Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
ECONOMICS COMMENTARY — Sep 18, 2023
Nearshoring has become increasingly popular in recent years, particularly after the unprecedented disruptions to supply chains following the COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine. Mexico provides several nearshoring benefits including its proximity to the US, a well-developed infrastructure and a cost-effective labour pool. Mexico offers a large workforce of skilled professionals with a cost advantage over the United States, it has useful transport connections, investment incentives and a large number of trade agreements which can simplify trade and business operations for firms operating in North America.
The S&P Global Mexico Manufacturing PMI™ panel includes around 350 manufacturers in Mexico, which were invited to take part in a special nearshoring survey in July 2023. Firms offered their insights surrounding the impact of nearshoring on order books, their expectations for the year ahead and anticipated challenges. This report also analyses the results by detailed sector, region and company workforce size.
Listen now to our recent podcast episode on nearshoring to Mexico
Nearshoring is defined as the practice of relocating suppliers closer to the domestic market. Interest in nearshoring, and reshoring (where supply is relocated to the domestic market), has increased since the pandemic in response to the widespread disruption of supply chains across international borders, and notably from Asia to the West.
Around one-fifth of Mexican manufacturing PMI respondents stated that total demand (domestic and exports) for their goods had improved in the 12 months to July as a result of nearshoring, with an even higher proportion (31%) of firms forecasting growth opportunities in the year ahead.
Nevertheless, Mexican manufacturers identified several challenges or risks likely to prevent their company from fully capitalising on nearshoring-related growth opportunities. The top concern among businesses was the cost and availability of capital (41% of firms), followed by legal and regulatory obstacles surrounding labour laws, intellectual property, data privacy and taxation (34%). Security came third, while labour shortages was only seen as a risk factor by one-in-ten respondents.
Of the 14 broad areas of the manufacturing industry, Textiles & Clothing recorded the largest proportion of firms (45%) signalling sales growth over the past 12 months as a result of nearshoring. Firms in the Coke & Petroleum and Leather & Leather Products sectors also experienced positive sales developments in the past 12 months, with 33% and 31% respectively noting increases.
One-quarter of all companies in the Transport & Equipment sector ― which includes manufacturers of motor vehicles, railway, aircraft and motorcycles ― attributed higher domestic and international sales in the past 12 months to nearshoring. At the bottom of the 'current demand' sub-sector rankings were Metals & Metal Products (10%) and Rubber & Plastics (7%).
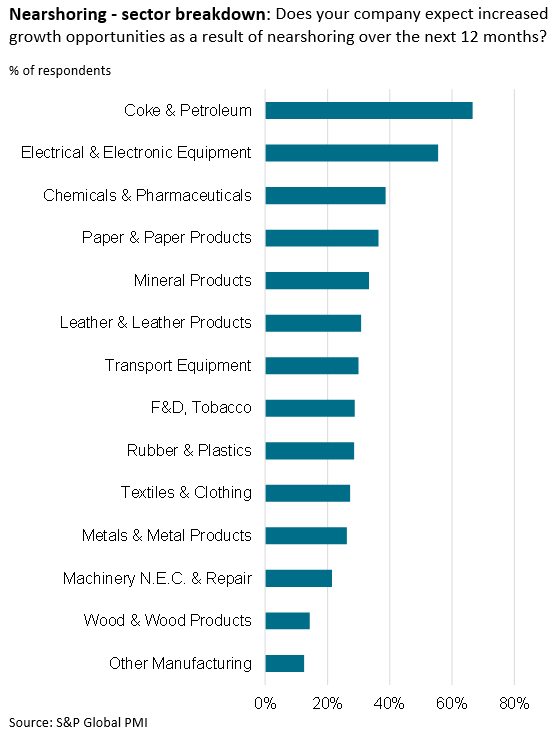
The Coke & Petroleum segment saw the largest proportion of companies expecting growth opportunities in the year ahead (67%). Electrical & Electronic Equipment came second (56%), followed by Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals (39%). Concurrently, exactly 30% of Transport & Equipment firms were optimistic about growth opportunities. Leather & Leather Products came sixth (31%) and Textiles & Clothing tenth in the rankings (27%). Lowest ranked in the 'growth opportunities' hierarchy were Wood & Wood Products (14%) and Other Manufacturing (13%).
Exactly one-quarter of all large companies indicated that demand for their products had improved over the past 12 months due to nearshoring, while 44% foresee growth in the year ahead.
By comparison, only 8% of small-sized manufacturers linked sales growth in the 12 months to July to nearshoring. That said, 25% expect to benefit in the coming year.
When listing potential challenges, firms were most concerned about the cost and availability of capital. Additional qualitative evidence highlighted worries surrounding Chinese imports and challenges for local firms to price competitively.
With respect to medium-sized firms, around 26% of panellists suggested that their order books improved on account of nearshoring. Moreover, 30% forecast further opportunities in 12 months' time. The top concern in this group was legal and regulatory constraints.
Breaking down the data by geographical regions, the largest proportion of manufacturers reporting demand growth as a result of nearshoring was located in the Gulf Coast (Nuevo León, San Luis Potosí, Tamaulipas and Veracruz). While 30% of firms had already experienced an upturn, 40% foresee opportunities over the course of the coming 12 months.
The North of Mexico (Baja California, Baja California Sur, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Durango, Sinaloa and Sonora) had the second-best outcome, with one-quarter of participants to the PMI survey attributing sales growth in the past 12 months in part to nearshoring and 32% signalling upbeat projections for the year ahead.
Circa 19% of panellists in the West region (Aguascalientes, Colima, Guanajuato, Guerrero, Jalisco, Michoacán, Nayarit, Oaxaca, Zacatecas) saw new order growth in the 12 months to July thanks to nearshoring, with 29% expecting to benefit from it in the coming year.
The lowest proportions of companies reporting higher sales volumes as a result of nearshoring were found in the East (7%) and Mexico City (17%). Nevertheless, a healthy percentage of firms in these areas anticipate growth opportunities in the year ahead (29% and 31% respectively).
The results from the PMI survey are encouraging and validate favourable media reports regarding nearshoring to Mexico. Its close proximity to the US, logistical strengths, trade agreements, substantial labour force and competitive minimum wage present several advantages for firms looking to best serve the US market whilst minimising supply-chain disruptions and managing costs.
The data indicate varying growth and expectations among the different sectors, regions and company sizes, signalling that the Mexican economy appears poised to reap substantial benefits from influxes of foreign direct investment.
Nevertheless, by addressing the potential challenges highlighted by manufacturers, policymakers could play a pivotal role in helping the nation to further capitalise on growth opportunities presented by nearshoring. With this awareness, companies can navigate the nearshoring process in Mexico more effectively, ensuring they maximise the benefits of this strategic business trend.
Pollyanna De Lima, Principal Economist, S&P Global Market Intelligence
Tel: +44 1491 461 075
© 2023, S&P Global. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI®) data are compiled by S&P Global for more than 40 economies worldwide. The monthly data are derived from surveys of senior executives at private sector companies, and are available only via subscription. The PMI dataset features a headline number, which indicates the overall health of an economy, and sub-indices, which provide insights into other key economic drivers such as GDP, inflation, exports, capacity utilization, employment and inventories. The PMI data are used by financial and corporate professionals to better understand where economies and markets are headed, and to uncover opportunities.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
Location