns, and as vaccination progress drove renewed optimism about the future.
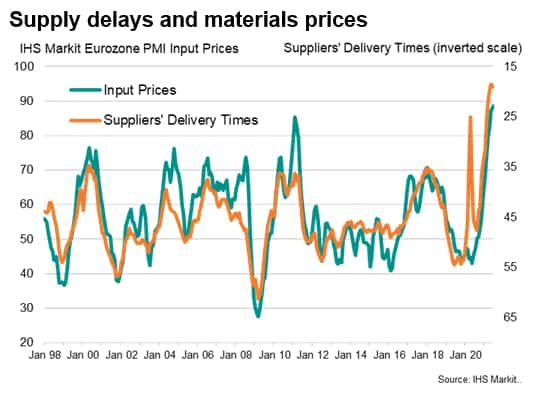
b. However, the good news is tempered by the expansion being accompanied by unprecedented price rises, in turn fueled in many cases by record supply chain delays. The speed of the recent upsurge in demand has led to a sellers' market as capacity and transportation constraints limit the availability of inputs to factories.
c. There are encouraging signs, however, suggesting that companies are expanding capacity to boost supply and meet rising demand, which should alleviate some of the upward price pressures. First, employment rose in June at the fastest rate recorded since the survey began in 1998 as firms hired more workers to meet demand. This workforce expansion should help reduce growth of backlogs of work in coming months. Second, the surge in hiring is being accompanied by an unprecedented spell of investment in machinery and equipment.
5. The European Commission will propose a ban on cages for farm animals by the end of next year. On 30 June, the EU executive decided to endorse a European Citizens' Initiative (ECI) called "End the Cage Age", which gathered signatures from over one million EU citizens in favor of the ban. The Commission said it will put forward a legislative proposal by 2023, which will first look at phasing-out cages for several farm animals before a full ban is potentially put in place by 2027. The proposal will come as part of the ongoing revision of the EU's animal welfare legislation under the Farm to Fork Strategy (F2F). Kyriadises added that the plans to phase-out and ultimately prohibit cages will be guided by independent scientific research. This will be accompanied by an analysis of the social and economic impacts of the ban, which is expected to be published before the end of 2022. There will also be a public consultation that will be carried out by early 2022. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Policy's Steve Gillman)
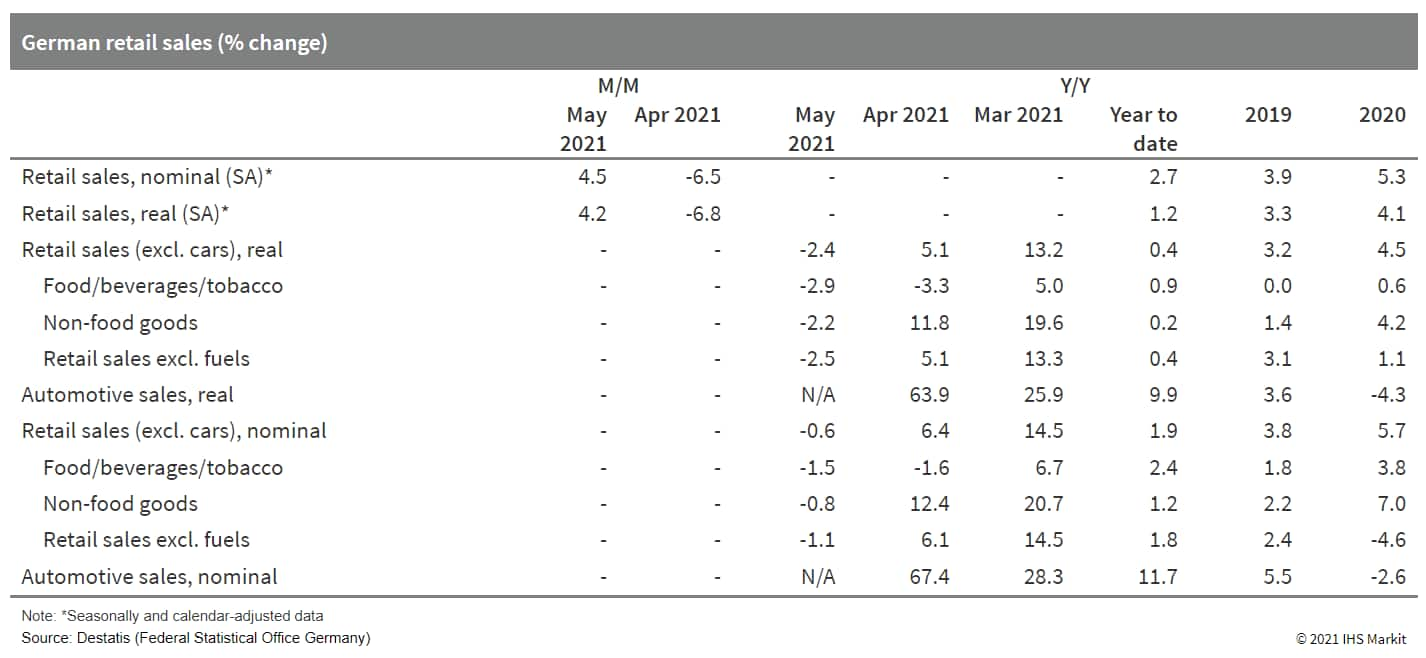
6. The interim decline in German retail sales in April - caused by another phase of tightened COVID-19-related restrictions - was duly corrected in May as stores became more easily accessible again. May's level of retail sales broadly matched the average observed during the second half of 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
a. According to Federal Statistical Office (FSO) data, real retail sales excluding cars rebounded by 4.2% month on month (m/m) in seasonally and calendar-adjusted terms during May, recouping much of April's 6.8% m/m decline.
b. May's renewed strength reflected the steps to open up the economy in the course of the month as the number of new COVID-19 cases receded. Many stores for non-essential goods were able to receive customers onsite again, albeit initially only by appointment ("click & meet" schemes) and/or based on a negative COVID-19 test.
c. May's breakdown by goods category, based on price-adjusted y/y data, reveals little difference between food and non-food sales this time. Among non-food sales, internet and mail order sales remained in the lead, up 13.2% y/y, with sales of pharmaceutical/cosmetic goods being a close second (up 12.3% y/y). All other major categories posted weaker sales than in May 2020, this being most pronounced for furniture/household goods/DIY (-18.6%), clothing/shoes (-18.3%), and sales at general department stores (-16.6%).
7. Tesla has won a victory in a legal challenge by German environmental groups over its plans to open a new factory in the country. According to a Reuters report, a German court ruled in favour of Tesla, after environmental groups Gruene Liga and NABU sought a court order to prevent preliminary functional testing of parts of the plant, which is under construction in Gruenheide just outside of Berlin. The two groups filed the injunction on the basis of a claim that Tesla had not sufficiently clarified what provisions it has made to prevent highly poisonous gas from escaping from the factory. The Administrative Court of Frankfurt (Oder) said on Tuesday (29 June) that it had rejected the emergency application of the two environmental groups. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
8. Mercedes-Benz trucks has launched the production version of its eActros battery electric vehicle (BEV) heavy truck after an extensive field testing program in real world situations. According to a company statement the eActros has a maximum battery capacity of around 420 kWh which can provide the truck with a more than useable range of 400 km depending on load and driving conditions. The battery packs each have 105 kWh of energy capacity and the eActros can be configured with either three or four of these packs. The eActros' drive unit features a rigid electric axle with two integrated electric motors and a two-speed transmission. Both liquid-cooled motors generate a continuous output of 330 kW as well as a peak output of 400 kW if the driving conditions require. The eActros also has regenerative braking that feeds electrical energy from braking back into the battery packs. The eActros is something of a milestone launch for Mercedes-Benz Trucks, as the world's leading truck brand's first BEV heavy truck. While a maximum range of 400km for the four battery pack version is impressive, operators will use the truck for relatively short duty cycles, which are likely to involve deliveries in urban environments and relatively short intercity hops. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
9. BMW i Ventures, the investment arm of BMW, has established a USD300-million venture capital fund, according to a company statement. The new fund will invest in early-stage and mid-stage startups in the fields of sustainability, transportation, manufacturing, and supply-chain management. In addition, the company has announced the appointment of Marcus Behrendt and Kasper Sage as new managing partners of BMW i Ventures. Behrendt said, "With Fund II we will refocus our investment thesis to even better serve the needs of the ecosystem and the BMW Group as a whole. Even more than before, circularity and sustainability will play a key role in our investment activities." (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
10. Nissan is suing Italian battery supplier FIAMM Energy Technology over claimed faults with batteries supplied for some variants of the automaker's Qashqai and Juke crossover utility vehicles, reports Bloomberg. According to the report, Nissan is claiming EUR122 million (USD145 million) from FIAMM, in a case filed at a London court. The lawsuit concerns the supply of 900,000 allegedly faulty batteries that left owners with problems starting their cars and saw Nissan hit with thousands of warranty claims. In its deposition, FIAMM has denied the allegations and insists that the batteries were manufactured to Nissan's specifications. FIAMM claims the cause of the failures was Nissan's own battery management system, which, it says, was faulty in its "design and operation". (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
11. Czechia's public debt-to-GDP ratio jumped to the highest level since 2013. With parliamentary elections approaching in October, fiscal tightening is not expected anytime soon. (IHS Markit Economist Sharon Fisher)
a. According to preliminary data from the Czech Statistical Office, Czechia's government deficit surged to 9.9% of GDP in the first quarter, while public debt reached 44.1% of GDP. In seasonally adjusted terms, the deficit reached 8.8% of GDP in the first quarter, up from 8.1% in the previous period.
b. Government revenues edged upwards by just 0.8% year on year (y/y) in the first quarter, boosted by rising social contributions and current transfers. In contrast, revenues were negatively affected by declines in income taxes and taxes on production and imports. Government expenditures soared by 14.1% y/y, driven by increases in social benefits, subsidies, capital transfers, and compensation of employees.
c. In comparison with the fourth quarter of 2020, public debt increased much faster than the deficit, as the government borrowed CZK230 billion (USD10.9 billion) more than its financing needs. According to the Finance Ministry, the country will need nearly CZK741 billion to finance the state debt this year, which is CZK12.3 billion more than previously expected.
12. As trade volumes continue to surge as compared to year-earlier levels, Turkey's merchandise-trade deficit began to deteriorate year on year (y/y) in May. For now, however, the cumulative trade deficit remains down slightly from the same period of 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew Birch)
a. In May 2021, Turkey's merchandise trade deficit grew 20.2% y/y in nominal, US dollar terms according to data from the Turkish Statistical Institute (TurkStat). With the worsening of the trade gap in May, the cumulative shortfall through the first five months of the year stood at USD18.277 billion - still down from the same period of 2020 by just shy of USD3 billion.
b. Both export and import volumes are surging y/y in recent months because of base effects caused by the onset of the global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus pandemic in March-May 2020. Given the Turkish government's support of domestic demand last year, the import base has been higher, contributing to a much stronger y/y rise of exports in recent months.
c. The sharp depreciation of the lira and subsequent improved export competitiveness should have buoyed Turkish exports even more strongly. However, domestic drought conditions have limited those gains. Agricultural exports increased by 25.2% y/y in January-May 2021, while all other categories of exports rose by 38.8% y/y in that same period.
d. The shifting gold trade affected headline balance. Excepting the trade of gold, Turkey's merchandise-trade deficit would have been little changed - USD18.308 billion - but that would have represented a worsening from the same period of 2020, by more than USD2 billion.
13. Iranian automaker SAIPA has announced the signing of an agreement with Mobile Communications of Iran (MCI) to build connected vehicles, reports SAIPA News. The project aims to allow the driver as well as the automaker to find faults in the vehicle (in real-time) and contact breakdown services before a breakdown occurs. Mehdi Akhavan Behabadi, MCI chief executive said, "This will offer a lot to customers, the most important aspect being a technical network monitoring the car." He added, "Based on this technology, the owner of the car can be informed about possible defects in the early stages of the problem and further damage and [potential] loss of life and property can be prevented. One of the key features of connected vehicles is the ability to monitor vehicle information, which reduces potential future costs by providing a status report." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
14. Full-time employment in South Africa continues to fall during Q1 whilst part-time working increases. (IHS Markit Economist Thea Fourie)
a. Total employment in the South African economy fell by 0.1% quarter on quarter (q/q) and 5.4% year on year (y/y) during the first quarter of 2021, according to the Quarterly Employment Statistics (QES) survey report released by the national statistical service, Statistics South Africa (StatsSA). The QES data show that jobs were shed in most sectors of the South African economy, with employment down by 13.9% y/y in construction, 10.0% y/y in transport, 8.2% y/y in business services, 7.9% y/y in manufacturing, and 6.6% y/y in the electricity sector. Only the mining and community services sectors recorded growth, of 0.7% and 0.9% respectively.
b. The QES survey report shows further that formal sector employment fell by 0.7% q/q and 6.5% y/y in the first quarter, while part-time employment increased 5.3% q/q and 4.6% y/y.
c. South Africa's number of employed was 552,000 lower in the first quarter compared with a year earlier. In the first quarter, the average monthly pay (including bonuses and overtime payments) of employees in the formal non-agricultural sector remained unchanged from the fourth quarter of 2020, at ZAR23,122 (USD1,622), but was up by 3.2% y/y.
Asia-Pacific
1. APAC equity markets closed lower; Mainland China -0.1%, Japan -0.3%, India -0.3%, South Korea -0.4%, and Australia -0.7%.
2. Baidu has partnered with Great Wall Motor (GWM) on automated valet parking (AVP) system, reports Gasgoo. Baidu's AVP system is likely to be first integrated with GWM's WEY Mocha model, which is expected to be launched in the market in the second half of 2021. The companies' partnership date back to 2016, when they agreed to collaborate on high-definition map positioning technology. GWM joined Baidu's autonomous vehicle (AV) platform, Apollo, as one of the first partners in July 2017. In 2018, the companies announced their strategic co-operation on intelligent connected cars, AV technology, shared vehicles, and big data. Until now, Baidu internet of vehicle (IoV) products are integrated on several GWM production models, including the second-generation Haval H6 and the H4 Pro. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
3. Japanese automaker Toyota has formed a 50:50 joint venture (JV) with Chinese fuel-cell manufacturer Beijing SinoHytec. According to a Gasgoo report, the JV is named Toyota SinoHytec Fuel Cell Co, which has a registered capital of JPY4.5 billion (USD40.5 million). The scope of the JV includes manufacturing, consigned processing, and sale of fuel cells and relevant auto parts. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
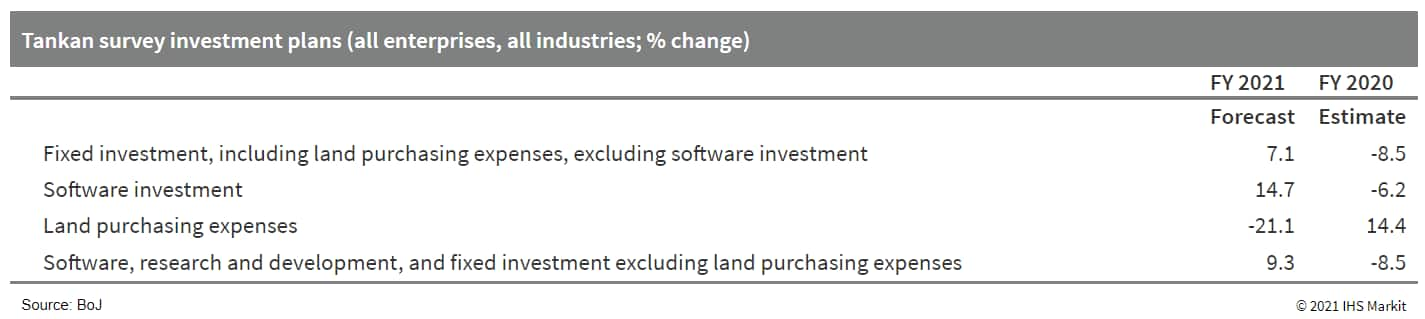
4. The Bank of Japan (BoJ)'s June Tankan, its short-term economic survey of Japan's enterprises, suggests continued improvement in business conditions. Stronger profit outlooks are supporting more upbeat fixed investment plans in 2021. The diffusion index (DI) of current business conditions for large manufacturing groupings in the BoJ's June Tankan survey moved up by nine points to 14 in the second quarter of 2021, returning to the highest level since the fourth quarter of 2018. The improvement was largely driven by solid external demand in line with the resumption of business activity in Japan's trade partners. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
a. The DI of current business conditions for large non-manufacturing groupings moved up by two points to 1. The first return to positive territory in five quarters was largely thanks to improvement in the DIs of wholesale and goods leasing. DIs improved even for industries that were most affected by the state of emergency, including personal services, transportation and postal services, and accommodation/eating and drinking services.
b. However, the DI for future business conditions for large manufacturing fell by one point, reflecting weaker outlooks or external demand for basic materials. In contrast, the future business conditions DI for small manufacturing rose by one point, highlighting expectations for continued increases in output prices.
c. The DI for future business conditions for large non-manufacturing groupings rose by two points thanks to expectations of progress in vaccine rollouts and the Olympic games. However, future business conditions DI for small non-manufacturing groupings fell by three points, in line with declines in construction, communication, and other groupings.
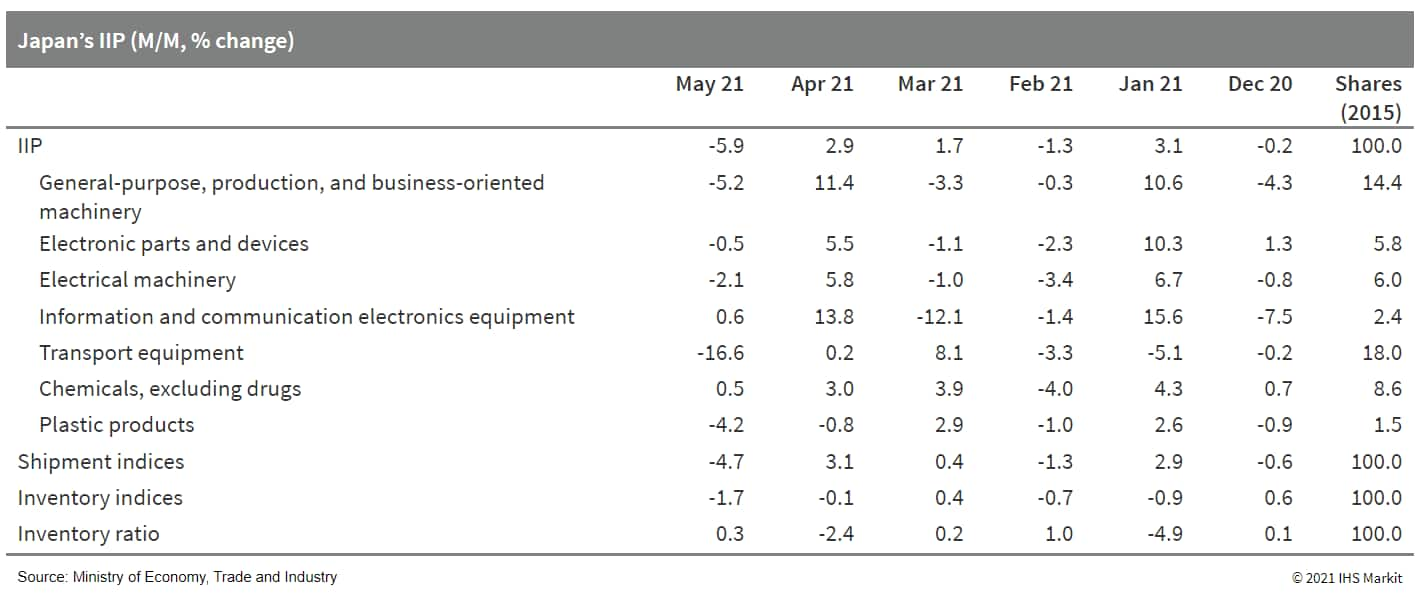
5. Japan's index of industrial production (IIP), which was released on 30 June, fell by 5.9% month on month (m/m) in May following two consecutive months of increases. Manufacturers' shipments also dropped by 4.7% and inventories continued to decline (down 1.7%). However, the index of inventory ratio rose slightly by 0.3% m/m. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
a. The contraction in the IIP was due largely to a 19.4% m/m decline in production of autos, but production in 13 out of 15 industries declined from a month earlier.
b. A 1.7% m/m drop in inventories largely reflected a 32.5% m/m decrease in inventories of autos to fill the gap of orders and production.
6. Japan's state of emergency has weakened the labor market. Japan's retail sales (released on 29 June) fell by 0.4% month on month (m/m) in May following a 4.6% m/m drop in April. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
a. The weakness largely reflected continued declines in sales of general merchandise, motor vehicles, and machinery and equipment. The extension of the state of emergency and expansion of the areas covered dampened sales of non-necessities.
b. The unemployment rate (released on 29 June) rose to 3.0% in May from 2.8% in April. The number of employees fell for the third consecutive month (down by 130,000), and the labor participation rate notched down to 62.0%. The state of emergency has weakened labor conditions. The ratio of new openings to new applications improved, but this largely reflected a decline in the number of new applications.
7. Japan's restaurant sales in March 2020 fell 5.2% compared with the same month in 2020 when the COVIS pandemic was at its peak, down for the 13th consecutive month and 19.6% less than the pre-pandemic level of March 2019, the Japan Foodservice Association (JF) estimates. Those figures cast a shadow on the whole sector as the Japanese government has declared in April 2021 a new state of emergency banning restaurants from selling alcohol and imposing a closure at 8:00 pm in 10 prefectures including Tokyo, Osaka, Kyoto, Aichi, Hokkaido, Hyogo, Okayama, Hiroshima, Fukuoka, and Okinawa, a recent report from the USDA notes. According to Reuters, containment measures are likely to be extended until mid-July or more ahead of the start of the Olympic games on 23 July. A final decision on the matter is expected by 8 July, but the USDA anticipated that the restriction on alcohol sales and shorter business hours might continue during the Tokyo Olympic/Paralympic Games which will conclude in early September. The Hotel, Restaurant and Institutional (HRI) industry showed steady growth in sales to USD305 billion in 2019. The COVID-19 pandemic severely impacted the sector with restaurant sales falling by 40% year-on-year in April 2020 due to mandatory closure. Overall industry sales declined 19.5% in April 2021 when compared with April 2019, before the pandemic. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Cristina Nanni)
8. SK Innovation plans to invest KRW30 trillion (USD26.5 billion) over the next five years to make the transition from a carbon-intensive model to green business, reports the Yonhap News Agency. The company aims to increase the ratio of eco-friendly business from the current 30% to 70% by 2025 to reduce its carbon footprint and create new business opportunities, says CEO Kim Jun. It will ramp up battery production capacity from the current 40 GWh to 200 GWh in 2025 to meet growing demand, raising the prospect of generating KRW2.5 trillion of earnings in 2025. SK Innovation is also considering spinning off its battery business in a bid to raise funds to step up its manufacturing capacity in the coming years. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
9. Indian Oil says that its board has given stage-one approval to build India's first styrene plant at the company's refinery and petrochemical complex at Panipat, India. The production capacity of the plant will be 387,000 metric tons/year and the estimated cost of the project is 44.95 billion Indian rupees ($604.50 million). The styrene facility would be commissioned by 2026-27, Indian Oil says. The company says India's styrene consumption is currently about 900,000 metric tons/year and that demand is expected to increase consistently over the next 15-20 years. "However, there is no domestic styrene capacity in India," and the country's demand is met through imports from Singapore, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia, creating a challenge for India's downstream styrenics industry, Indian Oil says. The company says that the project at Panipat will strengthen India's focus on harnessing opportunities in the petrochemical sector and synchronize with the Indian government's self-reliance campaign. It adds that the project will reduce India's import dependence substantially, and save foreign exchange amounting to about $500 million/year. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
10. Fugro and PTSC Geos and Subsea Services Company have announced a metocean service contract with Enterprize Energy Group for 3.4 GW Thang Long offshore wind farms (OWFs) in Vietnam. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Lopamudra De)
a. The contract includes provision, installation and operation for a SEAWATCH Wind Lidar Buoy and generating monthly Geo-data reports for the wind farm. Work will commence in July and the buoy will record continuous measurements for an initial period of one year to support wind resource mapping.
b. The integrated ZX 300 M lidar can record wind measurements up to 300 m above sea level. The Geo-data - air pressure, humidity, air and water temperature, wave height, and current measurements - will be used to support the wind farm's engineering and design. The Thang Long OWFs cover an area of 2,000 sq km, located approximately 20 to 50 km offshore Ka Ge Cape. It comprises five 600 MW phases with a final 400 MW phase.
c. The first 600 MW phase will feature 64 units of 9.5 MW Vestas wind turbines on jacket foundations and is expected to be completed between 2025 and 2026. The final phase of the wind farm is tentatively scheduled for completion between 2029 and 2030.
Posted 01 July 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.