Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
ECONOMICS COMMENTARY — Jun 16, 2023

By Rajiv Biswas
Taiwan's export-driven economy has continued to be hit by slumping exports, which fell by 16.9% year-on-year (y/y) in the first five months of 2023. Reflecting the significant downturn in exports, Taiwan's GDP contracted by 3.0% y/y in the first quarter of 2023, following negative growth in the fourth quarter of 2022.
With two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth recorded, Taiwan's economy entered a technical recession in the first quarter of 2023. A key factor driving the export slowdown has been weak demand for Taiwan's electronics exports in key global markets, notably the US, EU and mainland China.
Taiwan's economy recorded two successive quarters of negative growth during the fourth quarter of 2022 and the first quarter of 2023. This follows a period of strong economic expansion in 2021 and 2022. In 2021, annual GDP rose by 6.5% y/y. This was the fastest pace of annual economic growth since 2010, boosted by export growth of 29% y/y, with exports of semiconductors up by 27% y/y.
This was followed by continued positive GDP growth at a pace of 2.5% in calendar 2022, helped by strong global demand for electronics exports during most of 2022. Taiwan's merchandise exports rose by 7.4% y/y in 2022, buoyed by strong expansion in exports of electronics components, which rose by 16.4% y/y, while semiconductors exports rose by 18.4% y/y.
However, Taiwan's electronics sector exports, which are a key export, have weakened significantly during the second half of 2022 and early 2023, due to weak electronics demand in the US, EU and mainland China. The downturn in Taiwan's exports has been a key factor contributing to the economic slowdown.
Total merchandise exports fell significantly in the fourth quarter of 2022, contracting by 8.6% y/y. Taiwan's exports have remained weak during the first five months of 2023, with merchandise exports in May 2023 contracting by 14.1% y/y. Exports to mainland China and Hong Kong SAR declined by 19.4% y/y in May. Mainland China is Taiwan's largest export market, accounting for 28% of Taiwan's total exports, while Hong Kong SAR accounts for a further 14% of Taiwan's total exports.
Taiwan's total exports to the US showed a modest decline in May, down by 3.5% y/y, with recent export data showing a gradual improvement in the value of exports to the US over the past three months. Taiwan's exports of semiconductors to the US rose by 9% y/y in May, while Taiwan's exports of semiconductors manufacturing equipment to the US rose by 59% y/y.
Taiwan's manufacturing sector business conditions have remained weak in mid-2023. Industrial production fell by 22.9% y/y in April, with manufacturing output down by 23.5% y/y.
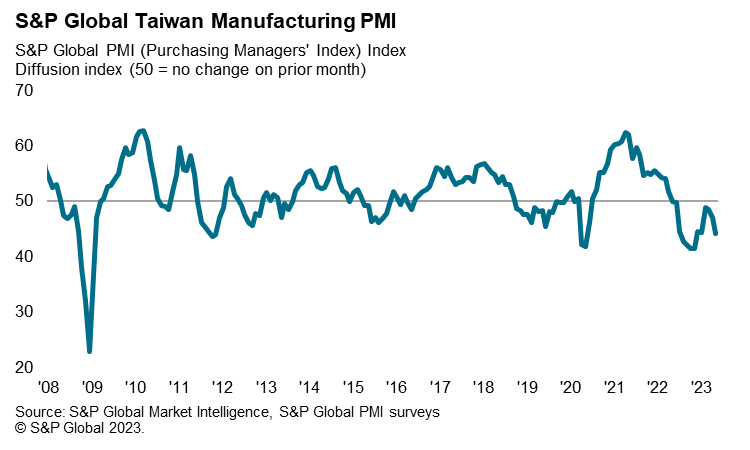
Business conditions across Taiwan's manufacturing sector deteriorated at a faster rate in May, according to the latest S&P Global PMI data. The S&P Global Taiwan Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) declined from 47.1 in April to 44.3 in May, to signal a sharp deterioration in business conditions midway through the second quarter.
Companies signalled the steepest reductions in output and total new business since the start of 2023 amid reports of weaker customer demand. Consequently, firms cut back on their buying activity and inventories, and trimmed their staffing levels at the quickest rate in over three years.
Total new business likewise fell at the sharpest rate since the start of 2023, with firms citing lower intakes of new work across both domestic and international client bases. Concurrently, the downturn in new export business gathered pace, with companies often citing reduced sales across key export markets such as mainland China, Europe and the US.
The improved availability of inputs and muted demand environment added downward pressure on purchasing costs. Notably, average input prices fell for the first time in six months in May. Cost savings were often passed on to clients, as firms cut their selling prices at a solid pace as part of efforts to stimulate sales.
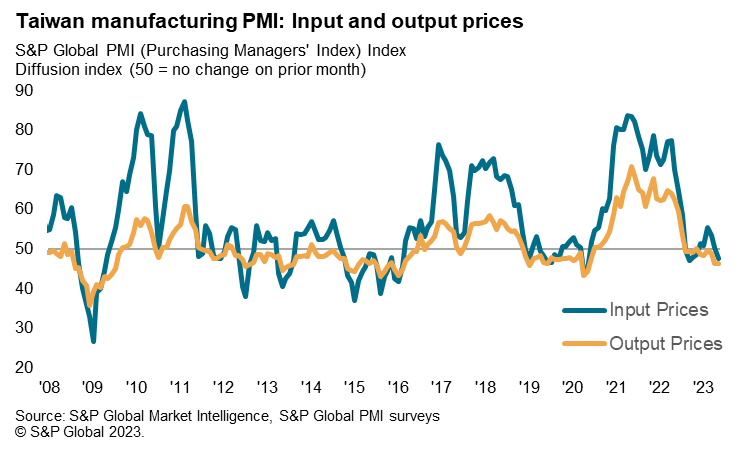
Taiwan's CPI inflation rate moderated to 2.0% y/y in May 2023, while core CPI excluding energy and food rose by 2.6% y/y, indicating retail inflationary pressures remain contained. Although inflation has been moderating in recent months, Taiwan's central bank raised its policy rate by 12.5% on 23 March 2023 in order to limit potential further inflation pressures, after having acted pre-emptively during 2022 with a series of modest tightening steps to contain inflation pressures.
The March 2022 tightening step of 25 basis points (bps) had been the first rate hike since June 2011, with the previous most recent change to policy rates having been a rate cut in March 2020 in response to the global COVID-19 pandemic. This was followed by a 12.5 bps increase in June 2022, a 12.5 bps hike in September 2022 and another 12.5 bps in December 2022.
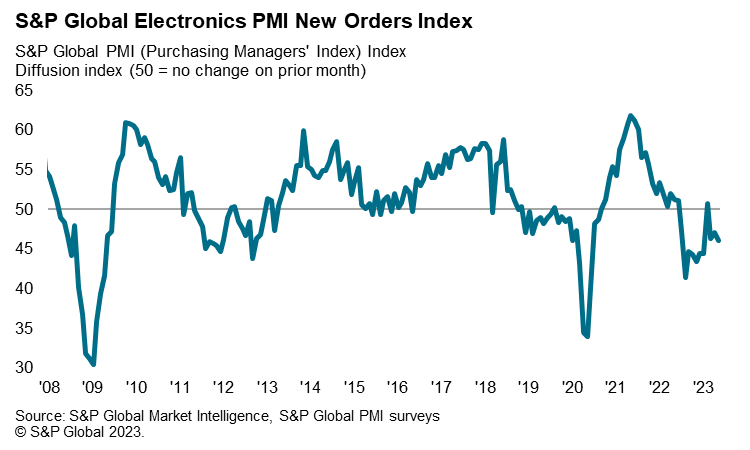
The near-term outlook for Taiwan's electronics sector remains weak, based on the latest S&P Global Electronics PMI survey results. The headline seasonally adjusted S&P Global Electronics PMI fell to 47.9 in May, down from 48.2 in April, to signal a third consecutive deterioration in operating conditions across the global electronics manufacturing sector. The latest reduction was moderate but the sharpest seen since June 2020, underpinned by a solid decline in new orders.
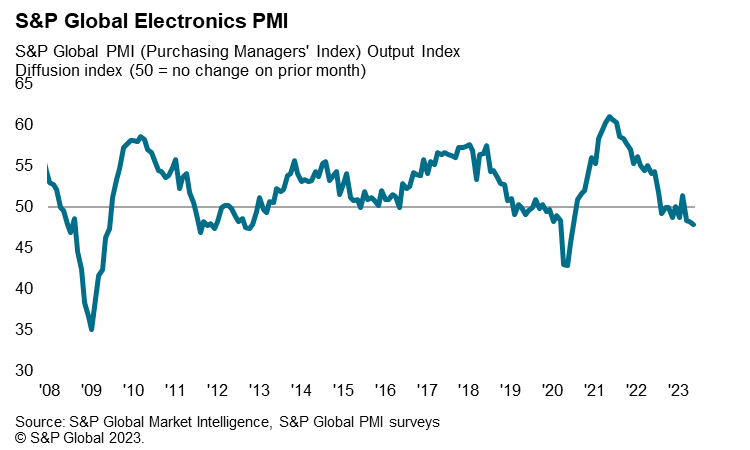
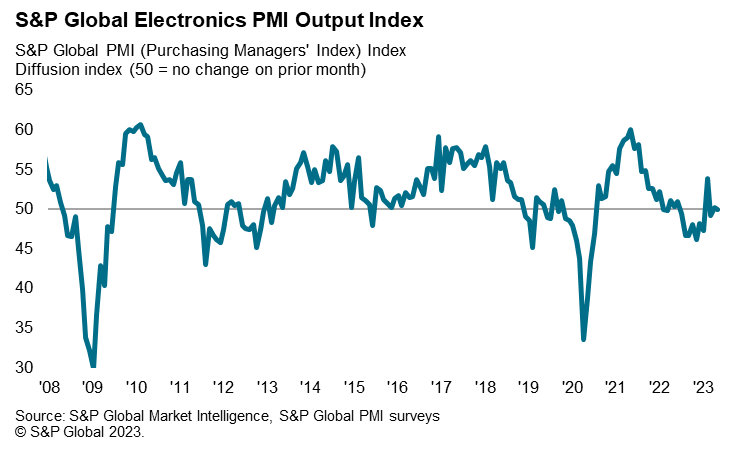
Global industry supply shortages for the semiconductors and electrical products industries have moderated in recent months, as supply-side bottlenecks have eased while weaker demand conditions have also contributed to improving supplier delivery times. Recent S&P Global Taiwan Manufacturing PMI Surveys for the first five months of 2023 indicated that the weaker demand environment supported a further improvement in supply chain performance.
The level of work outstanding at global electronics manufacturers declined for the eleventh month running during May, according to the S&P Global Electronics PMI survey. The rate of depletion was steep and unchanged from April, therefore being the joint-quickest for four months. Lower new orders and the easing of supply constraints allowed firms to work through unfinished business, according to panellists.
Global electrical and electronics industry supply shortages
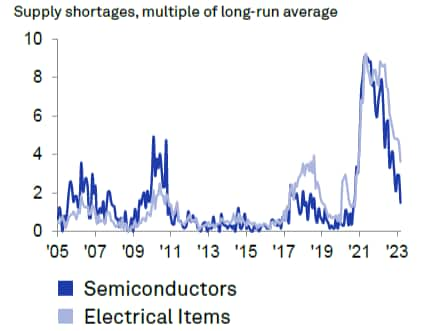
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence
After rapid economic growth in 2021 and continued firm expansion in 2022, Taiwan's economy is forecast to moderate in 2023, mainly due to the downturn in exports. This reflects continued weakness in key markets for Taiwan's electronics exports, notably the US, EU and mainland China. Taiwan's export orders fell by 25.7% y/y in March 2023, signalling continued near-term weakness for the manufacturing export sector.
Taiwan's medium-term outlook remains for sustained positive expansion at a moderate pace, underpinned by improving global electronics demand during 2024 and 2025. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the pace of digital transformation due to the global shift to working remotely, which has boosted demand for electronic devices such as computers, printers and mobile phones.
The medium-term outlook for electronics demand is underpinned by major technological developments, including 5G rollout over the next five years, which will drive demand for 5G mobile phones. Demand for industrial electronics is also expected to grow rapidly over the medium term, helped by Industry 4.0, as industrial automation and the Internet of Things boosts rapidly growth in demand for industrial electronics. Taiwan's electronics industry will continue to benefit from its leading role in production of advanced semiconductors as well as from its production of a wide range of other electronics products for consumer and industrial electronics.
Rajiv Biswas, Asia Pacific Chief Economist, S&P Global Market Intelligence
Rajiv.biswas@spglobal.com
© 2023, S&P Global Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.