Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
Financial and Market intelligence
Fundamental & Alternative Datasets
Government & Defense
Professional Services
Banking & Capital Markets
Economy & Finance
Energy Transition & Sustainability
Technology & Innovation
Podcasts & Newsletters
ECONOMICS COMMENTARY — May 07, 2021

By Rajiv Biswas
Taiwan recorded buoyant GDP growth of 8.2% year-on-year in the first quarter of 2021, helped by rapid growth of electronics exports to key markets, notably the US and China. Taiwan's economy has been resilient to the impact of the global Covid-19 pandemic, with continuing low levels of virus cases having helped to underpin domestic demand. Meanwhile rapid expansion in global electronics new orders since mid-2020 have helped to drive buoyant export growth, reflecting the dominant role of electronics products in Taiwan's manufacturing output and exports.
The combination of Taiwan's success in controlling domestic Covid-19 pandemic cases combined with rapid growth in exports resulted in Taiwan recording positive GDP growth of 3.1% in 2020. Helped by the strong export outlook for Taiwan's electronics sector, GDP growth rate is forecast to strengthen further to 4.6% in 2021, which would be the fastest pace of economic expansion since 2014.
Buoyant GDP growth in first quarter 2021
The Taiwan is in the unique position of having actually recorded a slight strengthening in GDP growth in 2020 compared with 2019, despite the severe global recession caused by the Covid-19 pandemic. Meanwhile almost every other economy in the world either plunged into recession or experienced a sharp growth slowdown in 2020, due to the economic shockwaves of the global pandemic.
Economic growth momentum improved further in the first quarter of 2021, with Taiwan's GDP growth up 8.2% year-on-year, boosted by base year effects from the pandemic-impacted first quarter of 2020. Economic momentum strengthened compared with the fourth quarter of 2020, when GDP rose by 5.1% y/y. Global electronics demand remains buoyant in key markets in the first half of 2021, with strong capital investment spending planned by Taiwan's semiconductor manufacturing firms.
Taiwan's exports rose by 27.1% y/y in March 2021, reflecting the strength of global electronics new orders. Taiwan's exports to mainland China and Hong Kong SAR rose by 35.5% y/y in March, while exports to the US were also buoyant, growing by 34.7% y/y.
Driven by strong global electronics orders as well as the rebound in global auto production, Taiwan's electronics and auto components manufacturing output has recorded rapid expansion. Taiwan's industrial production rose by 16.8% y/y in March, according to data from Taiwan's Ministry of Economic Affairs.
The IHS Markit Taiwan Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) climbed further in April, rising to 62.4, compared with 60.8 in March. This was the eighth successive month of expansion.
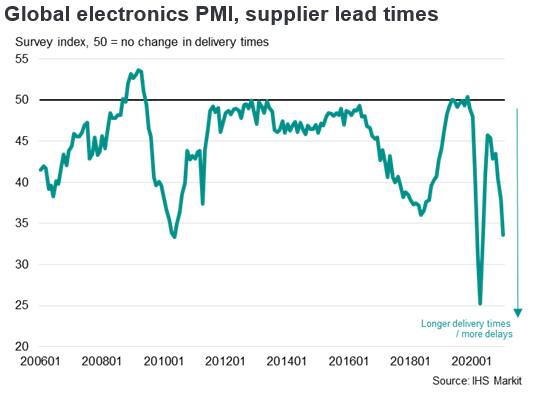
Supporting the improvement in the headline index was a sharper increase in overall new work. Total sales expanded at the steepest pace since March 2010, with companies commenting on robust demand both at home and abroad as market conditions continued to recover from Covid-19. Moreover, export orders expanded at the sharpest rate for over a decade.
However, material shortages and transportation delays drove a fresh record increase in suppliers' delivery times. This contributed to a rapid increase in average input costs, which in turn drove an unprecedented rise in prices charged.
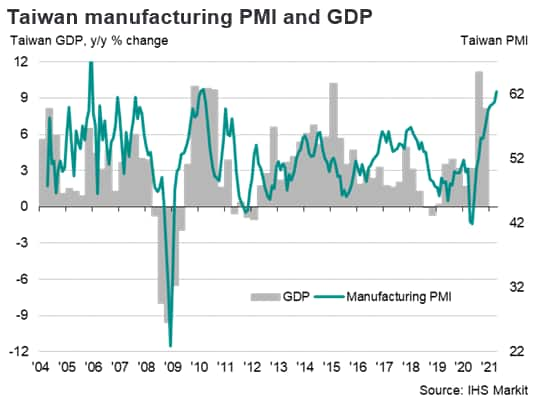
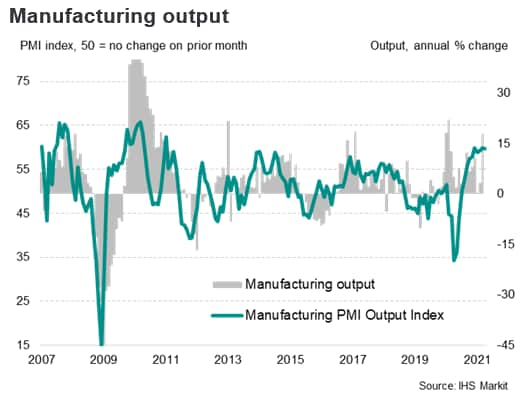
Global electronics sector boosts Taiwan's exports
The pandemic-driven surge in global electronics demand was a key factor underpinning Taiwan's strong economic performance in 2020, as the global shift to remote working and online shopping drove rapid growth in demand for computers, home electronics and smartphones. Despite the pandemic, which resulted in a sharp slump in world trade, Taiwan's exports actually rose by 4.9% y/y in calendar 2020, mainly due to strong exports of electronics, notably semiconductors. A key factor supporting buoyant electronics demand was strong exports to mainland China and Hong Kong SAR, which rose by 14.6% y/y in 2020, accounting for around 44% of Taiwan's total exports.
In the first half of 2020, Asian electronics production had suffered severe supply disruptions and slumping global demand due to the pandemic and lockdowns. However, the situation for Taiwan's electronics sector has now completely reversed, with the strong rebound in global electronics demand continuing in early 2021, this has created supply bottlenecks for Taiwan's electronics manufacturing firms, notably in the semiconductors industry, where Taiwan is a key global source of production. Global shortages of semiconductors having already resulted in disruptions to auto production for some major auto manufacturers during the first half of 2021.
Underscoring the strength of the recent electronics upturn, the headline IHS Markit Global Electronics PMI rose to 59.9 in March, up from 57.8 in February. The latest reading was the highest for 21 years, with new order growth accelerating sharply. The new orders index from the PMI survey rose from a low of 35.0 in May 2020 to a level of 59.7 in March 2021, its highest since November 2013. The health of all four monitored sub-sectors improved markedly in February, led by the communications category.
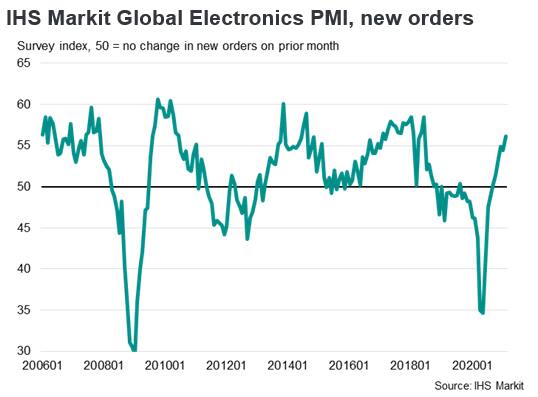
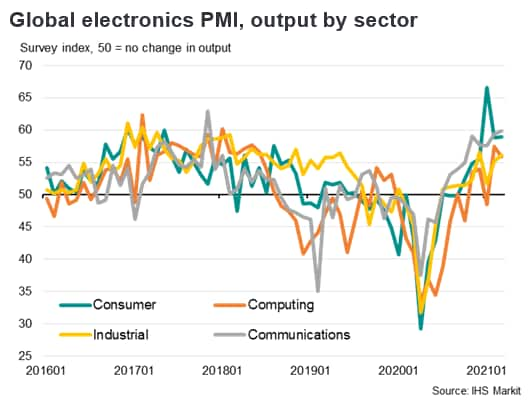
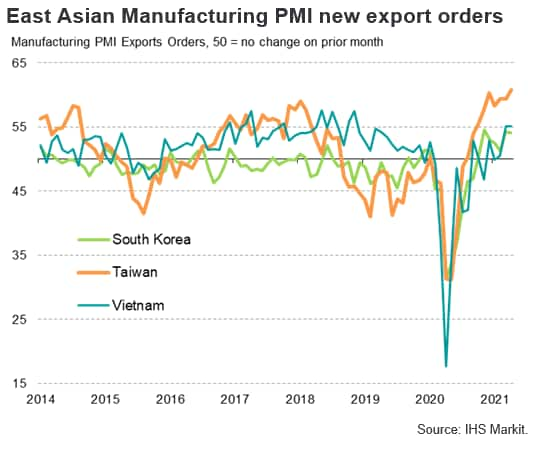
The new orders index from the PMI survey rose from a low of 35.0 in May 2020 to a level of 59.7 in March 2021, its highest since November 2013, as global electronics new orders have rebounded with the recovery of consumer demand in key markets.
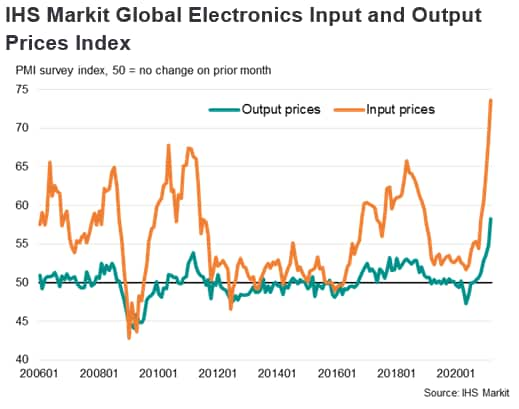
The near-term pricing outlook for the remainder of 2021, according to IHS Markit Pricing & Purchasing analysis for semiconductors and components generally, is that supply shortages are likely to continue to translate into price escalation. Printed circuit board assemblies are the most severely affected, but semiconductors, bare printed circuit boards, resistors, capacitors and connectors will all see price pressure. (See "Prices: Pricing Analysis - Semiconductors", by IHS Markit Pricing & Purchasing, 1st April 2021.)
In 2022, according to IHS Markit Pricing & Purchasing, moderating demand for electronic components and improving semiconductors production is expected to bring supply and demand closer to balance and lead to some price relief. Specific categories will show some resilience in pricing given the changing demand landscape. For example, the expansion of electronics in light vehicles will keep pressure on certain commodity electronic components.
Taiwan faces semiconductors shortages as demand soars
Taiwan's exports of electronics products have surged in the first quarter of 2021, rising by 24.5% y/y in March. This reflects strong global demand for computers, TVs and auto electronics, contributing to a severe shortage of semiconductor chips that has developed in recent months.
Chip stockpiling during 2020 due to US government sanctions on certain Chinese technology companies have also contributed to the shortages. Global auto manufacturers as well as smartphone producers are among the industry segments that have been impacted by these shortages. The US Department of Commerce added seven Chinese supercomputing firms to its entity list in early April 2021.
Global auto manufacturers as well as smartphone producers are among the industry segments that have been impacted by semiconductors shortages. According to IHS Markit Automotive research, vehicle manufacturers are finding increased disruption to the supply of systems using semiconductors in the first four months of 2021. Many automakers worldwide have reported disruptions to production due to shortages of semiconductors, including Ford, VW Group, GM, Honda and Mazda.
According to IHS Markit Automotive research, reports of disruption within the supply chain of semiconductors to the automotive sector began in late 2020 and have continued into the second quarter of 2021. (see IHS Markit Automotive, 3rd May 2021, "Semiconductor Supply Issue: Light Vehicle Production Tracker").
The extent of the shortages of critical electronics components has become so severe that high level consultations have been held with Taiwan involving key industry bodies as well as government officials from major industrial economies including the US and Germany. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) also joined the technology companies that participated in the White House Summit on 12th April on semiconductors shortages and supply chain vulnerabilities.
Global semiconductors shortages have also been impacted by temporary supply disruptions to semiconductors production in Texas due to power outages in February as a result of severe weather, as well production disruptions in Japan due to a fire in a Renesas Electronics semiconductors plant in mid-March.
The shortage of semiconductors has driven up capital expenditure plans, with Taiwan's TSMC, the world's largest chipmaker, having announced plans to increase capital spending on production and development of advanced chips to a range of USD 25 billion to USD 28 billion in 2021, a 60% increase on 2020. TSMC plans capital expenditure of USD 100 billion over the next three years to increase semiconductors capacity. A USD 12 billion investment in new production capacity in Arizona has been announced, with additional expansion in the US expected.
Taiwan's UMC, which also manufactures chips, in operating its semiconductors plants at full capacity, and plans to lift spending on new capital equipment by around 50% in 2021 in order to increase capacity.
A key risk to the near-term semiconductors production outlook in Taiwan is from the severe drought that is impacting on the economy. Drought conditions are estimated to be the worst for 56 years, and have resulted in water restrictions in some areas, including in a region that is a key hub for semiconductors manufacturing. Semiconductors plants have very high water consumption requirements, and although most plants have some water storage facilities, there is a risk of water supply shortages that could disrupt production if significant rainfall does not occur during the rainy season.
Taiwan economic outlook in 2021
Taiwan has been one of the world's most resilient economies during the pandemic-triggered recession of 2020. Economic indicators at the beginning for 2021 signal improving growth momentum for the Taiwanese economy over coming months, as the world economy and global trade rebounds during 2021. According to the latest IHS Markit survey of business conditions in Taiwan, the 12-month outlook for manufacturing production rose to its highest since April 2014 at the start of 2021, reflecting strengthening new orders. Taiwanese manufacturers were highly confident that output would rise over the next year. largely driven by expectations of a sustained and strong post-pandemic recovery both at home and abroad.
At the outset of 2021, global electronics demand has recovered significantly from the lows of the first half of 2020 when lockdowns disrupted production and consumer spending. Strong economic momentum in the US and China have been key drivers of rapid growth in Taiwan's exports in early 2021. With an improving global economic recovery expected during the course of 2021 as Covid-19 vaccines are progressively rolled out, global demand for electronics products is expected to be strong this year.
The impact of the pandemic has accelerated the pace of digital transformation due to the global shift to working remotely, which has boosted demand for electronic devices such as computers, printers and mobile phones. The easing of lockdowns in many countries has also triggered a rebound in consumer spending, helping to boost demand for a wide range of consumer electronics. Meanwhile auto demand has also shown a rebound after slumping during the first half of 2020, which is boosting demand for auto electronics.
The medium term economic outlook is also supportive for the electronics industry, with sustained strong world economic growth forecast over 2022-2024. The outlook for electronics demand is also supported by major technological developments, including 5G rollout over the next five years, which will drive demand for 5G mobile phones. Demand for industrial electronics is also expected to grow rapidly over the medium term, helped by Industry 4.0, as industrial automation and the Internet of Things boosts rapidly growth in demand for industrial electronics. These factors underpin the medium-term outlook for Taiwan's electronics sector exports and capital expenditure, which will be key drivers of economic growth.
Rajiv Biswas, Asia Pacific Chief Economist, IHS Markit
Rajiv.biswas@ihsmarkit.com
© 2021, IHS Markit Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI™) data are compiled by IHS Markit for more than 40 economies worldwide. The monthly data are derived from surveys of senior executives at private sector companies, and are available only via subscription. The PMI dataset features a headline number, which indicates the overall health of an economy, and sub-indices, which provide insights into other key economic drivers such as GDP, inflation, exports, capacity utilization, employment and inventories. The PMI data are used by financial and corporate professionals to better understand where economies and markets are headed, and to uncover opportunities.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
Location