Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global — 20 Jun, 2023 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
Nations Wrestle With Water Crises as Shortages Loom
The US Interior Department said June 15 that it will begin to develop multistate guidelines for water use in the Colorado River, the dwindling lifeline for more than 40 million people in the American Southwest.
The announcement followed a deal struck May 25 between the seven states of the region on short-term water reductions to avert a disastrous, drought-fueled shortage that would affect much of the country’s production of fruits and vegetables, along with electricity supplies for millions of homes and businesses. The agreement, which calls for an about 13% reduction in water use from the Colorado River, is only temporary: It is designed to last until 2026, when a previous set of guidelines, established in 2007 and proven to be inadequate in the face of persistent drought and population growth, expires.
Abundant rain and snow across the region this year “have helped mitigate declining reservoir levels, possibly delaying the need for the proposed severe curtailments in 2024 and providing greater flexibility in reaching a consensus solution between the seven affected states before the existing management guidelines expire in 2026,” wrote Jenny Poree, senior director and sector lead for utilities at S&P Global Ratings.
The reprieve will be temporary, as the US, like many other nations, is facing a reckoning over water supplies in an increasingly warmer and drier world. “The negotiations over a long-term agreement in the Southwest are expected to be more contentious and influential,” Poree said. “Water rights that were once viewed as certain are being questioned and may be superseded by state or federal efforts.”
In Mexico, where protests have erupted in recent years over the allocation of scarce water supplies in the country’s arid north, the number of states exposed to high water stress will almost double to 20 by 2050 from 11 in 2020, according to an April report from S&P Global Ratings’ Sustainability Insights. “Mexico experienced some of the most severe water shortages on record during 2022 because of low rainfall, population growth and warmer temperatures in its north and northeastern states,” S&P Global Market Intelligence analysts said.
Irrigated agriculture accounts for 70% of global freshwater withdrawal, according to the “UN World Water Development Report 2022,” and much of the world’s most abundant farmlands are at risk of water shortages in the coming decades. “Cropland in many of the world’s largest food-exporting countries faces exposure to water stress,” according to physical risk data from S&P Global Sustainable1.
The war in Ukraine, known as the breadbasket of Europe, has reduced exports of wheat and other basic foodstuffs, while climate change threatens to dramatically curtail production from small-scale farms across sub-Saharan Africa and East Asia.
Large agriculture producers are responding, but their efforts so far are inadequate in coping with the coming era of water scarcity. Only about half of major food and beverage producing companies have a publicly available commitment to sustainable agriculture, which focuses on preserving natural resources such as fresh water, according to the S&P Global Corporate Sustainability Assessment. Many of those commitments do not cover the full scope of their supply chain.
Today is Tuesday, June 20, 2023, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
Written by Richard Martin.
Brazil's Political And Economic Outlook
President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva is seeking to position Brazil, the largest economy in Latin America, as a country willing to expand and diversify its trade relations. The government is seeking to strengthen strategic sectors such as agribusiness, manufacturing, renewable energy and infrastructure, particularly via public-private partnerships. Even with emerging opportunities, companies operating in Brazil — or seeking to establish commercial relations with Brazilian counterparts — will face economic, political and regulatory challenges. In this episode, S&P Global experts provide their perspective on the country’s economic and risk landscape.
—Listen and subscribe to Economics & Country Risk, a podcast from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on the global economy >
Asia-Pacific Office REITs: Rising Stress Is Manageable For Most

Asia-Pacific office REITS and landlords face dilemmas similar to peers elsewhere in the world. Tenants are downsizing. Vacancy rates are elevated and new supply could exacerbate this burden. Higher interest rates are pressuring capitalization rates and asset values. All that said, S&P Global Ratings believes this region's office-focused REITs are in better shape than global peers. Hybrid-working practices are taking root in this region, but not as disruptively as elsewhere. The allure of working from home is not as strong in Asia's high-density cities, where residential spaces are generally small and commute times short.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on capital markets >
Mapping El Nino's Impact On Crop Yields, Global Food Trade In 2023-24
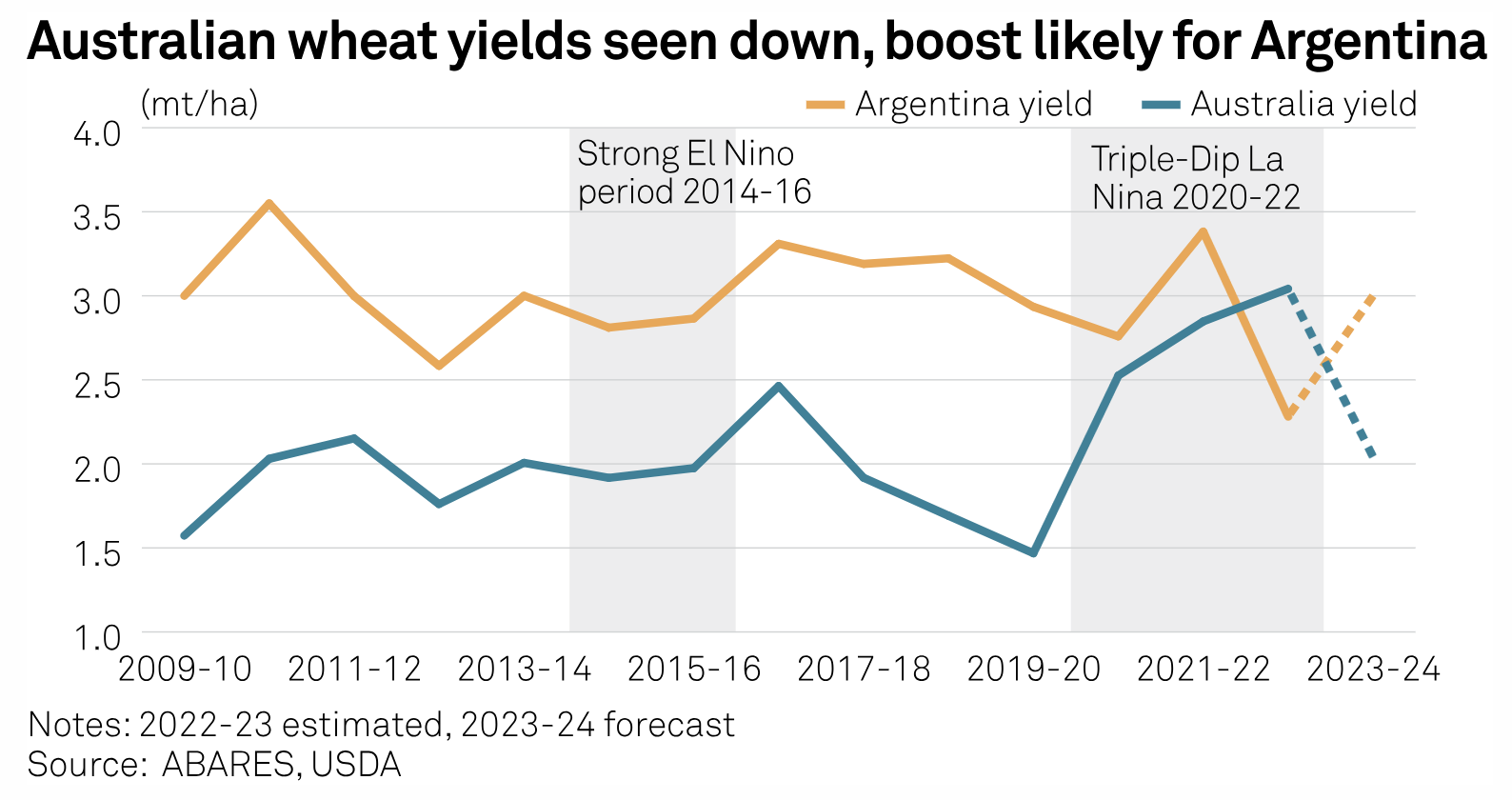
An emergence of El Nino phenomenon could affect global agricultural yields and alter trade flows in the 2023-24 season, according to agricultural bodies, meteorological agencies and trade analysts. The US Climate Prediction Centre said June 8 that weak El Nino conditions were observed across equatorial Pacific Ocean. The agency claimed there were 56% chances of the conditions strengthening during November-January. In the meantime, the Australian Bureau of Meteorology on June 6 stepped up its probability forecast to "El Nino Alert" from "El Nino Watch", indicating higher chances of an El Nino forming in late-2023.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
Heat Wave's Ferocity Ebbs In Texas, But Peakload Record Set To Crumble June 19-21

The Electric Reliability Council of Texas on June 15 did not forecast the system breaking its 80.1-GW peakload record on June 16, unlike the previous day's forecast, but did forecast peaks above that level June 19-22, as a heat wave strengthened day-ahead and week-ahead on-peak prices while becalming natural gas prices. ERCOT North day-ahead on-peak power for June 16 delivery rose about $49 to trade near $79/MWh on the Intercontinental Exchange, weekend off-peak rose $6 to around $57.50/MWh, and next-week's package surged about $27 to more than $87/MWh. Meanwhile, Houston Ship Channel spot gas gained just a penny to $2.10/MMBtu for June 16 delivery.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on sustainability >
New Iraqi Budget Law Strengthens Baghdad's Hand Over Kurdistan Region's Oil Sector
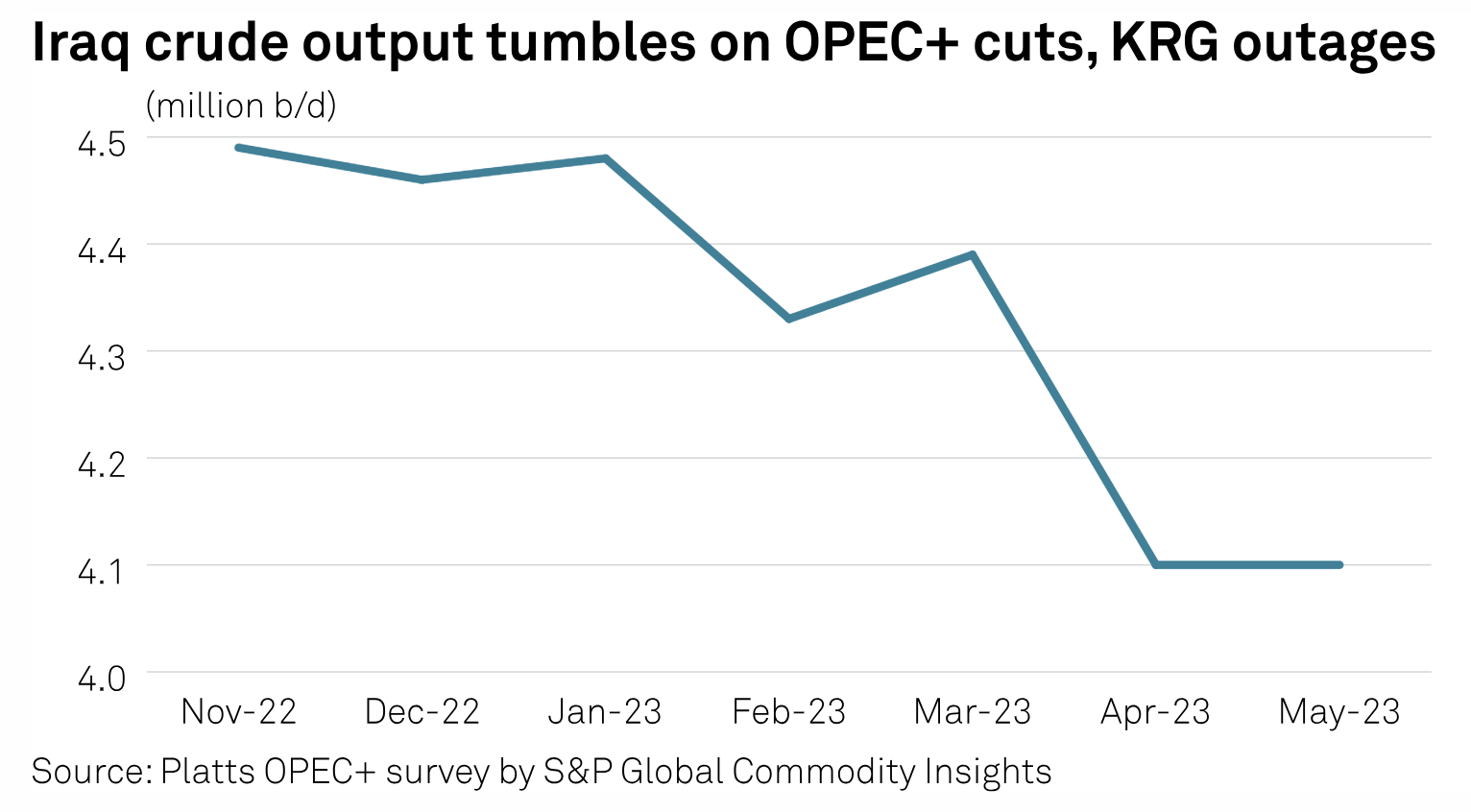
Already reeling from the months-long suspension of its crude exports, Iraq's semiautonomous Kurdistan region may see its lifeblood oil sector further hemmed in with the passage of the federal budget. The budget, passed June 12 following four days of late-night voting and intense debates within Iraq's parliament — including on controversial amendments decried by Kurdish officials — calls for $152 billion in spending, allocated for the years 2023, 2024 and 2025.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Streaming Price Hikes Hit Latin America
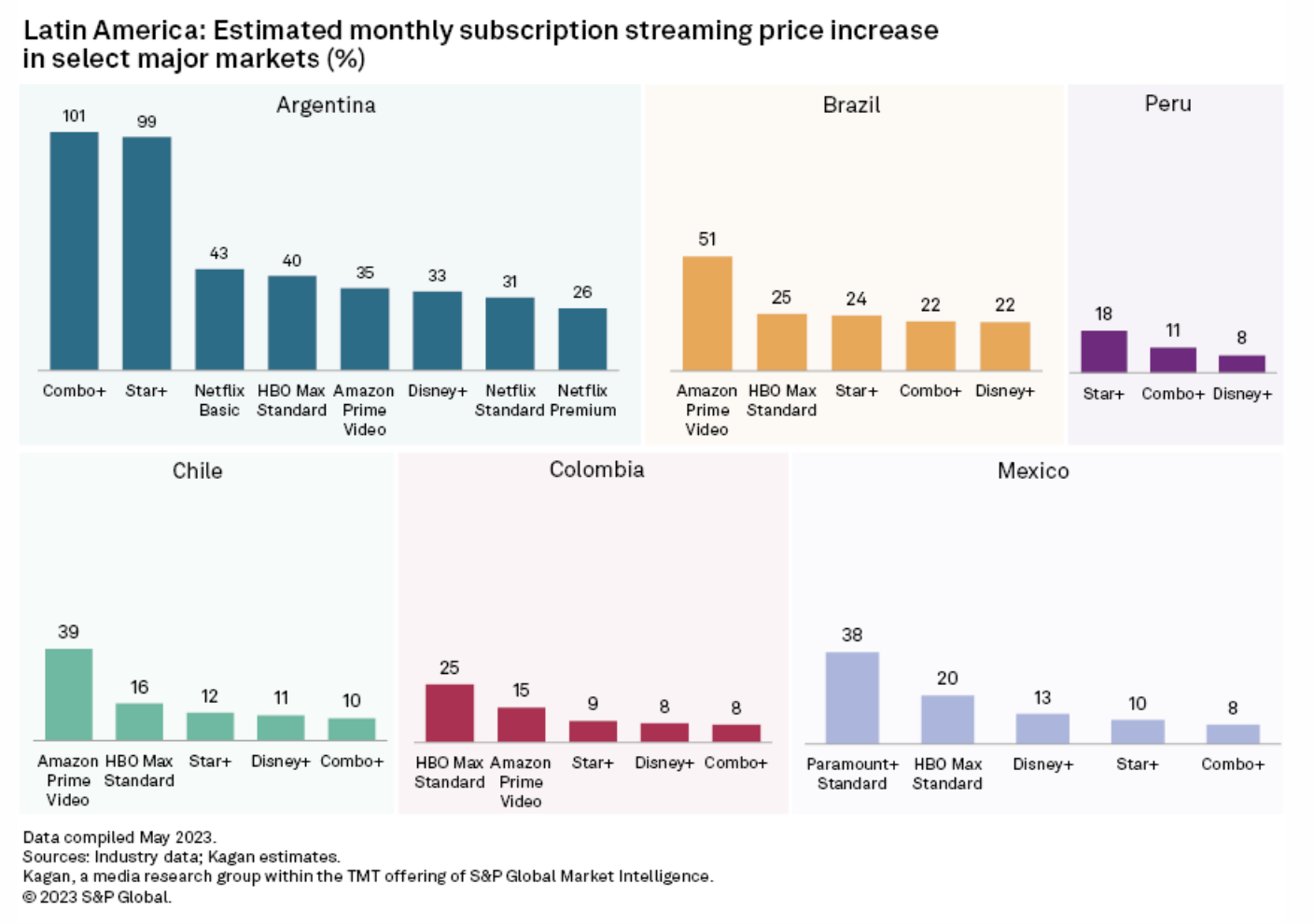
Consumers across Latin America were greeted with higher streaming bills during the first half of the year as most global over-the-top providers rolled out price increases to help squeeze more value from their offerings. Rising inflation and content investments have also triggered higher subscription streaming fees in major markets around the region. Kagan has updated the OTT Services & Devices database with recent price hikes carried out by global streaming operators such as Amazon.com Inc., Walt Disney Co., Warner Bros. Discovery Inc., Netflix Inc. and Paramount Global in select major Latin America markets such as Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Mexico and Peru.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Content Type
Theme
Location
Segment
Language
