Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
BLOG — Oct 23, 2023

By Chris Rogers
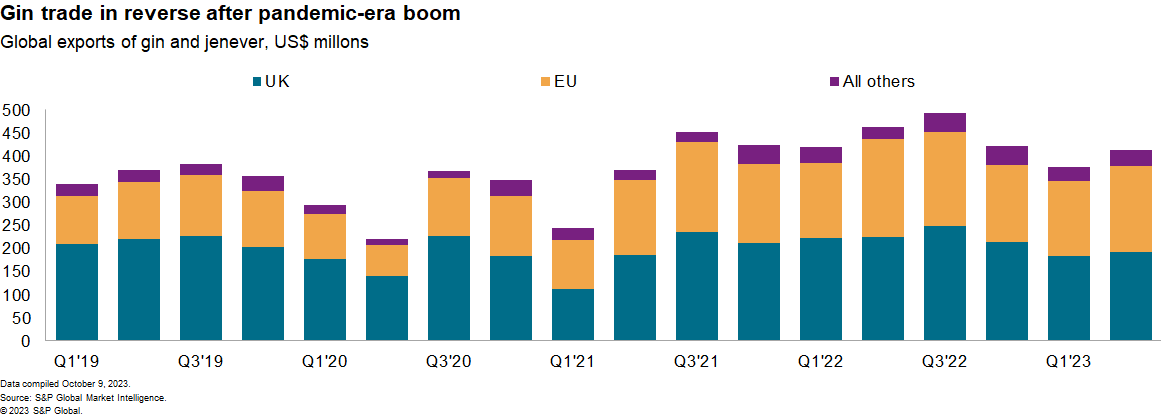
The supply chains for gin beverages are facing falling volumes and increasing complexity. Global exports of gin products fell year over year in the 12 months to June 30, 2023, with UK exporters also facing a drop in export values per liter in the past year compared with 2019. This trend may reflect greater health consciousness as well as a slowdown in demand following pandemic-era lockdown consumption expansion.
The slowdown was led by a 6.1% slide in exports from the UK, which represented nearly half of global shipments in the 12 months to June 30, 2023. A decline in domestic sales will make UK producers more reliant on export markets than in the past. UK membership of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) trade group may help boost exports to Asia with a reduction in export duties.
Bottling expenses
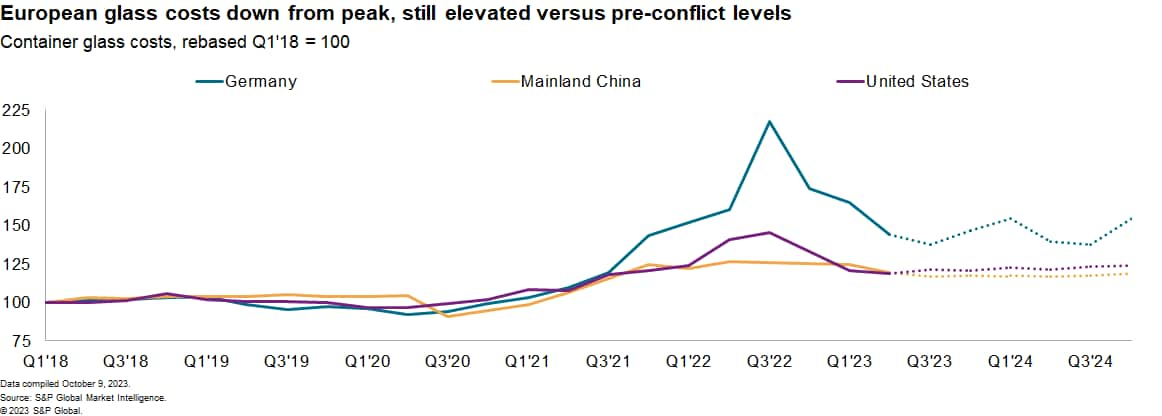
The cost of container glass used in bottles soared in 2022 because of conflict-related energy price rises. Container glass prices in Europe more than doubled between the first quarter of 2021 and the third quarter of 2023 and subsequently fell by 34% by the second quarter of 2023.
Energy prices in the wake of the conflict in Ukraine have been the main differentiator between Europe and the rest of the world. Prices in mainland China and the US have proven less volatile.
Global glass prices — including both container glass and flat glass for windows — are set to decline in the second half of 2023 before stabilizing in early 2024. Glass production costs are nonetheless expected to remain around 2019 levels due to increased raw materials costs.
The bottles used by UK gin producers are typically made domestically. The UK also imported around 1.86 billion bottles in the 12 months to July 31, 2023, across the pharmaceutical and food/beverages sectors. That was 8% higher than a year earlier.
Botanicals sourcing
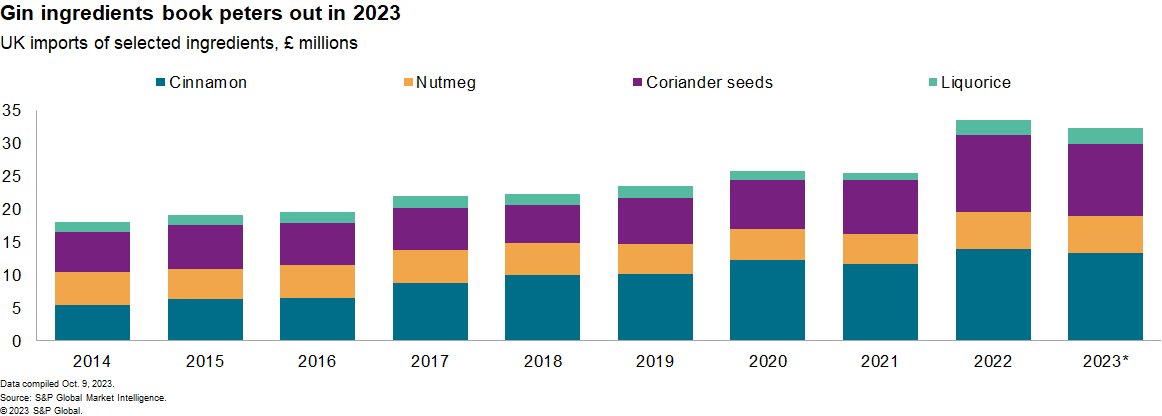
Sourcing of botanicals, the ingredients used to flavor gin, are led by suppliers from Vietnam (nutmeg, cinnamon), India (coriander seeds) and Indonesia (cinnamon and nutmeg). The sector is fragmented and the UK imports indirectly via EU countries, making for complex ethical sourcing and risk assessment decision-making.
UK imports of botanicals used across a wide range of gins increased by 9% annually between 2017 and 2022. That's been led by an increase in shipments of cinnamon and in coriander seeds. We see signs of a slowdown, with a 3% decline in the 12 months to Aug. 31, 2023, compared with calendar year 2022.
With a push toward sustainable sourcing across supply chains — securing environmentally robust and ethical suppliers — the location of sourcing of botanicals is more critical than ever.
Vietnam accounted for 29% of global cinnamon exports and 4% of nutmeg but represented just 16% of UK cinnamon imports and 29% of nutmeg. UK sourcing of both spices included supplies from France and the Netherlands, perhaps indicating the sourcing from blenders who may also have sourced from Vietnam. That can represent a challenge detecting the "real" source of products from a supply chain reporting perspective.
Sourcing of spices is also highly fragmented. The top 10 direct global buyers of Vietnamese cinnamon and nutmeg represented just 25% of purchases in the 12 months to Aug. 31, 2023.
Given the sourcing patterns of the key spices, the EU Deforestation Free Regulation may be particularly relevant for gin suppliers looking to sell into the EU as a growth market, as outlined in Deforestation rules' impact on supply chains.
Ingredients sourcing also faces a thicket of export and import regulations, challenges regarding ethical behaviors regarding how business is done, and variations in local labor practices. A weighting of risks that matter — such as corruption risks, regulatory burdens and labor risks — needs to factor into the sourcing decision-making process.
Sign up for our Supply Chain Essentials newsletter
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.