US equity/credit indices and government bonds all closed sharply lower on the day. All major APAC equity markets closed higher, while most European markets were modestly lower. European government bonds were lower and European iTraxx closed wider across IG and high yield. WTI closed higher, while Brent, the US dollar, gold, silver, and copper all closed lower on the day.
Americas
- US equity markets closed sharply lower; Russell 2000 -3.7%, Nasdaq -3.5%, S&P 500 -2.5%, and DJIA -1.8%.
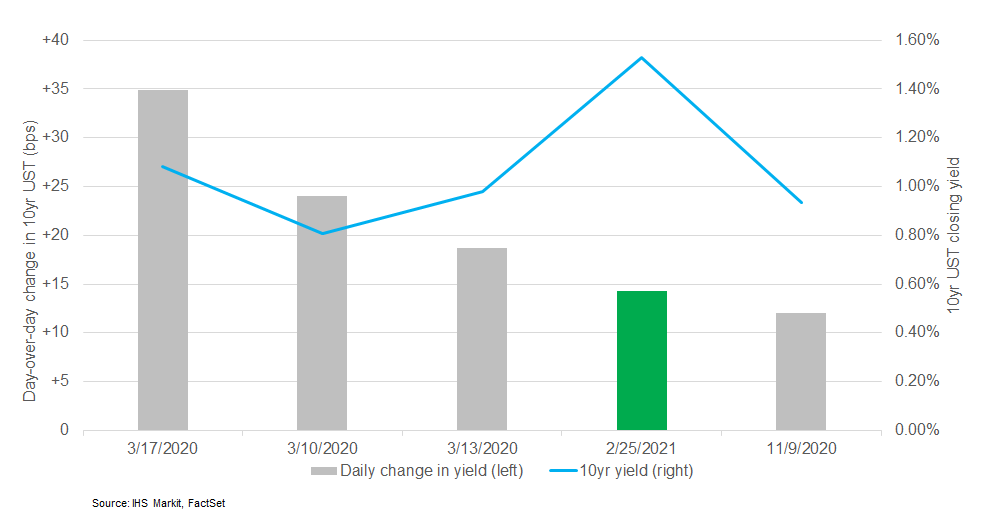
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +15bps/1.53% yield and 30yr bonds closed +6bps/2.30% yield. Today was the fourth largest day-over-day increase in 10yr yields since the beginning of 2020.
- CDX-NAIG closed +4bps/56bps and CDX-NAHY +22bps/313bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.1%/90.13.
- Gold closed -1.3%/$1,775 per ounce, silver -0.7%/$27.67 per ounce, and copper -0.7%/$4.26 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +0.5%/$63.53 per barrel.
- The acting head of the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has ordered the agency to review how publicly traded companies have been disclosing climate-related risks in their filings. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Amena Saiyid and Kevin Adler)
- In a 24 February statement, SEC Acting Chairwoman Allison Herren Lee ordered the agency's corporation finance division to "enhance its focus" on which companies are complying with the 2010 guidance, which was the first time the SEC acknowledged that climate-related impacts can have a material effect on a company's bottom line.
- "As part of its enhanced focus in this area, the staff will review the extent to which public companies address the topics identified in the 2010 guidance, assess compliance with disclosure obligations under the federal securities laws, engage with public companies on these issues, and absorb critical lessons on how the market is currently managing climate-related risks," Lee said.
- Although the decade-old guidance was seen at the time as a significant action, it did not establish any metrics or standards for reporting risk. This omission on SEC's part gave rise to a variety of voluntary frameworks and standards that have since resulted in a patchwork of climate risk reporting regimes and incomplete and inadequate disclosures from companies.
- IHS Markit Head of Americas Regulatory Affairs Salman Banaei said the ensuing rulemaking will most probably build on the updated guidance and define specific disclosures in a manner consistent with the widely used international voluntary climate risk reporting frameworks like the one developed by the Task Force for Climate-Related Financial Disclosures, which require a reporting format and cadence.
- US seasonally adjusted (SA) initial claims for unemployment insurance fell by 111,000 to 730,000 in the week ended 20 February. The previous week's level was revised down by 20,000 from 861,000 to 841,000. Even as initial claims trend down, they remain at historically high levels—the high during the Great Recession was 665,000. (IHS Markit Economist Akshat Goel)
- Seasonally adjusted continuing claims (in regular state programs), which lag initial claims by a week, fell by 101,000 to 4,419,000 in the week ended 13 February. The insured unemployment rate edged down 0.1 percentage point to 3.1%.
- There were 451,402 unadjusted initial claims for Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) in the week ended 20 February. In the week ended 6 February, continuing claims for PUA fell by 166,906 to 7,518,951.
- In the week ended 6 February, continuing claims for Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC) rose by 1,003,701 to 5,065,890, a series high. With the latest extension to 24 weeks for PEUC, eligible recipients can receive up to 50 weeks of unemployment benefits between the regular state programs and PEUC.
- The Department of Labor provides the total number of claims for benefits under all its programs with a two-week lag. In the week ended 6 February, the unadjusted total rose by 701,102 to 19,042,686.
- US manufacturers' orders for durable goods rose 3.4% in January, surpassing the consensus expectation by a wide margin. Manufacturers' shipments of durable goods rose 2.0%, and inventories declined 0.3%. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- Roughly one-fifth of the increase in durable-goods shipments was accounted for by civilian aircraft, reflecting the return to service (in December) and resumed fulfillment of orders of Boeing's 737 MAX line of aircraft. Profit margins from these resumed deliveries will boost first-quarter GDP, as the production costs are already reflected in prior GDP reports (when the production occurred).
- This development also shaped durable-goods inventories, as their overall decline was more than doubly accounted for by civilian aircraft. Resumed deliveries of aircraft are depleting inventories.
- More broadly, today's report highlights the relative strength of durable goods manufacturing. As of January, orders for durable goods were 4.2% above the February 2020 level, in stark contrast to services, where indicators of activity are still well below their pre-pandemic peaks.
- Orders and shipments of core capital goods continued their rapid climb in January on top of upward revisions to December. They are both well above their pre-pandemic trends and point to robust growth of equipment spending in the first quarter.
- The US Pending Home Sales Index (PHSI) fell 2.8% in January to a still-solid 122.8; this was up 13% from a year earlier. (IHS Markit Economist Patrick Newport)
- The index for the South eked out a 0.1% January gain; the other three regional indexes were down. Compared with a year earlier, the South was up 17%, the West 12%, the Northeast 10%, and the Midwest 9%.
- Lawrence Yun, the National Association of Realtors (NAR)'s chief economist, wrote: "Pending home sales fell in January because there are simply not enough homes to match the demand on the market."
- Transactions are also down because rising home prices have eroded savings from lower mortgage rates. These headwinds have picked up. The 30-year fixed rate mortgage (Freddie Mac), which also came out this morning (25 February), jumped 24 basis points in the last two weeks to 2.97%.
- Housing prices have shot up at unprecedented rates in the last six months—and with inventory lean in most places, they are likely to continue rising at above-average rates in the first quarter.
- Applications to buy homes remain strong but are declining: the Mortgage Bankers Association's Purchase Index tumbled 12.0% last week, and its four-week moving average was down 5.4%.
- ExxonMobil has completed the initial phase of a plant trial of an advanced recycling process for converting plastic waste into raw materials for production of polymers. ExxonMobil intends to use results from the trial, at existing facilities in Baytown, Texas, to scale up advanced recycling capabilities at other global facilities, targeting a circular solution for converting difficult-to-recycle plastic waste into feedstocks for virgin-quality plastics. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- ExxonMobil also announced today that it has formed a joint venture (JV) with Agilyx's Cyclyx International business to develop solutions for aggregating and pre-processing large volumes of plastic waste that can be converted into feedstocks. ExxonMobil holds a 25% equity interest in Cyclyx with Agilyx owning the remaining 75%. Advanced recycling involves breaking down plastic waste to its molecular building blocks that are then used as raw material in the process of making virgin-quality plastics.
- Pending successful completion of the next phase of the Baytown plant trial, ExxonMobil Chemical plans to market commercial volumes of certified circular plastics later this year. Cyclyx will help supply ExxonMobil's advanced recycling projects and aims to do the same for other customers.
- US-based air taxi startup Joby Aviation is planning to go public through a merger agreement with Reinvent Technology Partners, a special-purpose acquisition company (SPAC). This will bring the market value of the combined entity to USD6.6 billion, reports TechCrunch. The deal includes USD690 million of cash from the SPAC and USD835 million of financing from private investors including the Baupost Group, funds and accounts managed by BlackRock, Fidelity Management & Research LLC, and Baillie Gifford. As part of the agreement, the combined company will be listed on the New York Stock Exchange and the deal is expected to close in the second quarter of 2021. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
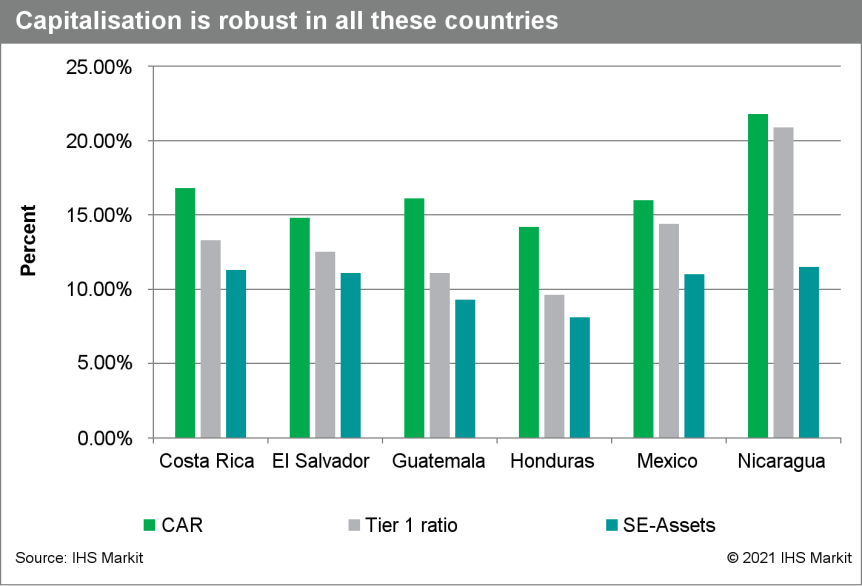
- IHS Markit analyzed the main banking indicators for El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, and Nicaragua. Our key findings highlight that credit growth has been contained; however, the sharp decline in economic activity has affected profitability, and very likely asset quality. During 2021 we expect a very moderate recovery in credit growth and profitability, although asset quality is likely to have declined. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Alejandro Duran-Carrete)
- Most banking sectors in the region experienced a sharp rise in assets driven by the substantial increase in deposits led by the COVID-19-virus pandemic.
- Asset allocation was rather concentrated in liquid assets as a response to the rapid increase in demand deposits. At the end of 2020, liquid assets grew on average by a substantial 27% y/y, contributed to mostly by Honduras, where there was a rise of 81% y/y. Banks appear to be hesitant to disburse more credit, not only because of the sharp economic contraction, but also because of the rapid increase in demand deposits.
- The sector's non-performing loans (NPLs) remain contained. NPLs stood at 2.6% in 2020, rising by 0.3 percentage point compared with the previous year.
- Banks' provisions rose in expectation of a future deterioration of their assets. Throughout 2020, banks increased their reserves-to-total loans ratios, resulting in an average rise by 1.1 percentage points when compared with 2019.
- Following a more cautious strategy from investors during the second quarter of 2020, most of these banks experienced a contraction of foreign liabilities. Costa Rica, El Salvador, and Nicaragua experienced a decline in their foreign liabilities with a yearly contraction by 8.2%, 25%, and 17.8%, respectively.
- Capitalization remained at comfortable levels in most countries. Measures such as the capital adequacy ratio (CAR) or the Tier 1 ratio increased, contributed to by the larger holding of liquid assets.
- Credit growth is likely to be low, particularly during the first half of 2021, but we expect some recovery in the disbursements to the household segment, although higher expectations of economic growth could revise this forecast towards a faster pace of lending.
- Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer BYD has launched an upgraded version of the eT3 van in Brazil, reports Automotive Business. The vehicle comes with an updated battery bank that leads to a reduction of vehicle weight to 1,700 kilograms from 1,870 kg, a 100-kilometre-per-hour speed limiter, and a fast-charger DC charging system, which can charge the batteries from 20% to 80% in 30 minutes and to full charge in 2 hours. The vehicle now has a range of up to 300 km (compared to the previous 180-km range). According to the automaker, the vehicle's urban fuel consumption is equivalent to a gasoline (petrol) vehicle fuel consumption of 56 km per liter. The vehicle has a payload capacity of 720 kg. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Most European equity markets closed lower except for Spain +0.6%; Germany -0.7%, France/Italy -0.2%, and UK -0.1%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed sharply lower; Italy +11bps, France/Spain +8bps, Germany +7bps, and UK +5bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +2bps/51bps and iTraxx-Xover +12bps/263bps.
- Brent crude closed -0.1%/$66.11 per barrel.
- In a press release, ExxonMobil Corporation announced the signing of an agreement to sell its non-operated central and northern North Sea (UK) upstream assets to Neo Energy for a total consideration of over $1 billion plus contingent payments of approximately $300 million based on potential for increase in commodity prices. The transaction is expected to close by the middle of 2021. Under the deal, Neo Energy will acquire a portfolio of 21 assets, including 14 fields and associated infrastructure. However, ExxonMobil will retain its non-operated share in southern North Sea upstream assets, and its share in the Shell Esso gas and liquids infrastructure that supplies ethane to its Fife ethylene plant. Neo said the acquisition will add 140 MMboe of net reserves and 40,000 boe/d of net production to its portfolio. (IHS Markit Upstream Companies and Transactions' Karan Bhagani)
- Subsea 7 has entered into a USD500 million five-year amortizing loan facility. Backed by a USD400 million guarantee from UK Export finance, Subsea 7 has as two-year availability period during which to draw on the facility. The facility has a five-year tenor which begins at the end of the availability period or when the facility is fully drawn, if earlier. The facility can be used for general corporate purposes, including to provide working capital financing for services provided from the UK. The facility is guaranteed by Subsea 7. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Mark Rae)
- In February, the European Commission's economic sentiment index for Austria has rebounded to an 11-month high of 92.0, following a brief corrective dip in January to 88.7. Although the renewed tightening of COVID-19 virus-related restrictions after Christmas has had some dampening impact, it is remarkable that the indicator now stands at a higher level than during the third quarter of 2020 ahead of November's second lockdown. This holds all the more as the loosening of restrictions on 8 February, including the reopening of the non-essential retail sector, may have come too late to be fully reflected in the current survey. That said, the latest level of 92.0 still underperforms its eurozone equivalent (93.4) and its own long-term average of 100.0. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- Sensible 4 has begun autonomous bus trials for the public in the rural commune of Gjesdal in southwestern Norway. The pilot scheme will continue until 4 March and is part of the EU-funded FABULOS project, which has been running in Norway since late January without passengers. Three autonomous Toyota Proace vehicles are being deployed to carry passengers for a drive at Ålgård and Myrengveien. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
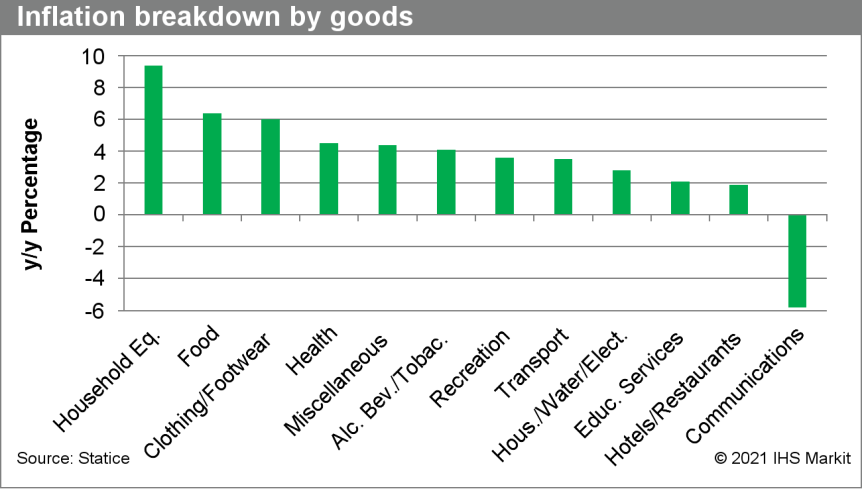
- Iceland's consumer price index rose by 4.1% year on year (y/y) in February, according to figures released by Statistics Iceland. Prices had increased by 4.3% y/y in January, which had been the highest inflation rate in almost eight years. (IHS Markit Economist Diego Iscaro)
- Inflation had averaged 2.8% in 2020, following readings of 2.8% in 2018 and 3.0% in 2019. While inflation had ranged between 1.7% and 2.6% during the first half of 2020, a weakening of the krona as a result of lower tourism revenues has led to an acceleration of the inflation rate from July.
- The prices of household equipment, food, and electricity continued to be the main drivers of the headline inflation rate in February. On the other hand, communication costs fell sharply.
- South African Finance Minister Tito Mboweni announced the government's latest budget on 24 February, specifying the government's intention to cut the public-sector wage bill by more than USD20 billion over the next three years. The government's new budget projected public-sector debt at 88.9% of GDP in 2025/26, compared with 95% of GDP over the same period that Mboweni announced when delivering the Medium-Term Budget Policy Statement (MTBPS) in October 2020. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Langelihle Malimela)
- Public-sector wage levels are already the subject of a legal challenge. If the Constitutional Court rules in favor of public-sector unions in an ongoing dispute with the government over salary increases for fiscal year (FY) 2020/21, the finance ministry will be forced to revise its debt projections upwards and to adjust its expenditure framework for 2021.
- Budgetary projections also rely on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-pandemic-related developments. If the Department of Health experiences significant delays in its vaccination program against the COVID-19 virus during 2021, this is likely to force occasional lockdowns in parts of the economy, in turn implying that growth will be likely to fall short of the government's 3.3% projection.
- Large state-owned enterprises (SoEs) are unlikely to receive much-needed bailouts during 2021, encouraging prolonged labor strikes.
- Above-budget wage costs or revenue slippage threatens to delay implementation of the proposed reduction of corporate tax in April 2022. Mboweni announced that government has collected approximately USD6.9 billion more than it had projected in the MTBPS in October 2020, with the extra funds to be spent primarily on social services.
Asia-Pacific
- Most APAC equity markets closed higher; South Korea +3.5%, Japan +1.7%, Hong Kong +1.2%, Australia +0.8%, Mainland China +0.6%, and India +0.5%.
- Shanghai announced on 25 February a 2021-25 action plan on accelerating the development of the new energy vehicle (NEV) industry in the city. By 2025, the municipal authorities expect annual NEV output in the city to reach over 1.2 million units. The authorities also expect battery electric vehicles (BEVs) to account for more than 50% of new vehicle sales in the private vehicle market. In addition, the city will continue to encourage the adoption of NEVs in the ride-hailing market. According to the action plan, 50% of vehicles in ride-hailing services should be NEVs. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Geely Auto and Volvo Cars announced on 24 February that the two companies have agreed to deepen their collaboration to involve a wide range of core business areas to deliver synergies and tap new growth opportunities. Compared to a full merger plan, this arrangement in the form of an alliance will help both companies tap into each other's resource pool to cope with rising costs associated with the launch of EVs and new technologies, without potentially going through restructuring. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Fisker and Foxconn, the company known for making consumer electronics including the iPhone and Xbox, announced they have signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to jointly develop a new battery electric vehicle (BEV); their discussions are expected to lead to a formal partnership agreement in second quarter 2021. Fisker is approaching the market with what it calls an asset-light approach, looking to partners for manufacturing, while Foxconn has announced its own BEV platform and several partnerships aimed at entering the electric vehicle market. Although these two companies have announced plans to work together on a potential new BEV, both companies have multiple other partnerships and vehicle plans. Neither seems to be putting all its eggs in one basket. The MOU indicates the talks have reached a formal and promising stage, but the discussions could still result in the two companies taking separate paths. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- State-owned oil and gas major Indian Oil Corporation Ltd (IOC) will partner with Israeli startup Phinergy for the development, manufacture, assembly, and sale of aluminium-air (AI-air) electric vehicle (EV) batteries in India, reports the Times of India. Commenting on the development, IOC research and development (R&D) director SSV Ramakumar said, "The Registrar of Companies has given us permission to form the joint venture [JV] company. NITI Aayog has also given us permission. All leading Indian passenger car makers and heavy commercial vehicle manufacturers are on board." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
- Vietnam's La Gan Wind Power Development Corporation has signed various memorandums of understanding (MOU) with various suppliers for foundations and harbor services. The company is developing the La Gan project on behalf of owners Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners, Novasia Energy, and Asia Petroleum Energy. The MOU companies include CS Wind Corporation, PSC Mechanical and Construction, South Petroleum Construction JSC, and Vietsovpetro. La Gan will help to facilitate knowledge transfer in the areas of foundation design, facilities, logistics and infrastructure requirements in order to raise the standards of these suppliers to international standards. The 3.5 GW La Gan wind farm will be built in two phases, a 500 MW to be completed by 2024, and the remaining to be completed between 2026 to 2030. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
Posted 25 February 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.



