All major APAC and most US equity indices closed lower, while all European indices were higher on the day. US government bonds closed sharply higher, while benchmark European bonds closed mixed. European iTraxx and CDX-NA closed wider across IG and high yield. The US dollar and natural gas closed higher, while oil, gold, silver, and copper were lower on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- Most major US equity indices closes lower except for DJIA flat; S&P 500 -0.5%, Nasdaq -1.4%, and Russell 2000 -2.3%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -6bps/1.81% yield and 30yr bonds -8bps/2.09% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed +2bps/62bps and CDX-NAHY +11bps/348bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed +0.9%/97.26, which is the highest close since July 2020.
- Gold closed -2.0%/$1,793 per troy oz, silver -4.8%/$22.68 per troy oz, and copper -2.0%/$4.42 per pound.
- Crude oil closed -0.8%/$86.61 per barrel and natural gas closed +6.1%/$4.28 per mmbtu.
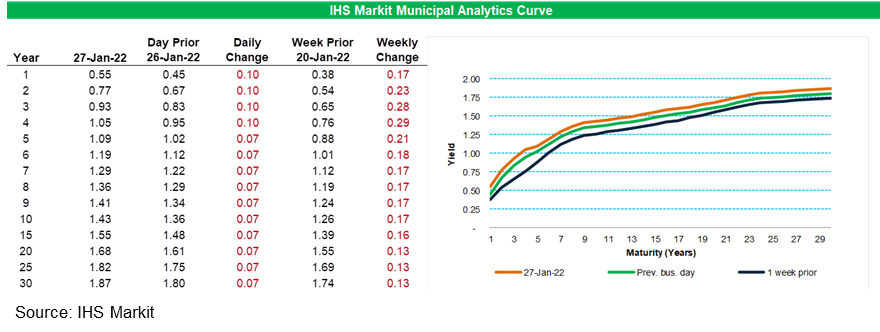
- IHS Markit's AAA Tax-Exempt Municipal Analytics Curve (MAC) sold-off 10bps for 4-year and shorter paper and was 7bps weaker across the remainder of the curve, with the curve 13-29bps worse week-over-week.
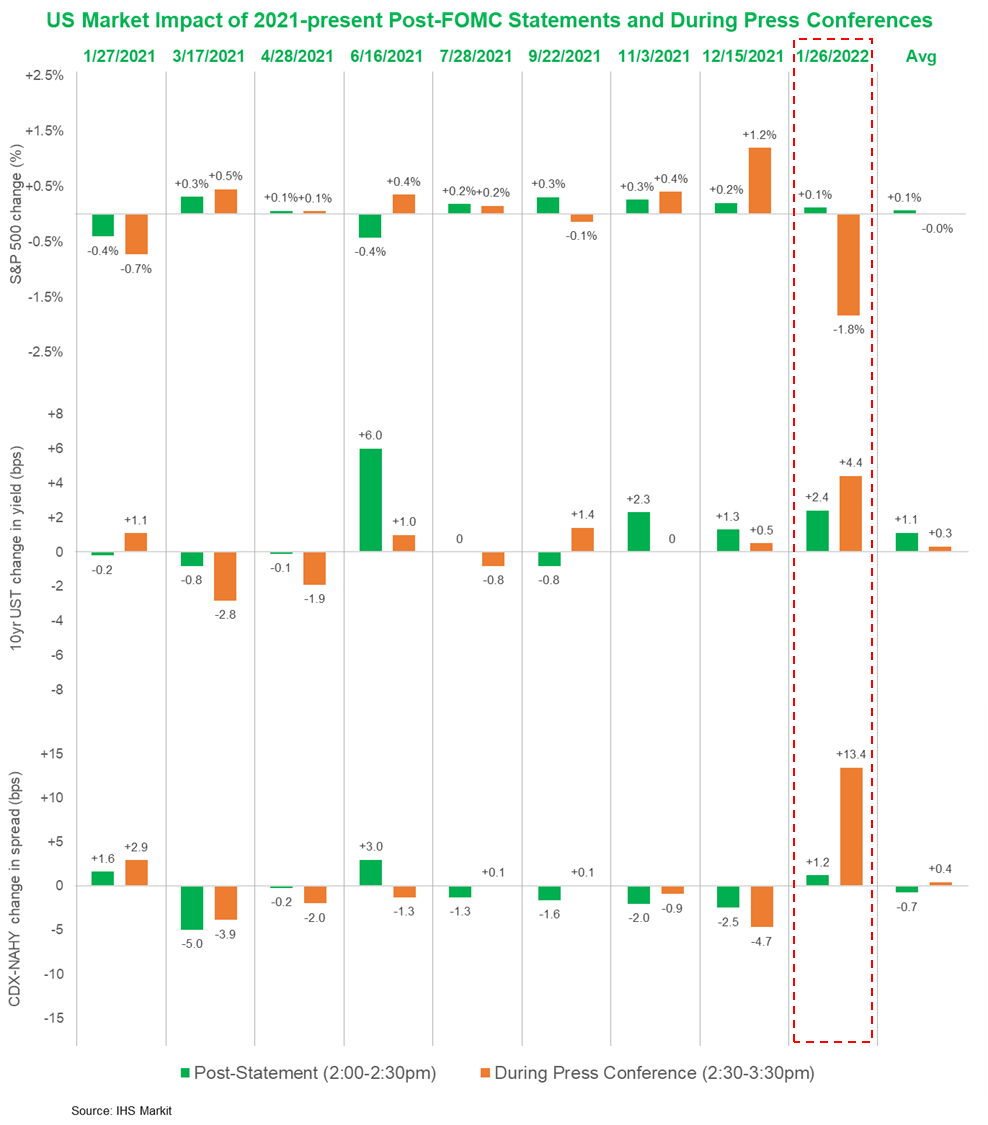
- Chair Jerome Powell's press briefing yesterday at the conclusion of the Fed's policy meeting leaned decidedly hawkish. Following a statement from the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) all but guaranteeing that the Fed would begin to raise interest rates at the next scheduled meeting, on 16 March, the Chair repeatedly stressed developments that are likely to lead the Fed to take multiple steps in coming months to reduce the extraordinary amount of monetary stimulus implemented during the pandemic. The Fed will stop bond purchases in March, as planned. It will begin to raise interest rates in March and expects it will be appropriate to raise interest rates several more times over the coming year to bring inflation back down toward target. It is likely to begin shrinking its balance sheet, which surged some $4.7 trillion since the pandemic began, around the middle of this year. Shrinkage will start earlier and be decidedly faster and larger than during the last episode of balance sheet normalization, from October 2017 to July 2019. (IHS Markit Economists Ken Matheny and Lawrence Nelson)
- The below chart separates the market reaction to every 2021-present FOMC meeting 30 minutes after the release of the statement and upon the conclusion of the press conference across the S&P 500, 10yr UST, and IHS Markit's CDX-NAHY (performance measurement only during the periods of 2:00-2:30pm ET for the statement release and between 2:30-3:30pm ET for the press conference). Yesterday's sell off (highlighted in red) during the press conference was the worst over the past year of meetings across all three of those major US benchmarks.
- US GDP rose at a 6.9% annual rate in the fourth quarter according to the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA)'s "advance" estimate, 0.5 percentage point lower than our latest tracking estimate. GDP growth increased sharply from 2.3% in the third quarter but continues to reflect the resurgence of COVID-19 cases and the ongoing supply chain problems. Federal government assistance to households, businesses, and state and local governments declined materially. (IHS Markit Economists Ken Matheny, Michael Konidaris, and Lawrence Nelson)
- Relative to our tracking estimates, personal consumption expenditures (PCE) were higher than expected but inventory investment was lower. The former reinforced our expectation for robust growth of PCE in the first quarter, while the latter suggested less of a decline in the pace of inventory building in the first quarter. The combination implied an upward revision to our forecast of fourth-quarter GDP growth to 1.9%.
- The upturn in GDP growth in the fourth quarter was led by PCE, which grew at a 3.3% annual rate, up from 2.0% in the third quarter, and by inventory investment, which increased by $240 billion, contributing 4.9 percentage points to GDP growth. Also contributing to the faster GDP growth were business fixed investment (up 2.0%) and net exports (up $51 billion). These were partially offset by declines in both federal (down 4.0%) and state and local (down 2.2%) government consumption and gross investment.
- Prices accelerated further in the fourth quarter, roughly in line with our expectations. The GDP price index rose at a 6.9% rate, up from a 6.0% increase in the third quarter. The core PCE index rose at a 4.9% rate, up from a 4.6% increase in the third quarter.
- US manufacturers' orders for durable goods declined 0.9% in December, a bit more than expected. Shipments of durable goods rose 0.8%, and inventories of durable goods rose 0.7%. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- The advance report also includes estimates for nondurables shipments and inventories, which declined 0.1% and 0.5%, respectively.
- Nominal figures in the manufacturing sector continue to be boosted by rapid price gains. IHS Markit analysts constructed a shipments-weighted producer price index (PPI) for manufactured durable goods, and that price index rose 12.9% over the 12 months of 2021. Using this to deflate nominal orders for durable goods left them essentially flat last year.
- Moreover, even as nominal orders for durable goods continue to trend further above the February 2020 level, real orders recovered that level about one year ago and have made no progress since.
- Rapid price gains and reduced order and shipping volumes are symptoms of ongoing supply bottlenecks impacting the manufacturing sector.
- Core orders and shipments were both revised higher for November and were stronger than the IHS Markit assumptions for December. Consequently, the forecast of growth of equipment spending in the first quarter has been raised by 0.6 percentage point to 14.7%.
- Manufacturers' inventories rose at a rapid clip last year, but this too reflects rapid price gains in the manufacturing sector. When expressed in terms of real replacement cost, manufacturers' inventories declined 3.3% over the 11 months through November (the last available data point on this basis).
- The Pending Home Sales Index (PHSI) fell 3.8% in December to 117.7, following a 2.3% November drop. All four regions saw month-on-month declines for the second straight month. (IHS Markit Economist Patrick Newport)
- Low inventory, not weaker demand, likely accounted for the end-of-year slump. According to Lawrence Yun, the National Association of Realtors' chief economist, "Pending home sales faded toward the end of 2021, as a diminished housing supply offered consumers very few options."
- The Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA)'s weekly Purchase Index (four-week moving average) has hardly budged recently and remains at high levels despite a recent surge in borrowing rates. According to the MBA, activity remains strong on higher priced homes.
- The 30-year fixed rate mortgage (Freddie Mac) has climbed to 3.55%, up from 3.05% five weeks ago.
- The PHSI leads existing home sales by a month or two. The latest two PHSI readings point to lower existing home sales in January or February or both.
- Pending home sales declined in December by more than IHS Markit analysts had assumed, implying fewer brokers' commissions in the first quarter than previously forecast. This shaved 0.1 point from the forecast of first-quarter GDP growth, which now stands at 1.9%.
- State labor markets continued to recover and posted rising employment levels in December, firmly leaving behind the disruption of the Delta variant surge. This most recent data was collected prior to the arrival of the current Omicron variant wave. While gains in total private nonfarm employment were solid nationwide, the Northeast far outpaced the rest of the country. Leisure and hospitality hiring in New York and Massachusetts made great strides as the industry moves out of a deep job deficit. While the Midwest expanded further, lackluster manufacturing hiring and declines in business services and financial activities in Nebraska, the Dakotas, and Minnesota restrained the region from seeing stronger job growth. Healthy gains in trade, transportation, and utilities and in hospitality services propelled the South and West. Over the year, the hardest-hit states of the Northeast and West bounced back the most in 2021 compared with states in the South and Midwest. (IHS Markit Economist James Kelly)
- The Texas Alliance of Energy Producers' Texas Petro Index showed a 28.8% year over year improvement in December capping a year of recovery from contractions in 2019 and 2020. Creator of the Texas Petro Index (TPI) and Alliance Petroleum Economist Karr Ingham stated: ""The Texas upstream oil and gas industry endured a punishing two-year contraction, the second year of which was at the hands of COVID, which finally came to an end with the January 2021 trough in the Texas Petro Index. The index has been steadily on the rise since then with higher prices, a growing rig count, and a return to at least modest growth in industry employment." The monthly TPI released on January 26 showed a December 2021 improvement at 172.6, up from December 2020's 134.0. According to the alliance release: "The TPI reached its cyclical low point of 131.2 in January 2021, and has increased by 31.6% since then, marking an 11-month and counting expansion thus far. The Texas Petro Index remains well below its pre-contraction level, however; the December 2021 TPI is about 19% below the most recent cyclical peak of 213.6 established in February 2019." Ingham is bullish the TPI can continue to rise this year, "…assuming continued steady growth in upstream activity levels in Texas." However, the TPI is unlikely to match a 314.0 peak reached in November 2014 due to increases in efficiency. As Ingham explained, ""Simply put, fewer rigs, employees, and other resources are required to produce record and growing volumes of crude oil and natural gas. Even as production continues to grow, other upstream indicators remain well below prior levels, keeping the index in check." Highlights of the TPI included (IHS Markit PointLogic's Annalisa Kraft):
- Natural gas prices paid to producers averaged $5.79/mmbtu for the year, the highest annual average since 2008. While natural gas prices were trending higher in 2021 anyway, the upward price spike in February 2021 in response to Winter Storm Uri clearly pushed the average significantly higher…natural gas prices were moving upward to the highest levels since 2014 in the second half of the year.
- The Texas statewide rig count has increased each month since the record low 105 rigs at work on average in August 2020. The December 2021 monthly average rig count of 275 reflects the addition of 170 rigs since then, and the count continues to climb. The Texas rig count remains well below the 533 rigs at work on average in October and November 2018, and the 904 rigs at work on average in November 2014.
- Over 8,700 original drilling permits were issued in 2021, an increase of nearly 40% compared to the 2021 annual total, which was the lowest in the entire history of the TPI analysis dating back to 1995.
- Nearly 18,600 direct upstream oil and gas jobs have been added thus far in the current expansion, including nearly 16,500 over the last 12 months. However, that follows the loss of over 83,000 jobs over the course of the entire contraction, 63,000 of which were shed during 2020 alone. As of December, estimated upstream industry employment in Texas was 175,925, compared to the low point of 157,330 in September 2020, and the most recent cyclical employment peak of over 240,000 jobs in December 2018. Direct upstream oil and gas employment in Texas achieved its all-time high of over 307,000 jobs in December 2014.
- Hyundai Mobis has invested USD4 million in US-based radar startup Zendar, according to a company statement. Through this investment, Hyundai Mobis aims to develop imaging radar optimized for Level 4 autonomous vehicle (AV) technology. Imaging radar expands radar's current ability beyond identifying bulky objects to more precisely recognizing a vehicle's environment by processing data from radars on the vehicle. Youngbin Kim, head of the planning division at Hyundai Mobis, said, "We will continue to elevate our status as a leading mobility platform company that combines software and hardware through the development of our own technology and cooperation with global companies with various source technologies." Radars support AVs with object detection and navigation in severe climatic conditions, such as fog, rain, and snow. Hyundai Mobis, through its 'Transformation X-Y-Z' strategy, aims to shift its focus from being an automotive hardware component supplier to a software and platform-oriented company. It has unveiled the M.Vision X and M.Vision POP concept vehicles for urban shared future mobility. In 2020, Hyundai Mobis announced plans to invest KRW9 trillion (USD7.5 billion) to develop future car technologies over the next three years. The company has also developed Level 2 automated vehicle technology and aims to mass-produce Level 3 technology by 2022. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Electric vehicle (EV) startup Rivian has reached a production level of 200 delivery-ready units per week, after missing its production target for the fourth quarter of 2021, reports Bloomberg, citing sources familiar with the matter who declined to be identified. According to the report, the sources said that Rivian's production had been averaging about 50 units per week up to the end of December 2021, with output lower at its plant in some weeks over coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases and supply-chain bottlenecks. Reportedly, the sources also stated that adding production of the R1S sport utility vehicle (SUV) alongside the R1T pick-up at the plant was also a source of production slowing. Reportedly, Rivian has built some saleable R1S models but still has some pre-production work to complete. Reportedly, Rivian is working on the Amazon van on a separate production line, but the pace of production has not been made clear. Rivian is due to deliver the first 10,000 units of the van to Amazon by the end of 2022, as part of a 100,000-unit order due to be supplied by the end of 2030. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Autonomous shuttle startup May Mobility has raised USD83 million in a Series C funding round led by Mirai Creation Fund II, according to a company statement. New investors Tokio Marine and Toyota Tsusho participated in the round, as well as existing investors Toyota Ventures, Millennium Technology Value Partners, Cyrus Capital Partners, 1843 Capital, BMW i Ventures, and Bay Lake Ventures. The company plans to use the infused capital in the next two years to increase its engineering headcount, expand its global customer pool, enhance rider experience, and invest in technology advancements such as driver-out operations. May Mobility CEO Edwin Olson said, "With this initial Series C funding, our latest group of global strategic investment partners will enable us to rapidly deploy our technology on Toyota's autonomous-ready platforms, including the Sienna Autono-MaaS. We will continue to challenge the status quo of transit by reshaping the future of the autonomous vehicle industry." May Mobility deploys autonomous vehicles (AVs) to solve transportation challenges by providing first/last-mile services that fill gaps in existing transport infrastructure. Currently, it is operating autonomous shuttles in Grand Rapids, Michigan; Arlington, Texas; Indianapolis, Indiana (all United States); and Hiroshima (Japan). May Mobility offers low-speed autonomous shuttles produced through a partnership with Magna and operated in test programs. To date, May Mobility has provided more than 300,000 autonomous rides and raised USD166 million in funding. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- All major European equity markets closed higher; UK +1.1%, Spain/Italy +1.0%, France +0.6%, and Germany +0.4%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy -4bps, Spain -1bp, France +1bp, Germany +2bps, and UK +3bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +2bps/58bps and iTraxx-Xover +8bps/280bps.
- Brent crude closed -0.6%/$88.17 per barrel.
- Volkswagen (VW) Group's software unit Cariad has entered into a partnership with Bosch to develop advanced driver-assistance systems for consumer vehicles, according to a company statement. The partnership aims to develop automated functions that will allow drivers to temporarily take their hands off the steering wheel. The companies will jointly build a standardized software platform to offer Level 2 and 3 automated capabilities for vehicles sold under the VW brands suitable for volume production. The first of these functions are to be installed in 2023. Cariad CEO Dirk Hilgenberg said, "Automated driving is key to the future of our industry. With our cooperation, we'll strengthen Germany's reputation for innovativeness. Bosch and Cariad will further enhance their expertise in the development of pioneering technologies. This underscores our ambition to deliver the best possible solutions to our customers as soon as possible." To create new revenue streams in the future, carmakers are increasingly focusing on software-related services for vehicles. VW has bundled all its software efforts into one unit, Cariad, which will power passenger vehicles that will be "Level 4 ready" by 2025. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Final investment decision has been taken by partners Ocean Winds and Banque des Territoires for the 30MW Eoliennes Flottantes du Golfe du Lion (EFGL) pilot project in the French Mediterranean Sea. The signing of contracts with main industrial and financial partners, and project implementation will follow shortly. The EFGL project is located 16 kilometers offshore Leucate, Aude, and Le Barcares, Pyrénées-Orientales, and features three 10 MW turbines installed on Principle Power's WindFloat floating foundation concept. The project claims the most powerful turbines to be installed on a floating foundation. EFGL is scheduled to be complete at the end of 2023 and will operate for 20 years. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
- Nestlé has announced a new plan to tackle child labor risks in cocoa production, which involves an income accelerator program, aiming to improve the livelihoods of cocoa-farming families, while also advancing regenerative agriculture practices and gender equality. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Policy's Sandra Boga)
- A cash incentive will be paid directly to cocoa-farming households for certain activities such as, enrollment of children in school and pruning among several others. Nestlé's new plan also supports the company's work to transform its global sourcing of cocoa to achieve full traceability and segregation for its cocoa products. As Nestlé continues to expand its cocoa sustainability efforts, the company plans to invest a total of CHF1.3 billion by 2030, more than tripling its current annual investment.
- The income accelerator program will offer a new approach to help support farmers and their families in their transition to more sustainable cocoa farming, it added. The incentives will encourage behaviors and agricultural practices that are designed to steadily build social and economic resilience over time. With Nestlé's new approach, cocoa-farming families will now be rewarded not only for the quantity and quality of cocoa beans they produce, but also for the benefits they provide to the environment and local communities.
- These incentives are on top of the premium introduced by the governments of Ivory Coast Ghana that Nestlé pays (LID) and the premiums Nestlé offers for certified cocoa. This cocoa is independently audited against the Rainforest Alliance Sustainable Agriculture Standard, promoting the social, economic and environmental well-being of farmers and local communities.
- Cocoa-farming communities currently face immense challenges, including widespread rural poverty, increasing climate risks and a lack of access to financial services and basic infrastructure like water, health care and education. These complex factors contribute to the risk of child labor on family farms, it explained.
- The program rewards practices that increase crop productivity and help secure additional sources of income, which aim to close the gap to living income and help protect children. By engaging in these practices, families can additionally earn up to CHF500 annually for the first two years of the program. The higher incentive at the start will help accelerate the implementation of good agricultural practices to build future impact.
- Otonomo Technologies Limited, an Israel-based connected car data startup, has tied up with Audi as a vehicle data platform partner, according to company sources. Through this partnership, Otonomo's mobility intelligence platform will be able to clean, harmonize, and secure vehicle data provided by Audi's connected cars and make this accessible through its application programming interface and user-friendly platform. Thomas Geiger, Audi project manager extended vehicle, said, "Otonomo's mobility intelligence platform unlocks the value of connected vehicle data while maintaining GDPR [General Data Protection Regulation] compliance." He added, "We see the enabling of services for multi-brand solutions through Otonomo's customers, from start-ups to major corporates in their industries, as a key differentiator. We believe this will fast track the adoption of vehicle data-driven applications." The data collected by Otonomo can be used to innovate traditional service offerings such as insurance, vehicle safety, and stolen vehicle recovery. It will also help in the development of data-driven business models that are uniform across multiple brands and form one streamlined contract, thereby lowering the barriers to entry for insurance companies and other service providers. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
- The monetary policy committee (MPC) of the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) left its key policy rate, the monetary policy rate (MPR), unchanged at 11.5% during its January meeting. The MPC kept the liquidity ratio at 30% and the cash reserve ratio at 27.5%, while the asymmetric corridor around the MPR remained unchanged at between plus 100 and minus 700 basis points. (IHS Markit Economist Thea Fourie)
- Price pressures in the Nigerian economy remain prevalent, leaving headline inflation well above the CBN's inflation ceiling of 9%. In December 2021, a seasonal increase in prices associated with the festive period pushed headline inflation up to 15.6%, ending an eight-month period of consecutive declines. The MPC considers the upward bump in headline inflation during December as temporary, with price pressures in the economy easing in coming months as domestic food supply improves and food inflation slows.
- Economic growth concerns remain, the MPC warns. Oil sales continue to dwindle, despite stronger global oil prices, resulting in a persistent reduction in remittance of oil revenues to the government's Consolidated Revenue Fund. The Nigeria National Petroleum Company (NNPC) has been urged to address this anomaly urgently. Furthermore, the MPC remains supportive of the removal of the national fuel subsidy, but advises robust engagement will all stakeholders in the economy beforehand and a gradual, stepped implementation of the lower fuel subsidy to limit the economic fallout. The CBN expects GDP growth of 3.1% in 2021 and a better outcome in 2022.
- Nigeria's banking sector remains resilient, with non-performing loans ratio (NPLs) trailing down to 4.85% in December 2021, from 5.10% in November. The capital-adequacy ratio fell marginally to 14.54% in December 2021, while the liquidity ratio remained well above its prudential limit at 41.3%.
- Risks to the inflation and GDP growth outlook remain significant and include the evolving COVID-19 pandemic, rising interest rates in developed economies, and security concerns, which could disrupt domestic food supply. The fragile nature of the economic recovery overrides current inflation concerns, the MPC states.
Asia-Pacific
- All major APAC equity indices closed lower; India -1.0%, Australia -1.8%, Mainland China -1.8%, Hong Kong -2.0%, Japan -3.1%, and South Korea -3.5%.
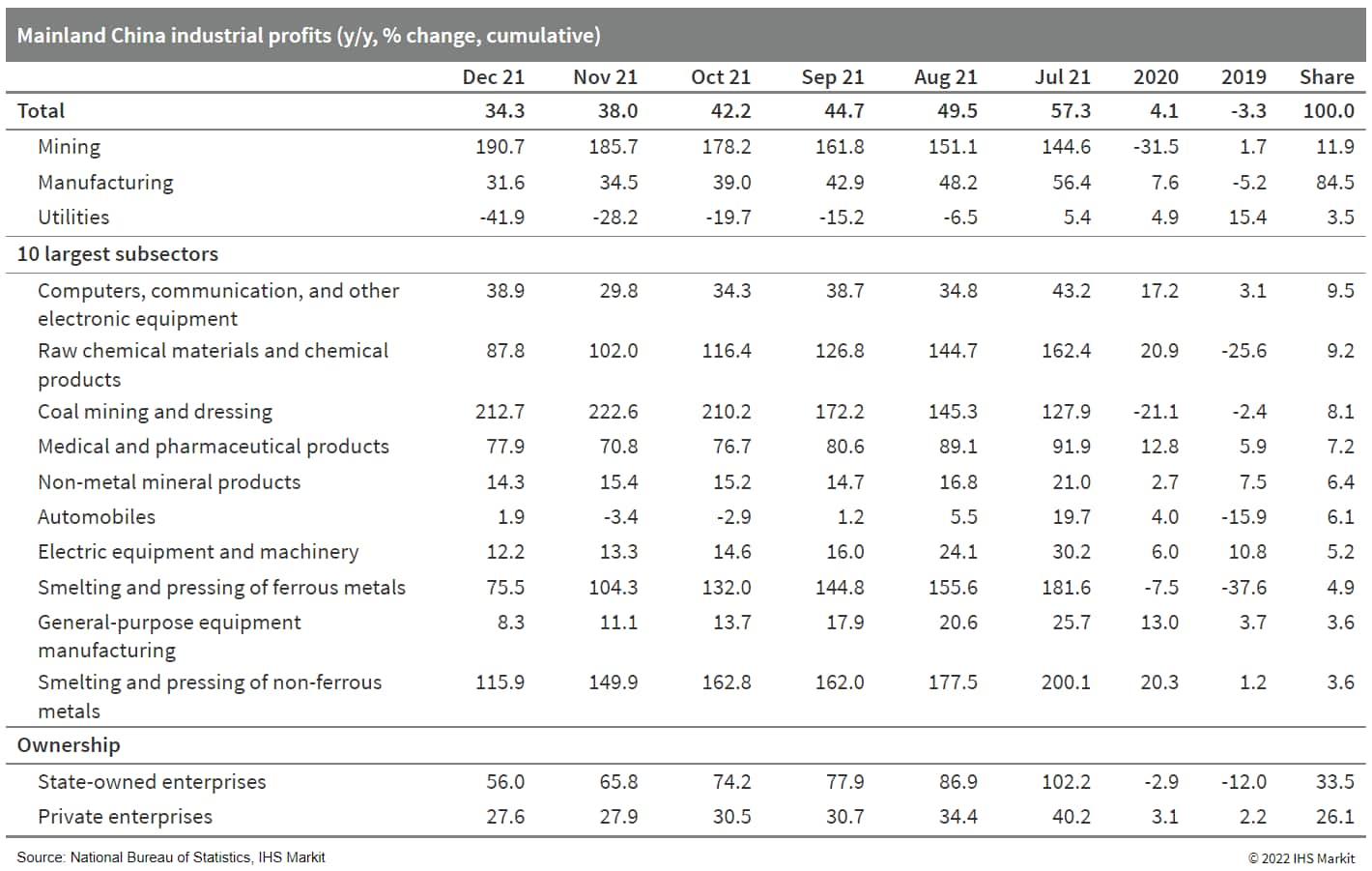
- Mainland China's industrial profits expanded by 34.3% year on year (y/y) in December 2021, down by 3.7 percentage points from the first 11 months of the year. On a two-year (2020-21) average basis, industrial profits increased by 18.2% y/y cumulatively through December 2021, 0.7 percentage point lower than the previous month's reading. For December 2021 alone, industrial profit growth slid by 4.8 percentage points to 4.2% y/y, according to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). (IHS Markit Economist Lei Yi)
- The cumulative profitability ratio came in at 6.81% by the end of December 2021, edging down by 0.17 percentage points from the end-November reading but higher by 0.76 percentage point year on year. Specifically, the decline in the mining segment led the profitability ratio weakening across sectors, with global commodity prices retreating in December (see mainland China: 13 January 2022: Mainland China's consumer price inflation declines in December on falling food prices; producer price inflation moderates further). While the full-year profitability ratios of the mining and manufacturing sectors remain higher year on year, that of the utility sector, at 3.28%, was only about half of end-2020 level—largely due to the sector's 21.1% y/y operating cost increases outpacing the 15.5% y/y rise in operating revenue.
- Out of the 41 industrial subsectors, 32 (78.0%) reported year-on-year profit gains in 2021, up by 6 subsectors from 2020. Up to 31 (75.6%) subsectors recorded industrial profits exceeding pre-pandemic (2019) levels, with the high-tech manufacturing, upstream mining, and raw material manufacturing segments all recording two-year average profit growth rates of above 30% y/y. Midstream to downstream equipment and consumer goods manufacturing, on the other hand, only registered profit growth of 13.5% y/y and 14.4% y/y, respectively on a two-year average basis.
- The average liability-to-asset ratio of industrial enterprises came in at 56.1% by the end of 2021, lower by 0.1 percentage point compared with the previous year. The inventory of finished goods was cumulatively up by 17.1% y/y, down by 0.8 percentage points from the first 11 months of 2021.
- China's auto market will continue to play a central role in accelerating the global auto industry's transition to electrification over the next few years, IHS Markit's latest forecasts show. Data from the China Passenger Car Association (CPCA) indicate that retail sales of passenger new energy vehicles (NEVs), including battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs), reached 475,000 units in China in December 2021, taking the country's full-year passenger NEV sales to a record of 2.99 million units, surging 170% year on year (y/y). The strong momentum will be carried into 2022 and propel the country's NEV production to reach new heights through 2025. According to IHS Markit's latest forecasts, China's NEV production volume is expected to approach 9.5 million units in 2025, accounting for 30% of the country's total light-vehicle production. The projections take into account factors such as an increase in NEV models, preferential policies for NEVs, the wider availability of public EV charging stations and automakers' continual efforts to speed up new car deliveries. The penetration rate of NEVs reached 22.6% in December 2021 in the Chinese passenger vehicle market, according to CPCA data. Chinese OEMs have outperformed their JV counterparts to lead sales growth in the NEV segment. This is in part thanks to Chinese OEMs' early involvement in the NEV sector and their ability to respond quickly to consumer demand changes. The success of the Wuling Hongguang Mini EV has encouraged a number of local OEMs to launch budget models. However, we do not expect the segment to become a key one for EV manufacturers from a longer-term point of view. Consumers buying such vehicles tend to be highly price-sensitive, and the size of the A segment should also constrain the sales growth potential of such vehicles. Through 2025 IHS Markit still expects the C and D segments to be the two largest segments by production volume in the Chinese BEV market. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Plus has partnered with logistics firm Worldex to deploy new-energy autonomous container trucks in trunk-line transportation scenarios, reports Gasgoo. In five years, the partners intend to deploy a fleet of 3,000 heavy-duty autonomous trucks. In addition, the companies will work on developing mass-producible Level 4 autonomous heavy-duty trucks. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- NIO is said to be planning to shift its secondary listing from Hong Kong SAR to Singapore as early as this year, after its application for a listing in Hong Kong was held up by local authorities over issues about its structure and a user trust, reports IFR. William Li, NIO's chairman and CEO, transferred an aggregate amount of 50 million ordinary shares in NIO to the NIO User Trust. The core aim of the user trust is to enable users to enjoy the proceeds from the company's shares while creating a user ecosystem. In a separate report by etnet, NIO is said to have recently set up a wholly owned subsidiary specializing in the insurance brokerage business in China. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Chinese automaker BYD has entered into an agreement with the municipal government of Xiangyang to build a new EV battery manufacturing site in Xiangyang, Hubei province, according to Hubei Daily. The first phase of the project is said to involve an investment of CNY10 billion (USD1.57 billion) and will be focused on the construction of an electric vehicle (EV) battery plant with 30GWh capacity. The report did not provide details on the new plant, such as incentives provided by the government of Xiangyang and the construction timeline for the first phase of the manufacturing plant. According to local media report, BYD already has eight EV battery plants in China with an additional nine production sites under construction. Apart from its self-owned battery plans, BYD has entered into cooperation with automakers such as Changan Auto and FAW Group on EV battery manufacturing. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Vietnam's Nghi Son Refinery and Petrochemical (NSRP) has cut its overall production and might be forced to shut in February, three industry sources told OPIS on Thursday. (IHS Markit Chemical Market Advisory Service's Chuan Ong)
- A market analyst in China said that production at NSRP's 700,000 mt/yr paraxylene (PX) unit was also cut to an unknown rate, and has disrupted market supply.
- "Some PX buyers in China received cancellation notices for their February arrival PX from Vietnam," said a broker from South Korea.
- The company has dropped overall production at its 200,000 b/d refinery to around 80% mid-week, according to a market source in Singapore.
- A spike in PX price mid-week was a response to the supply disruption, more so than a looming shutdown, the broker added.
- The OPIS PX price assessment advanced around 2% during Wednesday's session, up $19.5/mt to $998.5/mt CFR China.
- Market rumors that NSRP was facing cashflow issues were unconfirmed -- NSRP was heard to have cut crude imports from Kuwait while seeking funding.
- Australian farming imported input costs rose significantly in 2021 due to supply shortages and freight rates, with fertilizers particularly affected. The sector's production costs accounted for 61% of revenues in 2021, up from around 50% in 2020. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jose Gutierrez)
- Fertilizers (in the form of phosphates and urea) are essential in continuing to grow crop yields and account for 11% of total production costs. Urea prices rose by f111% to $695/ton (fob China, granular) from January-October, according to IHS Markit. Meanwhile, diammonium phosphate (DAP) prices grow by 91% to A$790/ton, from January-November 2021.
- Energy (electricity, natural gas and fuel used for vehicles, coldstores and irrigators) costs rose by 20% y/y in 2021, according to farming associations.
- Freight rates are essential to set prices for agricultural exports and input imports and they rose through Q1-Q3, starting to stabilize in Q4. Container freight rates fell by 11% from June-September 2021, after rising by 47% from January-June.
- The main crop export prices rose between 30-60% y/y from January-December 2021, with cattle, wheat and canola growing the most.
- Prices for Australian agricultural products are likely to rise in 2022, especially for cattle, dairy, almonds, and winter crops (wheat, barley, oats, canola, and chickpeas) as the result of rising fertilizer prices which started just as the previous production was harvested.
- Traditionally, irrigation water prices were a key production cost, especially in the Murray-Darling Basin (South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria states, all of them in the South East, the most productive area of the Australian agriculture industry). However, the 2020-21 and 2021-22 rainfall average has been well above the 2019-20 level and most players expect favorable rains in the 2022-23 season.
- Fertilizers will be at the core of farming costs, especially for cereals, stone fruit, grapes and almonds, where prices have started high in January 2022. In addition, fertilizer costs will depend on Chinese supply and its cost. Meanwhile, the agricultural price growth level will depend on South East Asian and Chinese demand, once the sea freight rates between Australia and Asia have stabilized. General Australia's Consumption Price Index (CPI) growth averaged 3.5% in 2021, slowing to 1.3% in Q4 2021. This is above the 3% goal of the Reserve Bank of Australia, but clearly behind the US and the EU, where inflation crossed the 6% level this December.
- Annual food price inflation in Australia climbed to 1.9% in Q4 2021, up from 1.3% in Q3. Prices rose faster for oils and fats (5.4% in Q4, up from 4.3% in Q3) and dairy products (1.8% against 0.1%). On the other hand, there was a rebound in pork prices (0.7% against -0.4%); poultry (0.1% against -0.4%); cereal products (1.3% against -1.4%); and honey and spreads (0.5% against -0.4%).

Posted 27 January 2022 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.





