All major US, European, and APAC equity indices closed higher today. US and benchmark European government bonds closed lower. European iTraxx and CDX-NA credit indices closed almost unchanged on the day across IG and high yield. The US dollar, oil, and copper closed lower, while gold, silver, and natural gas were higher on the day.
Americas
- US equity indices closed higher with the DJIA +0.5% and S&P 500 +0.4% closing at new record highs for a second consecutive day; Russell 2000 +0.3% and Nasdaq +0.1%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +4bps/1.59% yield and 30yr bonds +3bps/2.27% yield.
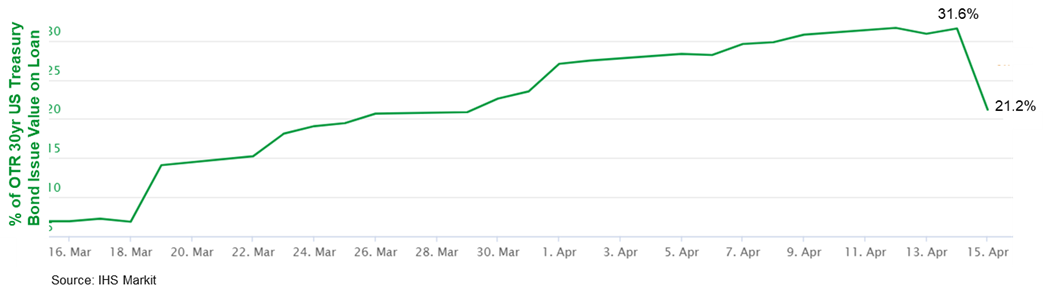
- The below chart of IHS Markit's securities lending data indicates that the total value of the on-the-run 30yr US Treasury bonds on borrow declined sharply from 31.6% on Wednesday to 21.2% yesterday (Thursday), which may indicate an uptick in short covering helped to fuel some of the day's substantial rally.
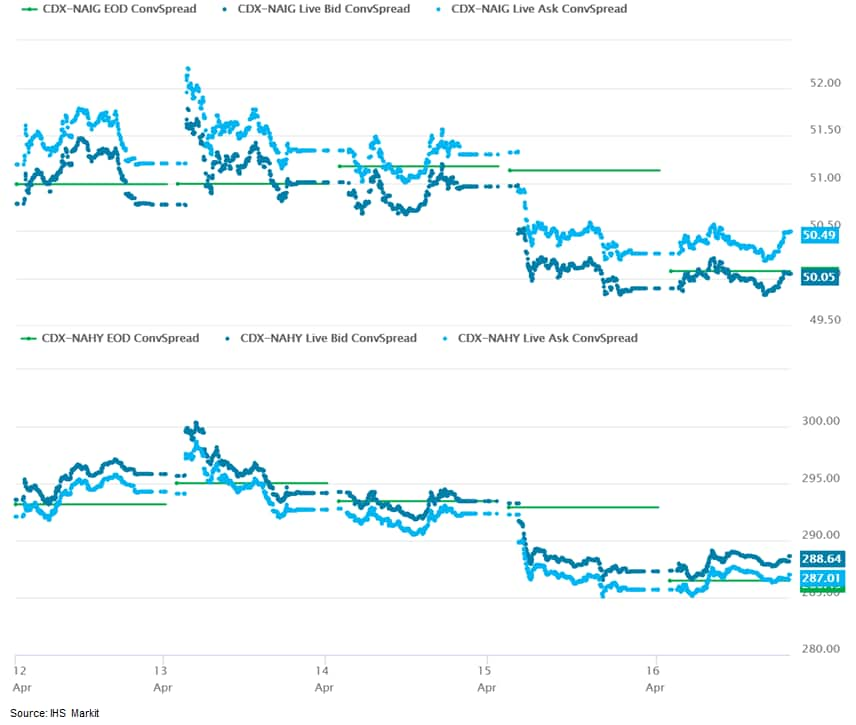
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/50bps and CDX-NAHY +1bp/287bps, which is -1bp and -5bps week-over-week, respectively.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.1%/91.56.
- Gold closed +0.8%/$1,780 per troy oz, silver +0.5%/$26.11 per troy oz, and copper -1.2%/$4.17 per pound.
- Crude oil closed -0.5%/$63.19 per barrel and natural gas closed +0.8%/$2.68 per mmbtu.
- Surging COVID-19 infection rates in Brazil and India have continued to raise global concerns, with India now reporting more than 200,000 cases in a single day for the first time. In Brazil, high community replication rates have resulted in potential escape mutants beginning to emerge, as variants of the aggressive P1 Manaus strain. Meanwhile, a new study conducted by Oxford University has indicated that the risks of cerebral vascular thrombosis from COVID-19 itself are 8-10 times higher than from vaccination with AstraZeneca (UK), Pfizer (US), or Moderna (US) vaccines. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Janet Beal Ewa Oliveira da Silva)
- The US University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index rose 1.6 points (1.9%) to 86.5 in the preliminary April reading. The increase followed a larger gain in May and took the headline index to a new COVID-19-era high, although it remained 14.5 points below its February 2020 level. The reading is consistent with our forecast for robust growth in consumer spending in the second quarter. (IHS Markit Economists David Deull and James Bohnaker)
- April's increase was entirely due to the index measuring views on the present situation, which rose 4.2 points to 97.2. The one-year expectations index was unchanged at 79.7.
- Consumer sentiment rose mainly among upper-income households in early April. Sentiment reported for households earning more than $75,000 a year rose 4.7 points to 92.4. Continued increases in equity markets, which in April have scored a run of record highs, likely contributed. Meanwhile, sentiment for households earning less than $75,000 a year edged down 0.2 point to 81.1.
- Stimulus checks authorized in the American Rescue Plan Act continue to be distributed, but the majority of the disbursements occurred in mid-March and likely contributed to that month's sizable gain.
- Buying conditions were mixed in April. The index of buying conditions for large household durable goods slipped 2 points to 126 but remained elevated, while that for vehicles rose 3 points to 117. The index for homes, however, fell 7 points to 120, an 11-month low as home affordability has fallen owing to both higher mortgage rates and rising home prices.
- US single-family permits jumped 4.6% (plus or minus 1.9%; statistically significant) in March; this followed a 9.8% February plunge that was weather-related. The South, which accounted for 57% of single-family permits last year, drove these numbers in both months, plunging 14.5% in February and rebounding 8.0% in March. (IHS Markit Economist Patrick Newport)
- Housing starts soared 19.4% to a 1.739 million rate (plus or minus 13.7%, statistically significant) in March—the highest since June 2006; single-family starts jumped 15.3% (plus or minus 17.4%, not statistically significant) to a 1.238 million rate, their highest since December 2006; multifamily starts climbed to a 501,000 rate, only the fifth time this century that they have exceeded the 500,000 threshold.
- The first-quarter numbers were eye-popping: quarterly permits jumped 10.0% to a 1.790 million rate as multifamily permits soared 25.9% to a 586,000 rate—their highest since 1986—and single-family permits edged up 3.6% to a 1.205 million rate. Quarterly starts reached levels last seen in the third quarter of 2006.
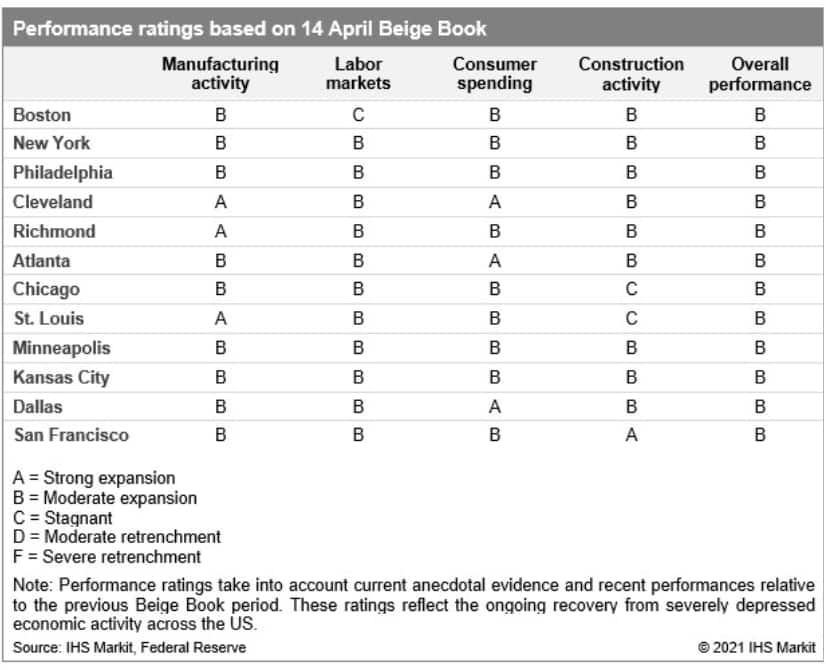
- The easing of more pandemic containment measures, an accelerating vaccination campaign, and the arrival of stimulus money all supported a pickup in economic activity across the country from late February to early April according to the US Federal Reserve's latest Beige Book report, containing anecdotal information from regional business contacts. (IHS Markit Economist James Kelly)
- The Midwest and South saw greater consumer spending at restaurants and hotels as leisure travel increased sharply.
- While retail sales supported the West, leisure and hospitality activity remains well below pre-pandemic levels.
- Manufacturing activity in Texas rebounded from the February winter storm and power outages as new orders and production moved higher throughout the country.
- Employment gains were strongest in the upper Midwest as construction, healthcare, and manufacturing workers were in high demand.
- The reopening of restaurants and leisure businesses in the South was hampered only be a lack of available staff. While home demand stayed elevated, high materials prices and supply-chain disruptions limited homebuilding growth, especially in the South.
- PPG Industries today reported first-quarter net income up 55% year-on-year (YOY), to $378 million, on net sales up 15%, to $3.9 billion. Adjusted earnings totaled $1.88/share, easily beating analysts' consensus estimate of $1.56/share, as reported by Refinitiv (New York, New York). Selling prices increased 2% YOY, and volumes were up 7%, "reflecting continued, broad, global economic recovery," PPG says. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- Performance coatings segment sales grew 16% YOY, to $2.3 billion, while segment operating income increased 40%, to $386 million. Volumes grew by 5% YOY, and selling prices were up 2%.
- Industrial coatings segment sales were up 14% YOY, to $1.6 billion, while segment operating income grew 35%, to $245 million. Volumes were up 10% YOY, and selling prices also ticked higher.
- Cruise Automation has raised USD2.75 billion in a new funding round, with the investors including Walmart. Reuters reports Cruise Automation as saying on the issue, "We are focused on our path to commercialization right now but the IPOs happening in the space right now are a great indication of the strength of the industry and the opportunity self-driving presents." Walmart CEO John Furner reportedly indicated in a blog post that the grocery chain's investment in Cruise Automation is meant to help support its efforts to create a home-delivery logistics network that is "fast, low-cost and scalable". (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- TuSimple is planning to test autonomous semi-trucks without human back-up drivers on public roads in Arizona (United States) in the fourth quarter of this year, reports the Wall Street Journal. The company will conduct a "driver-out" pilot program without a human behind the wheel on an approximately 100-mile route between Tucson and Phoenix. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- JPMorgan Chase, the largest bank in the US, said on 15 April it plans to invest more than $2.5 trillion over 10 years to advance climate action and sustainable development, joining other major US investment houses such as Bank of America and Morgan Stanley in making trillions of dollars of pledges. Also, in the last few weeks BlackRock, the world's largest asset manager, announced a series of investment funds to expand its cleantech activity. IHS Markit expects global capital spending in the renewable power sector in 2021 will rise 8.5% year on year to $255 billion, basically a bounce back year after the COVID-19 pandemic. But spending will increase. IHS Markit expects $1.3 trillion of renewables capital investment from 2021 through 2025. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Kevin Adler and OPIS' Abdul Latheef and Jeremy Rakes)
- Peru's economic activity fell by 2.1% in seasonally adjusted monthly terms in February, according to Peru's National Institute of Statistics and Information (Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática: INEI). This marks the first monthly decline since April 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Jeremy Smith)
- A renewed surge in COVID-19 cases prompted a fresh lockdown throughout February, affecting most of the country. The transportation, hospitality, and restaurant sectors took the brunt of the impact as these activities were the most heavily restricted.
- Although the extent of the setback cannot be fully assessed until Peru's quarterly national accounts are released next month, it is evident that the economic impact caused by the February lockdown was not nearly as severe as that of a year ago. Monthly output fell by 40.5% y/y in April 2020 compared with a 4.2% y/y decline in February 2021.
- Peru has banned the registration, import, national formulation, distribution and commercialization of the acaricide, dicofol, the Ministry of Agrarian Development reports. The national agricultural health service, the Senasa, issued the ban through resolution 0021-2021-MIDAGRI-SENASA-DIAIA in the official gazette on April 15th. The organochlorine acaricide is classified as a persistent organic pollutant (POP) by the Stockholm Convention and is related to other banned active ingredients, the Ministry notes. It is highly persistent in the environment, moderately toxic to mammals, and extremely toxic to fish, crustaceans, mollusks and algae. The substance is bioaccumulative, accumulating in the fatty tissues of humans and can travel long distances through air and water. (IHS Markit Crop Science's Robert Birkett)
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Major European equity indices closed higher; Germany +1.3%, Italy/France +0.9%, and UK/Spain +0.5%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed lower; France/Germany/UK +3bps and Italy/Spain +2bps.
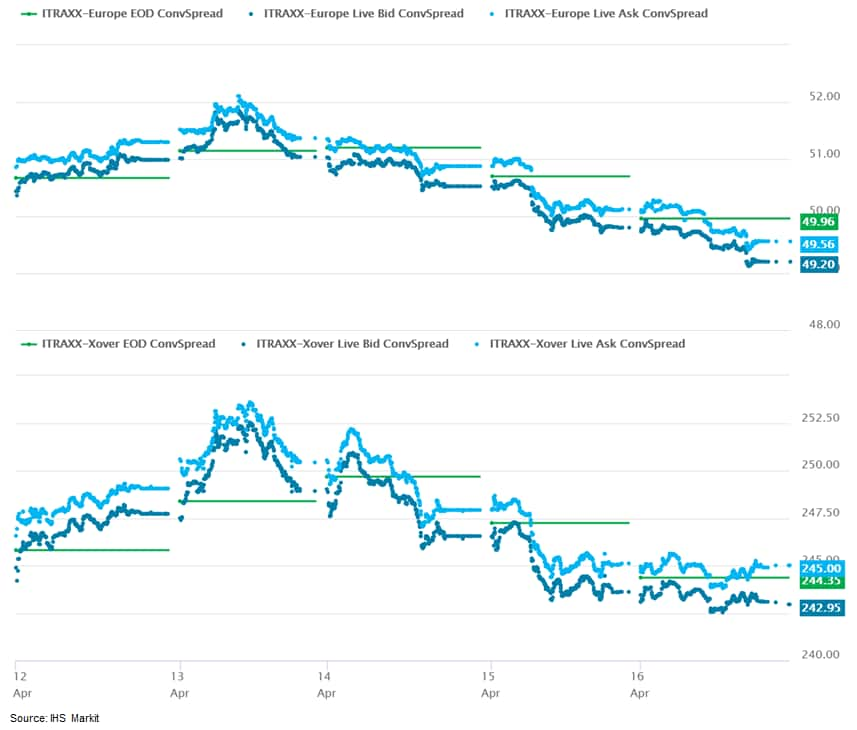
- iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/49bps and iTraxx-Xover flat/244bps, which is -1bp and -2bps week-over-week, respectively.
- Honda has announced that it is offering owners of its e battery electric vehicle (BEV) its own domestic smart charging service. According to a statement, 'e:PROGRESS' offers customers a "connected charger, advanced intelligent software and UK-first dynamic energy tariff to charge their car at the most cost-effective times". This includes the Honda Power Charger S+ (4G), which connects remotely to e:PROGRESS to schedule access to low-cost electricity. It also uses software developed by smart charging and aggregation specialist, Moixa, and "can set a charging schedule to ensure the car is always adequately charged when it's needed based on the requirements of the owner, while optimizing the use of low-price clean energy". (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Eurozone industrial production declined by 1.0% month on month (m/m) in February, broadly in line with the market consensus expectation (of -1.1% m/m, according to Reuters). (IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- Weakness was broad-based across all types of production in February, with capital goods (-1.9%) recording the biggest m/m decline.
- Despite February's fall, the second in three months, the level of overall eurozone industrial production is just 1.3% below where it was in February 2020 prior to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) shock, with strength in various leading indicators pointing to an imminent "crossover" above the pre-pandemic level.
- Eurozone export values, meanwhile, fell by 2.5% m/m in February, the second successive decline following eight straight increases from May 2020. With import values jumping by 3.4% m/m, the eurozone trade surplus tanked in February, dropping to EUR18.4 billion (USD22 billion) from EUR28.7 billion in the prior month, the lowest surplus since June 2020.
- With industrial production on track for only a modest gain in the first quarter of 2021, and trade figures looking less supportive than in prior quarters, eurozone GDP is likely to have contracted more markedly than in the fourth quarter of 2020 (-0.7% q/q) given the expected weakness in consumer expenditure due to COVID-19 virus-containment measures.
- On 14 April, the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) published two interlinked reports on climate change. (IHS Markit Economist Brian Lawson)
- The first flagged that climate risks comprise both acute and chronic events, and face "increasing uncertainty", with regulators needing "plausible ranges of scenarios" and more granular data to assess risks.
- It concludes that existing risk frameworks, based on credit, market, liquidity, operational, and reputational risks, can be applied successfully to climate risk, but favours a comprehensive mapping of gaps in existing coverage, which would require research by a broad community.
- The second report suggests that climate risk requires detailed granular and forward-looking analysis of both physical and transition-related risks.
- BIS concludes that banks and regulatory bodies are at "an early stage" of establishing "robustly quantifiable" frameworks to assess climate risks, with banks suffering "limitations" in in-house risk-measurement capacity, evidenced by widespread recourse to external sources.
- Automotive component supplier Continental has partnered with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to develop a platform for automotive software, according to a company statement. The platform, named Continental Automotive Edge (CAEdge), connects vehicles to the cloud and features a virtual workbench offering numerous options to "develop, supply and maintain software-intensive system functions". As part of the companies' first project, camera and radar data from a vehicle fleet will be imported into the CAEdge platform and used to create a virtual simulated environment to test highly automated vehicles. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Total Produce has agreed a USD500 million five-year credit agreement with the New York branch of Rabobank in addition to a USD940 million seven-year loan facility with Bank of America. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Hope Lee)
- The borrowing is set to bolster its balance and give it greater buying power once the deal is completed.
- The Bank of America deal was made on condition that the proposed merger between Total Produce and Dole and its anticipated listing on the New York Stock Exchange as Dole plc, proceed as planned.
- The loans will be used "to refinance the existing Total Produce and Dole debt facilities, with the exception of the Dole vessel financing and certain other group bilateral facilities", Total Produce said.
- On 15 April the US Department of Treasury revealed a series of punitive measures against Russia, which among other things, further tightened sanctions on Russian government debt sale. (IHS Markit Economist Lilit Gevorgyan)
- The new executive order signed by US President Joe Biden bans from 14 June the participation of US financial institutions in the primary market for the ruble-denominated Russian sovereign debt (OFZ, Obligatsyi Federalnovo Zaima), issued by the Bank of Russia, the National Wealth Fund and the country's Finance Ministry.
- This measure comes in addition to the ban, first introduced in 2019, on the acquisition of Russian non-ruble sovereign bonds on the primary market.
- As of end-February, 22% of the OFZ market was held by foreign investors, down from 31.8% in June 2020, with the total market of around USD40.7 billion. The US investors make up nearly half of the foreign-held OFZs.
- In a statement the US Department of the Treasury explained that the sanctions were in response to "malign activity" by the Russian authorities, including cyber-hacking, election interference, use of chemical weapons. It has blacklisted 30 entities, and 10 Russian officials will be expelled from the US.
- The RUB/USD pair was trading at 72.9 on 17 March, but depreciated to 77.4 on 12 April, in reaction to a sharp rise in geopolitical tensions.
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey (TCMB) held its main policy rate - the one-week repo rate - unchanged at its scheduled, 15 April meeting. The rate remained at 19.0%, to which it was raised at the previous policy setting meeting in March. The 200-basis-point rise in March triggered President Recep Tayyip Erdoǧan to replace the TCMB governor the following day. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew Birch)
- The TCMB did, however, remove a pledge to tighten monetary policy further in its press release alongside the MPC meeting. Instead, the Bank pledged to keep the main policy simply above the prevailing inflation rate and to use all of its policy tools to achieve the Bank's medium-term inflation target of 5%.
- The immediate reaction from the lira was mixed. Rallying in the hours before the decision, the lira firmed further immediately after the announcement before sliding through mid-afternoon, finally rallying once again in late trading, ending the day at TRY8.064/USD1, 0.2% stronger from the previous day and up by 1.0% from two days prior.
- Nigeria's headline inflation rate accelerated to 18.2% year on year (y/y) in March, from 17.3% y/y in February and 12.3% y/y in the same month last year. (IHS Markit Economist Thea Fourie)
- Headline inflation averaged 17.3% y/y in the first quarter of 2021, from an average of 12.2% in the same period of last year.
- Food inflation was the biggest contributor to the annual increase in Nigeria's consumer basket, rising to 22.9% in March, from 21.8% in February. Food categories that showed the strongest annual gains included bread and cereals, potatoes, yam and other tubers, meat, vegetables, fish, oils and fats, and fruits.
- Transport inflation rose to 14.7% y/y in March, from 14.1% y/y in the previous month.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed higher across the region; Mainland China +0.8%, Hong Kong +0.6%, and Japan/South Korea/Australia/India +0.1%.
- China's real GDP grew 18.3% year on year (y/y) in the first quarter of 2021 on the low comparison base in the same period last year amid the COVID-19 outbreak. The economy continued to recover as the first-quarter GDP rose 10.3% compared with the same period in 2019 and the quarter-on-quarter GDP grew 0.6% from the fourth quarter in 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- By sector, industrial and construction continued to lead the headline recovery with its value-added expanded by 24.2% y/y, while services GDP grew by 15.6% y/y.
- However, the recovery momentum continued to slow as the 2020-21 first quarter average first quarter GDP growth was down to 5% from 6.5% y/y in the previous quarter. The moderation was across sub-sectors as the growth of industrial and construction sector declined from 6.8% to 6.0% and that in the service sector was down from 6.7% to 4.7%.
- The industrial value-added growth declined from 35.1% y/y in Jan-Feb to 14.1% in March, and the 2020-21 average growth moderated from 8.1% to 6.8% during the same period. Additionally, the month-on-month growth at 0.6% notably declined from a month ago.
- Fixed-asset investment (FAI) increased 25.6% y/y in the first quarter, compared with 35% y/y in the first two months. The 2020-21 average growth at 2.9% was 1.2 percentage points higher than that of January-February.
- The 2020-21 average first quarter real estate investment increased 7.6% from 2019, unchanged from the reading a month ago. Floor space of new starts reported slower contraction and under construction floor space remained stable.
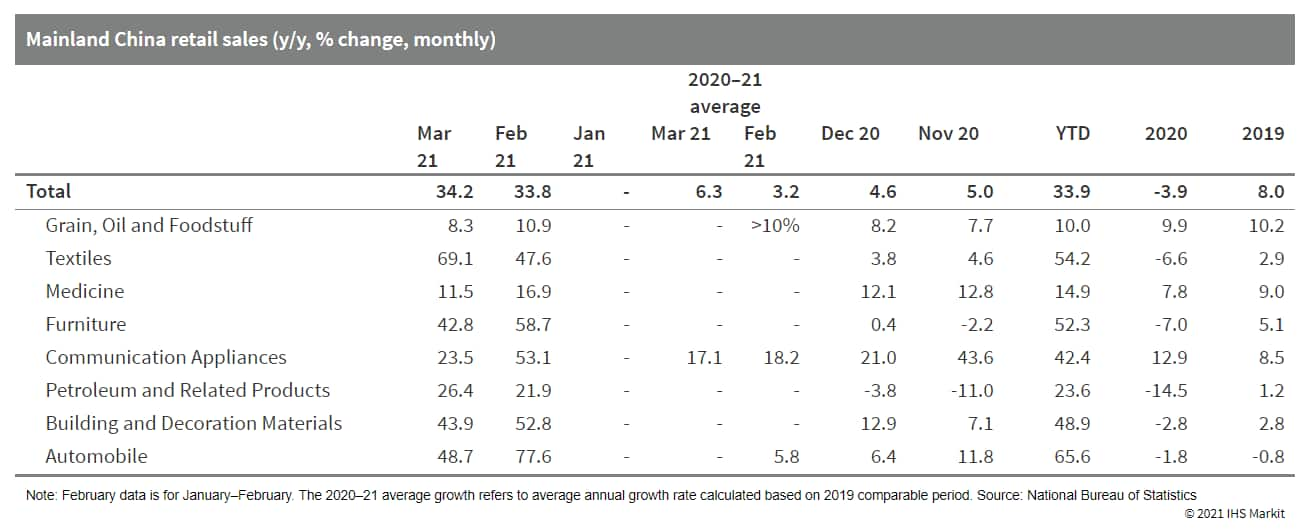
- Nominal retail sales increased 34.2% y/y in March, up from 33.8% y/y through February with the acceleration of vaccination process and eased controls on travel supported. The 2020-21 average growth accelerated from 3.2% in January-February to 6.3%, while it remained below an 8.7% y/y growth in March 2019. The first quarter retail sales increased 1.9% quarter on quarter, much higher than that of the q/q GDP growth.
- China's first autonomous bus line has started commercial operations in the Yongchuan district of Chongqing. Baidu has deployed three Robobuses, which are capable of Level 4 autonomous operations, for city trips on the 10-kilometer (km) two-way bus route. The Robobus is 5.9 meters long and can carry 19 passengers at a speed of 40 to 60 km per hour. The bus has a safety monitor on board for use in case of an emergency, but most of the driving operations are performed by the artificial intelligence system, reports China Daily. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Honda has partnered with AutoX to research autonomous vehicles (AVs) by testing on public roads in China, according to a company statement. AutoX's AV technology will be integrated with Honda's Accord and Inspire vehicles. Through these tests, Honda says it "aims to deepen understanding of China's traffic environment, establish the public acceptance and safety of autonomous driving technology, as well as to seek new autonomous driving technology solutions". (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- DEME Offshore and Japanese marine contractor Penta-Ocean Construction have agreed to establish a joint venture (JV) to focus on the construction of offshore wind farms in Japan. The new JV brings together DEME Offshore's marine engineering knowledge and decades of experience in the renewables sector, with the highly specialized marine construction technology of Penta-Ocean. The partners are currently in the process of establishing the JV company, whereby 51% of the shares will be owned by Penta-Ocean and 49% by DEME Offshore. The two companies have agreed to establish the joint venture company by June this year. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Genevieve Wheeler Melvin)
- The South Korean government plans to increase investment in research and development (R&D) on key technologies for next-generation vehicles, reports the Yonhap News Agency. The government will spend KRW367.9 billion (USD329.3 million) in supporting R&D for next-generation vehicles this year, up 37% from last year. It will focus on supporting R&D of six key technologies crucial to developing next-generation vehicles, including batteries, hydrogen fuel cells, self-driving communications, and automotive chips. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Tesla in a regulatory filing said that it experienced a 295% year-on-year (y/y) jump in its sales revenue in the South Korean market in 2020 to KRW716.2 billion (USD641 million), reports the Yonhap News Agency. Its annual operating profit increased by 429% y/y to KRW10.7 billion, and its net income surged by 507.7% y/y to KRW7.9 billion. The automaker sold 11,826 vehicles in the country last year, up from just 2,430 units sold in 2019, highlights the report, citing data released by the Seoul-based Carisyou Data Lab. The automaker did not release its sales data. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Hyundai Motor Group will collaborate with SK Innovation to develop batteries for its upcoming hybrid vehicles, reports the Maeil Business Newspaper. The two parties have agreed to develop a pouch-type battery optimised for vehicle electrification, which will be equipped on hybrid vehicles to be released by Hyundai and its affiliate Kia from 2024. To develop a safe and cost-efficient battery system for specific hybrid vehicles, the automotive group and SK Innovation will collaborate throughout the entire process, from design to product assessment and performance improvement. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
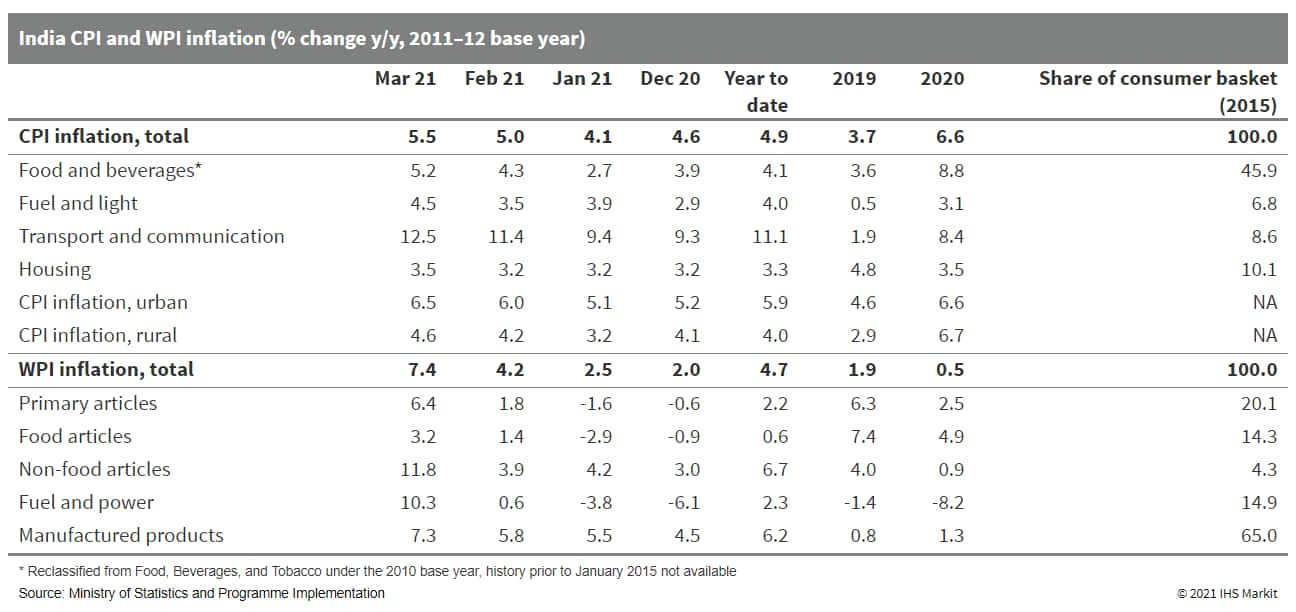
- Both retail and wholesale inflation accelerated sharply in India in March, reaching 5.5% year on year (y/y) and 7.4% y/y, respectively, while industrial output contracted 3.6% y/y in February. (IHS Markit Economist Hanna Luchnikava-Schorsch)
- India's consumer price index (CPI) inflation accelerated to 5.5% y/y in March, up from 5.0% in February, official government data showed.
- Food prices, the key driver of headline CPI inflation, continued to rise despite ample stocks of cereal and produce, with inflation for meat, eggs, dairy products, as well as oils and fats and non-alcoholic beverages all experiencing double-digit rates.
- Rising commodity prices also continued to feed into retail inflation, with the transport and communication group rising by 12.5% y/y and the fuel and light category up by 4.5% y/y.
- An acceleration in prices was evident in both rural and urban areas, with the highest inflation rate reported in the state of Andhra Pradesh (8.9% y/y), and the lowest in Rajasthan (3.0% y/y).
- Wholesale price index (WPI) inflation accelerated even faster and was up by 7.4% y/y in March - the highest monthly rate of inflation in more than eight years. Sharp increases in prices of crude oil, petroleum products, and basic metals, as well as low base affects from the previous year, were behind the rise.
- On a use-based approach, production of consumer durable goods recovered to 6.3% y/y after a brief slippage in January. However, that was the only category that showed expansion, with consumer non-durable goods output - as well as production of capital, infrastructure, and primary and intermediate goods - falling in annual terms.
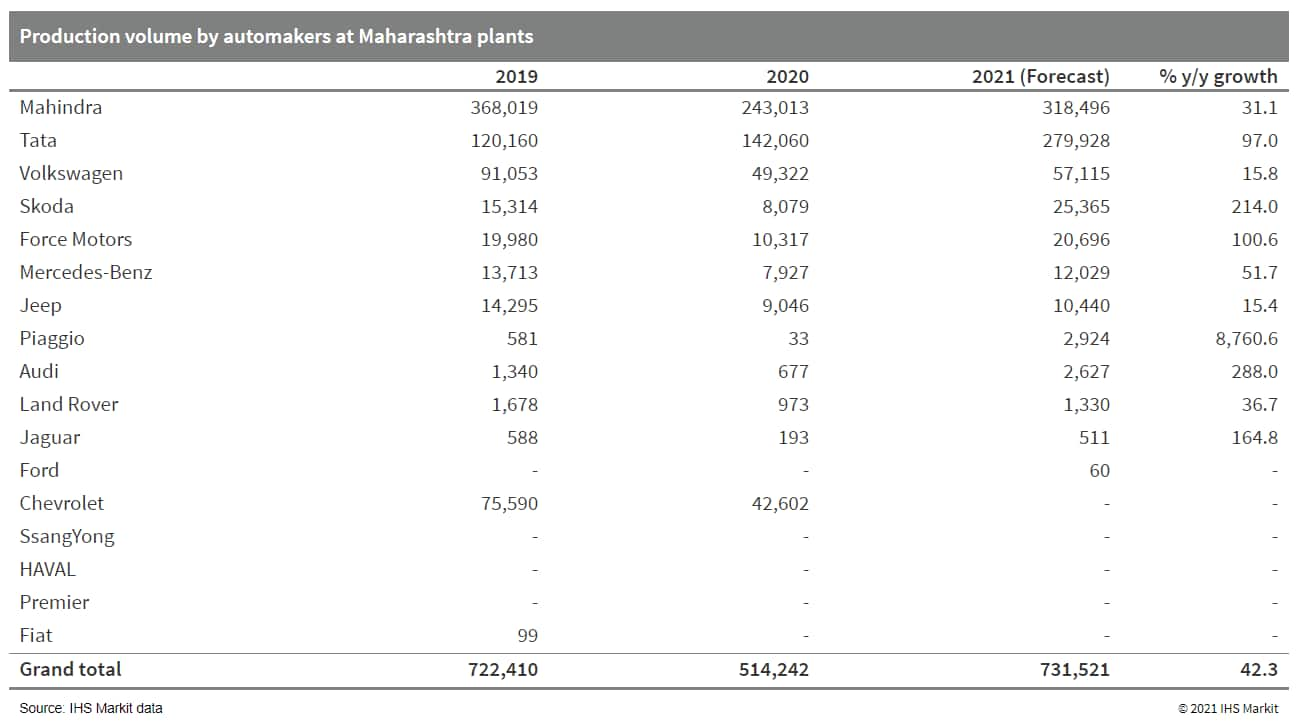
- IHS Markit has assessed the initial impact of the recently announced new set of restrictions to curb the spread of the COVID-19 virus in the Indian state of Maharashtra. There are a total of 8 manufacturers with 11 plants operating in the state, which are expected to be affected by the new restrictions. According to our initial assessment, we expect a daily production decline of 30-40% at the plants in the state. Maharashtra's daily light-vehicle production volumes total approximately 2,200 units per day, and if the restrictions are extended, the potential risk of production losses is estimated at 20,000-25,000 per month. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
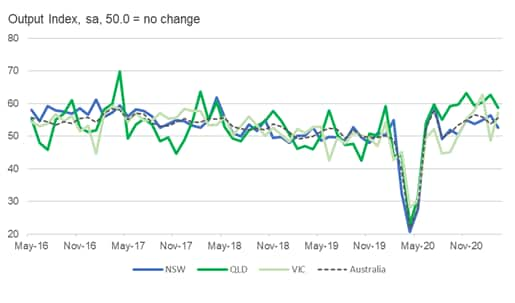
- In March 2020, Australia joined much of the world in enacting strict lockdown rules in order to contain the spread of COVID-19, resulting in an unprecedented economic downturn, as reflected in a sharp fall in the Australia PMI's Composite Output Index. (IHS Markit Economist David Owen)
- We monitored PMI data for three states and Queensland has seen a consistently stronger rate of output growth since the second half of 2020. The Composite PMI Output Index has averaged 59.8 from July 2020 to March 2021, compared to averages of just 53.7 in New South Wales and 52.7 in Victoria.
- Manufacturing and services data show that Queensland has excelled in both of these broad sectors during this period, although there was a greater outperformance among service providers. This could largely by explained by the number of COVID-19 cases by region: Queensland has only seen roughly 1,500 cases to date, compared to 20,000 in Victoria and 5,000 in New South Wales
- By contrast, Victoria saw a second wave of COVID-19 cases during the third quarter of 2020, leading to further social distancing restrictions and the closure of its border with New South Wales. Output fell sharply, albeit not as steeply as seen in the previous quarter.
- New South Wales has seen a more consistent recovery in output than in Victoria, with growth running close to the nationwide trend since the middle of 2020, and both the manufacturing and service sectors recording a stronger performance. In comparison to Queensland, however, average services growth was notably softer, with restrictions on hospitality capacity and inter-state travel noted as contributing factors.
Posted 16 April 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.








