Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Culture & Engagement
S&P Global — 23 Jun, 2023 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
A Steady Tailwind for Wind Power
Wind power skeptics traditionally point out that it only works when the wind is blowing. Investment in wind power has followed a similar dynamic. At times, strong gusts of capital have led to onshore and offshore wind farm construction. At other times, the industry appears caught in the funding doldrums, with investors doubting this most intermittent of power sources. Partly due to the Inflation Reduction Act in the US and partly due to energy security needs in Europe, wind power has been enjoying a moment. But markets, like the wind, can be fickle.
Europe leads the US in installed wind capacity, despite favorable environmental and political conditions in the US. The Biden administration implemented a countrywide goal of 30 GW of wind power by 2030 and put substantial funds behind wind power with the Inflation Reduction Act. Coastal states in the Northeast and mid-Atlantic have almost ideal conditions for offshore wind, with average 100-meter wind speeds above 8 meters per second. Forty projects are in development along US coastlines. Beyond the Atlantic coast, there are fixed-bottom wind projects in the Pacific Ocean, Gulf of Mexico and Lake Erie.
One indicator of the strength of offshore wind is the attention it is getting from offshore supply vessel companies. This industry, which traditionally services offshore oil and gas rigs, has begun to focus on the growth opportunity of wind power.
“Headwinds remain for offshore development in the US, from inflation to supply chain constraints and ongoing resistance from competing maritime industries and local residents,” Adam Wilson of S&P Global Market Intelligence wrote.
“Federal support has been given a boost on account of increased tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, and state legislations on all coasts are increasingly dedicated to getting offshore wind up and running. These factors, combined with favorable geographic forces in the form of strong winds, might finally be turning the corner, with two major offshore projects under construction.”
While the opportunities along US coasts for wind power are significant, many of the owners of projects under development are European. Globally, investment in renewable energy capacity has increased. Wind represents an estimated 25% of renewable energy capacity. Australia leads investment in renewables with an estimated $13 billion, followed by Europe and North America.
The EU has focused on renewables in a bid for energy security that market observers consider a “paradigm shift” for European energy policy. However, a recent auction of offshore wind concessions in Germany received multiple zero bids. The growing cost of capital remains a challenge for the European energy transition.
Today is Friday, June 23, 2023, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
Written by Nathan Hunt.
EMEA Structured Finance Chart Book: June 2023
Investor-placed securitization issuance for May 2023 was €9.5 billion — more than double the volume in May 2022. This means that overall issuance for the first five months of the year — at €36 billion — was down 21% compared with 2022. By contrast, European benchmark covered bond issuance has continued to be robust, already exceeding €106 billion--up 25% on volumes recorded in the first five months of 2022.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on the global economy >
Most Large Asia-Pacific Banks Set For Lending Income Growth In 2023, 2024

Most of the Asia-Pacific's largest banks are poised for lending income growth in 2023 and 2024, as they continue to gain from a combination of higher interest rates and positive growth prospects. In a sample of the region's 21 largest banks by assets, 12 are expected to log year-over-year increases in net interest income (NII) — the difference between interest revenues and interest expenses — in 2023, according to analyst consensus estimates compiled by S&P Global Market Intelligence. Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), the world's largest bank by assets, is expected to report the highest NII, at $103.39 billion in 2023 compared to $103.25 billion in 2022.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on capital markets >
China's Lagging Industrial Activity Leads To Higher Gasoline, Gasoil Exports In May
China's oil product exports rose sharply in May with resumption in gasoil sales to Europe and several rare gasoline shipments made within the Asian market amid growing need for some destocking activity due to tepid industrial fuel demand at home, market participants said June 21-22. Chinese oil companies exported 598,000 mt, or around 4.49 million barrels, of gasoil in May, almost a fivefold jump from 122,000 mt in the same period a year earlier, while gasoline shipments rose 62% year on year and 65.4% on the month to 1.363 million mt (11.5 million barrels) last month, data from the General Administration of Customs showed on June 21.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on global trade >
New Zealand Carbon Price Falls To Near 2-Year Low On Policy Uncertainty
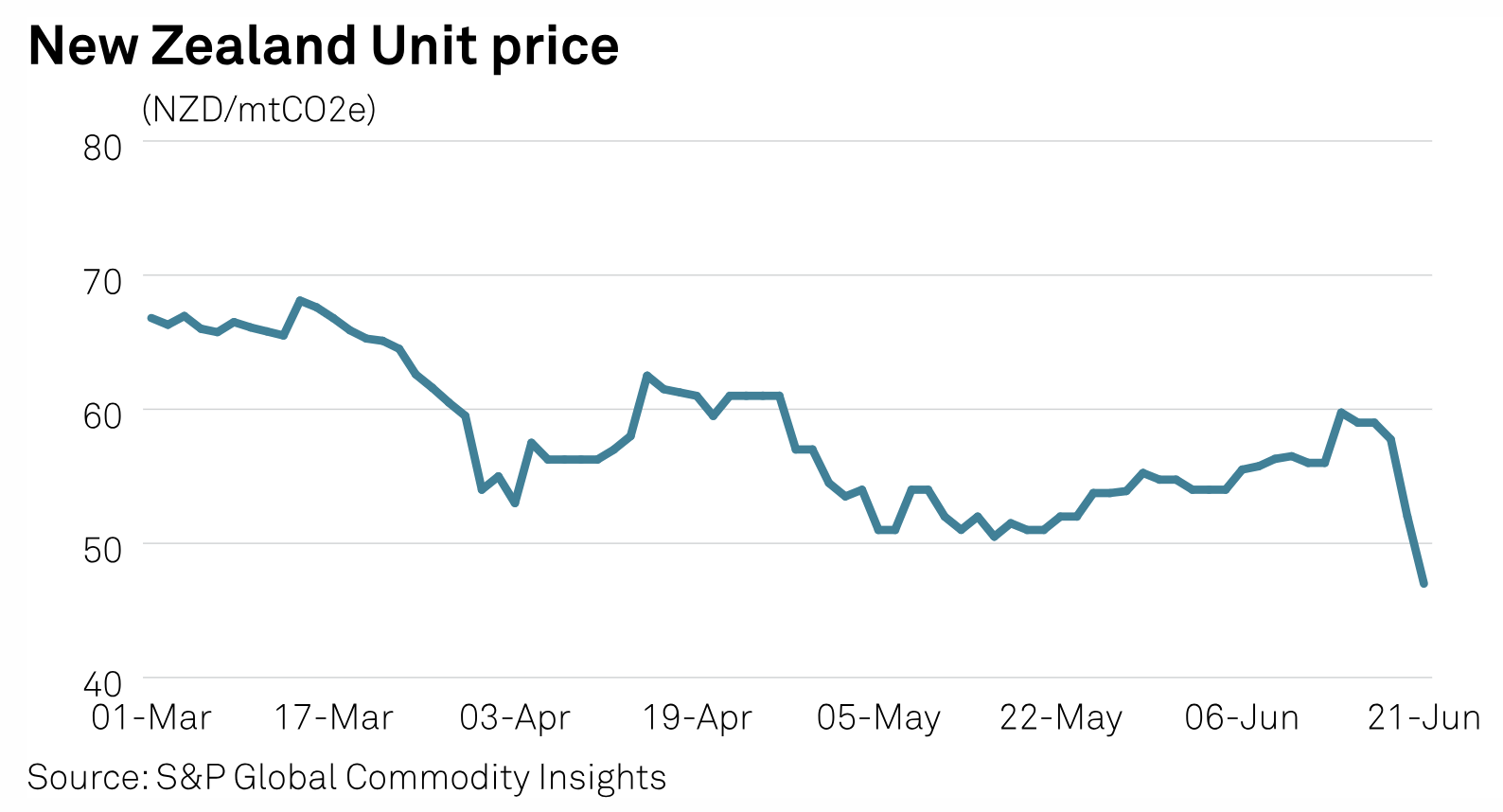
New Zealand's carbon price tumbled to a near two-year low on June 21 as initial bullishness after the failure of a carbon allowance auction was overtaken by uncertainty around government policy. Platts assessed the New Zealand Unit, or NZU price at NZ$47/mtCO2e ($29.17/mtCO2e) on June 21, S&P Global Commodity Insights data showed. This is the lowest price since the launch of the assessment on March 1, with the lowest assessed price earlier at NZ$50.50/mtCO2e on May 16.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on sustainability >
Listen: As Asian Crude Import Mix Evolves, How Relevant Are OPEC’s Cuts Still?
OPEC's kingpin Saudi Arabia has slashed its crude output by a further 1 million b/d in July, bringing the alliance's total cuts to 4.7 million b/d in the month, or about 5% of global capacity. But with Asia's crude import mix evolving since the Russia-Ukraine conflict, S&P Global Commodity Insights' Asia Oil Editor Neo Rong Wei spoke with Asia Oil News Managing Editor Philip Vahn and China Analyst Oceana Zhou about the impacts of these cuts, as well as factors affecting Asia's crude demand.
—Listen and subscribe to Platts Oil markets, a podcast from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Telcos Could Transform CpaaS Market With Significant Growth Forecast In Emerging Economies
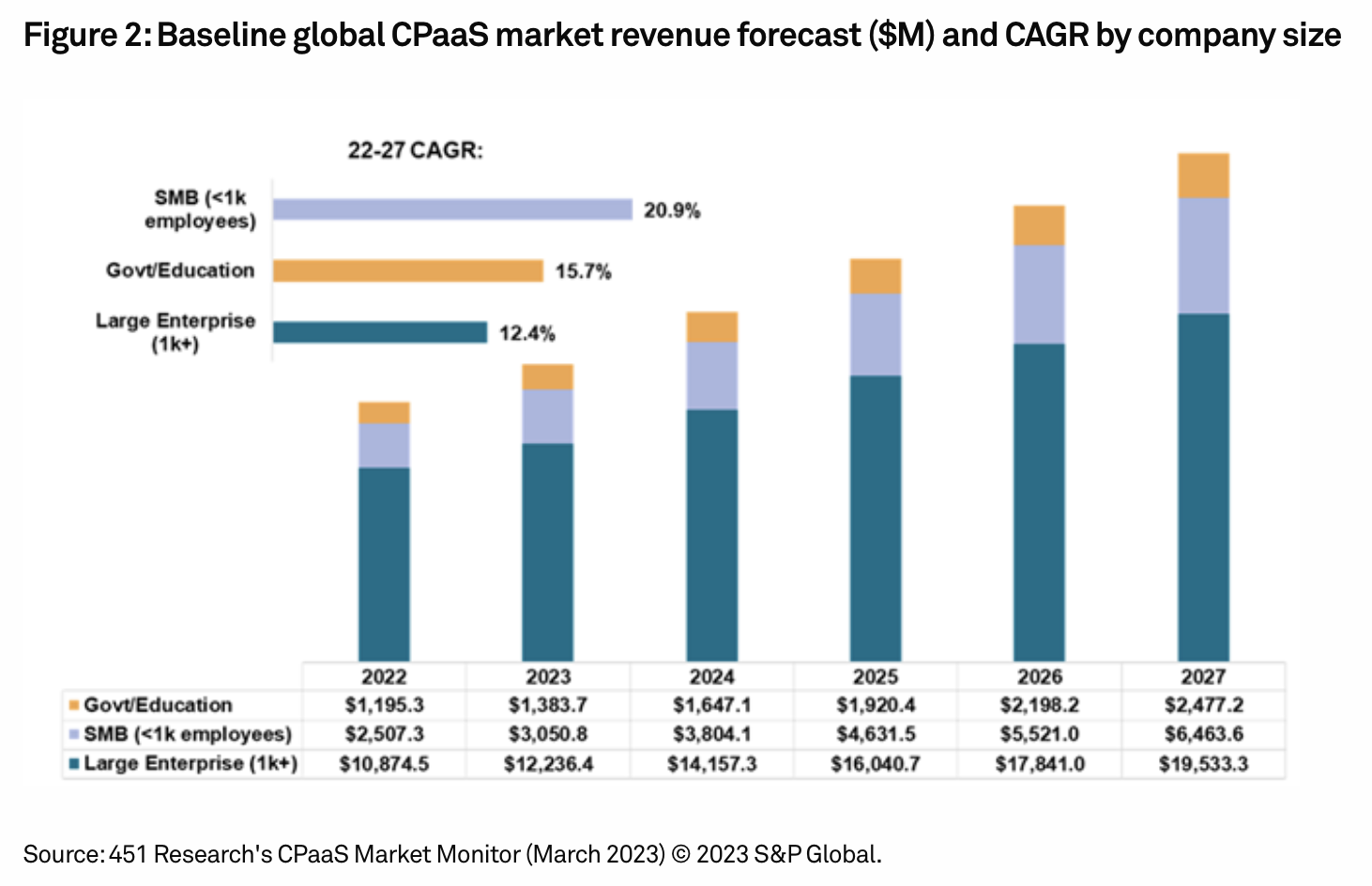
Like many technology segments, communications platform as a service (CPaaS) — comprising vendors that provide developers with embeddable communications capabilities for their applications — faces numerous challenges including labor shortages, rising interest rates and inflation. However, the recent 451 Research CPaaS Market Monitor data shows strong potential for continued growth and a significant opportunity for telcos in particular, with the CPaaS enablement segment that primarily services them outperforming the overall market. While already divergent, the growth trajectory for CPaaS and CPaaS-enablement vendors has the potential to widen further.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Content Type
Location
Segment
Language
