Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Research — 15 Sep, 2023
By Julber Osio, CFA and Erik Keith
As many markets worldwide already have commercial 5G services, new launches slowed in the first half of 2023 to just 10. This brought the total number of operators with active commercial 5G services to 249, spread across 97 markets worldwide as of June 30, 2023.


Several African markets had commercial 5G launches in the first half of 2023, such as Airtel and Mafab Communications Ltd. (MCOM) in Nigeria, MIC Tanzania Ltd. (Tigo) in Tanzania, VM SA Vodacom in Mozambique and QCell Ltd in Gambia. Vodacom's launch brings its parent company Vodafone Group PLC's 5G footprint to 16 markets, which is the largest worldwide.
As discussed in our last update, Kagan expects African operators to feature more in future commercial 5G launches as the region catches up with more established 5G markets in other parts of the globe. 5G pioneers in Africa, South Africa and Lesotho, have demonstrated that strong government support, especially in releasing spectrum and having a consistent regulatory environment, is key to supporting 5G. Other markets in the region have followed this track, as evidenced by several spectrum assignments and auctions in several African markets in the past year plus more planned spectrum releases in the coming years.
Asia-Pacific and Europe also saw launches, such as China Telecom (Macau) Co. Ltd. in Macau, 1&1 AG in Germany (which launched fixed wireless access 5G), Telekom Romania Mobile Communications SA in Romania, MTS Armenia CJSC in Armenia and Síminn hf. in Iceland.
Operators worldwide are slowly transitioning from initial non-stand-alone (NSA) to stand-alone (SA) deployments. At least 57 operators in 33 markets worldwide have activated 5G SA networks as of June 30, 2023. Operators in major 5G markets such as the US and mainland China have transitioned to 5G SA, but other markets have yet to follow the trend.
Spectrum harmonization, stand-alone 5G highlights
Spectrum choices for commercial 5G networks are unchanged. Mid-band spectrum between 3.5 GHz and 3.7 GHz remains the top choice, with at least 192 operators worldwide using such frequencies in their commercial 5G networks. Four out of the 10 new launches in the first half of 2023 used 3.5 GHz. The rest either used low-band spectrum for coverage or dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) over legacy 4G spectrum in other mid-frequency bands such as 2.1 GHz.
DSS is often used as a temporary solution by operators waiting to get access to harmonized 5G spectrum, so it is reasonable to expect some of these new launches to eventually move to 3.5 GHz in the future. In fact, most of the operators in Latin America that launched 5G using DSS frequency bands in 2020 have already moved to 3.5 GHz. As of June 2023, the extended AWS bands of 1.8 GHz and 2.1 GHz appear to be the most popular choices for DSS in commercial 5G networks.
At least 35 operators worldwide are using millimeter wave (mmW) spectrum for their commercial 5G networks, most of which are located in North America. Some European operators are slowly adopting the 26 GHz and 28 GHz bands, but 3.5 GHz remains the standard 5G band for many.
Asia-Pacific operators, on the other hand, seem to be pushing back on the use of mmW spectrum. South Korea canceled its 28 GHz licenses in November 2022 and May 2023 due to the inability of local operators to meet the requirements for network deployment. In the defense of local operators, the lack of demand from consumers did not justify capital spending on deploying network base stations. India's auction of 26 GHz in August 2022 was met with less intense bidding from operators compared to low- and mid-frequency bands. Mainland China, on the other hand, has not yet released mmW frequencies to local operators.
Judging from the number of announced future spectrum auctions, many markets worldwide are still prioritizing low- and mid-band spectrum over mmW spectrum. This will only be reinforced by the International Telecommunication Union's upcoming WRC-23 summit in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, later this year, which is set to decide on opening up more low- and mid-band spectrum for 5G.
China: Largest single market
China Mobile Communications Group Co. Ltd., more popularly known as China Mobile, remains the single largest mobile operator worldwide by any measure, including subscribers and base stations.
In terms of total mobile subscribers, China Mobile's official count is 985 million, as the operator reported at the end of June 2023. China Mobile claims that 721 million (73%) of these customers are "5G package" subscribers. (China Mobile defines a 5G package customer as a mobile customer who has subscribed to 5G tariff plans).
Another notable data point for China Mobile is its addition of 301,000 5G base stations during the first half of 2023, bringing its total 5G base station count to 1.8 million nationwide.
The second largest mobile network operator (MNO) in China, China Telecom Corp. Ltd., surpassed the 400 million mobile subscriber benchmark as of the end of June 2023, reaching 401.9 million in total, also with 73% defined as 5G package subscribers (approximately 295 million).
Meanwhile, China Unicom's mobile and 5G subscriber counts also increased, although Unicom only revealed its 5G package subscriber number, at about 232 million.
5G systems global vendor highlights
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (publ) and Nokia Oyj continue to dominate the 5G market in terms of total 5G trials, commercial deployments and contract wins. These vendors have effectively carried forward their established momentum from the second half of 2022, as evidenced in our previous 5G Tracker report.
While trials and win announcements are important, in our view, the most critical indicator of success in the 5G market remains the total number of live 5G networks supported (i.e., commercial deployments) by a vendor. As of June 30, 2023, both Ericsson and Nokia were well over the 250 mark globally — with Ericsson at 300 and Nokia at 263 — in terms of total 5G "relationships," i.e., trials, wins and network deployments.
The two Nordic-based vendors have provided the most extensive details on their respective 5G live networks, commercial 5G contracts/deals, and 5G wins and/or deployments with MNOs, as well as enterprise/private network and other 5G technology implementations.
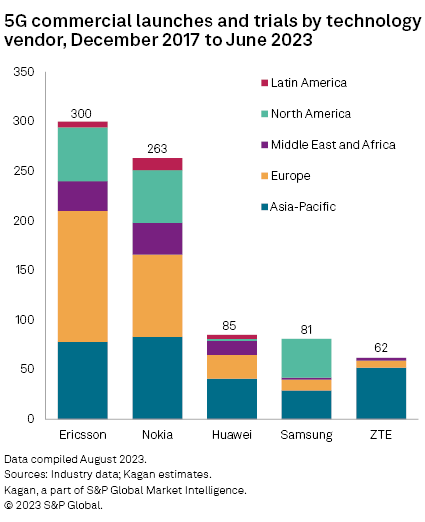
Ericsson
At the time of this publication, Ericsson claimed 147 live 5G networks (up from 143 at end-2022) in 63 countries, and 21 live 5G stand-alone networks. The first half of 2023 saw a substantial softening of 5G network build-outs and contract awards by MNOs and a corresponding drop in the wins/deployments won by the 5G systems vendors.
Ericsson has also claimed to have shipped more than 10 million 5G radios to date, including 1 million 5G radios manufactured in Poland for Nordic MNO Telia Co. AB (publ), a longtime customer.
During the first half of 2023, key mobile operator wins, or contract enhancements/expansions announced by Ericsson, included the following: Deutsche Telekom AG, Spark New Zealand Ltd., Vodafone Group PLC (Oman), Umniah Mobile Co. PSC (Jordan), Telia (Sweden), MIC Tanzania Ltd. (Tigo), Orange Espagne SAU (Spain), PT Telekomunikasi Selular (Indonesia), Telstra Group Ltd. (Australia), Swisscom AG, Singapore Telecommunications Ltd., Xplore Inc. (Canada), Emirates Telecommunications Group Co. PJSC (Etisalat, UAE), Debswana (Botswana), VMED O2 UK Ltd. (UK), Faroese Telecom (Faroe Islands) and Jersey Telecom Group Ltd. (Channel Islands), and several private/enterprise networks.
Nokia
Nokia Corp. also continued to generate increasing traction in the global 5G infrastructure market. As of this article's publication, Nokia indicated it had 303 commercial 5G deals, up from 266 in our previous tracker, and it had 103 live 5G networks supported, up from 96. This includes well over 100 5G operator contracts with service providers: 18 in the Americas, 47 in Europe, 28 in Asia-Pacific and 13 in the Middle East/Africa.
Key 5G customer wins or contract enhancements for Nokia in the first half of 2023 included NOW Telecom Co. Inc. (Philippines), China Unicom, Tele2 Sverige AB (Sweden), Antina Pte. Ltd. (Singapore), Comcast Corp. (US), MTN Group Ltd. (South Africa), AT&T Inc. (US), Jordan Mobile Telephone Services JMTS (Zain), Jordan Telecommunications Co. (Orange Jordan), Citymesh NV (Belgium), A1 Bulgaria (Bulgaria), Charter Communications Inc. (US), Emirates Integrated Telecommunications Company PJSC (Dubai) and Virgin Media O2 (UK).
Huawei
On the vendor front, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd. remains the overall 5G/small cell infrastructure market leader, due almost exclusively to the company's success in its home market of mainland China, and the broader Asia-Pacific region, where total 5G/small cell shipments dwarf those of other markets and regions.
While mainland China is the single largest telecom market worldwide, and Huawei has garnered the lion's share of mobile and 5G network infrastructure contract wins (and corollary revenue) in its home market, Huawei and other Chinese vendors have more limited prospects outside of mainland China and the Asia-Pacific region. Specifically, the Chinese vendors have been effectively shut out of the lucrative North American and European markets, where governments have implemented de facto bans on Chinese gear due to fears that this 5G equipment poses cybersecurity threats.
Still, the Chinese vendors have won several sizable 5G contracts in the Middle East and Africa regions. Huawei's total customer count remains officially undisclosed. However, the last reported number was well over 100 total operator wins/deployments, and it is feasible that Huawei may have at least as many private/enterprise/industrial network 5G deployments.
ZTE, Samsung
After the Big Three — Ericsson, Nokia and Huawei — ZTE Corp. and Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. round out the top five vendor list in terms of worldwide 5G deployments. Together, the top five vendors account for at least 95% of the global 5G RAN market revenues and unit shipments.
ZTE's customer roster, like Huawei's, is also kept under wraps, despite the fact that ZTE is a primary or secondary supplier in some of the largest 5G networks on Earth (i.e., the Big Three MNOs in China). During the first half of 2023, ZTE's publicly disclosed 5G customer wins/contract enhancements included Telkomsel (Indonesia), Telekom Malaysia, China Unicom, China Mobile and Advanced Info Service PCL (Thailand).
Meanwhile, Samsung continued to generate increasing momentum in the global 5G RAN market, thanks to its well-regarded open/virtual RAN solution set. Notable publicly disclosed customer wins/deployments for Samsung in the first half of 2023 included KDDI Corp. (Japan), DISH Network Corp. (US), Vodafone Deutschland GmbH (Germany), Vodafone ONO (Spain), and Naver Cloud Co. Ltd. (private network for Hoban Construction in South Korea).
Wireless Investor is a regular feature from Kagan, a part of S&P Global Market Intelligence.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
Research
Research