Most major European and US equity indices closed lower on Friday, while APAC markets were mixed. US and benchmark European government bonds closed lower. European iTraxx and CDX-NA closed wider across IG and high yield. The US dollar closed higher, while natural gas, oil, gold, silver, and copper were all lower on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- Most major US equity indices closed lower except for Russell 2000 +0.2%; DJIA -0.5% and S&P 500/ Nasdaq -0.9%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +4bps/1.37% yield and 30yr bonds +2bps/1.91% yield.
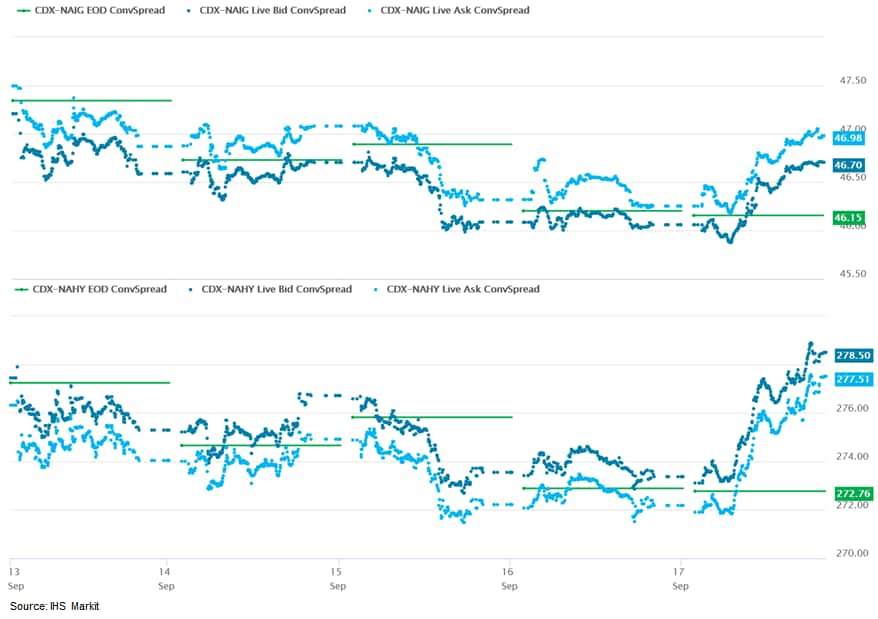
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/47bps and CDX-NAHY +5bps/278bps, which is flat and +1bp week-over-week, respectively.
- DXY US dollar index closed +0.3%/93.2.
- Gold closed -0.3%/$1,751 per troy oz, silver -2.0%/$22.34 per troy oz, and copper -0.8%/$4.25 per pound.
- Crude oil closed -0.9%/$71.97 per barrel and natural gas closed -4.3%/$5.11 per mmbtu.
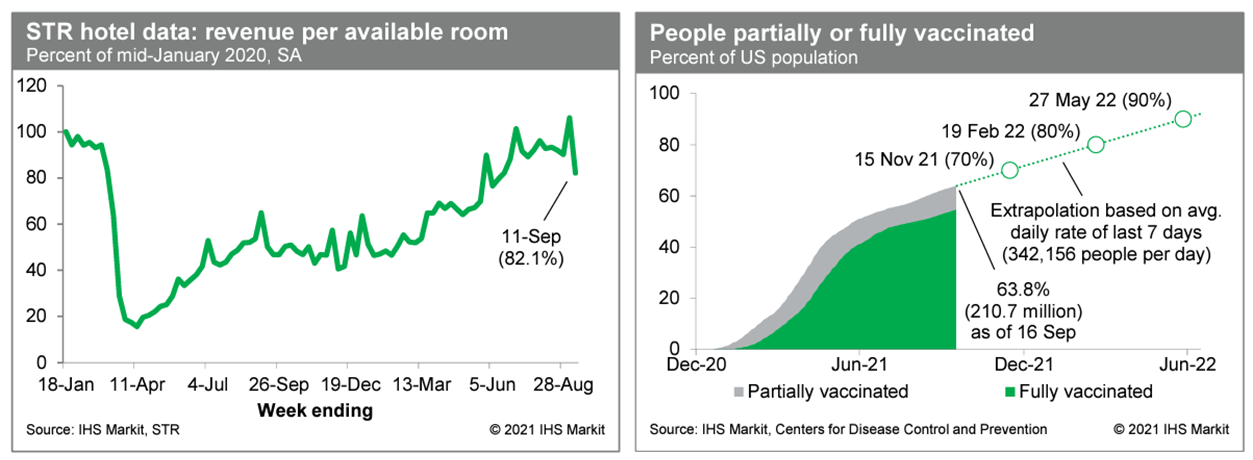
- Revenue per available room at US hotels last week, after seasonal adjustment, was 82.1% of the mid-January 2020 level, according to the IHS Markit estimate based on weekly data from STR. This was the lowest reading since early June. This series has been volatile over the last few weeks owing to the timing of the Labor Day holiday, but the underlying trend appears to be weakening, as would-be travelers are becoming more cautious in response to the recent surge of new COVID-19 infections. Averaged over the last seven days, about 342,000 people per day received a first (or only) dose of a COVID-19 vaccination, about the same as the prior week's rate. As of yesterday, 210.7 million US residents, or about 63.8% of the population, were at least partially vaccinated against COVID-19. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Joel Prakken)
- The US University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index increased 0.7 point from its August level to 71.0 in the preliminary September reading—still slightly below its nadir in April 2020 and nearly the lowest in a decade. (IHS Markit Economists James Bohnaker and William Magee)
- The increase was driven by a modest improvement in expectations, the index for which rose 2.0 points to 67.1. Views on the present situation worsened as that index declined 1.4 points to 77.1.
- The expected one-year inflation rate in the University of Michigan survey ticked higher by 0.1 point to 4.7% to match its July peak and the highest reading since 2008.
- Elevated inflation expectations over the near term are likely a reaction to higher prices for food, gasoline, and other retail goods, but consumers do not appear overly concerned with inflation over the longer term; the expected 5-to-10-year inflation rate was unchanged at 2.9%, which is well within the historical range over the past three decades.
- Views on buying conditions for big-ticket items remained depressed in early September. The index of buying conditions for large household durable goods, automobiles, and houses all slumped further to their lowest levels since the early 1980s. Limited inventories and high prices will likely remain hurdles into next year.
- The recent trend in consumer attitudes has become somewhat dislodged from spending. The depressed level of consumer sentiment is a reflection of anxieties about the spread of the Delta variant, higher prices for certain goods, and the winding down of stimulus and enhanced unemployment benefits. Although these concerns are warranted, consumer spending is likely to continue to recover thanks to solid employment and wage growth, as well as an elevated level of savings that have accumulated during the pandemic.
- The IHS Markit light-vehicle production forecast has been cut by 6.2% or 5.02 million units in 2021, and by 9.3% or 8.45 million units in 2022, to stand at 75.8 million units and 82.6 million units, respectively. For 2023 we have reduced the forecast by 1.05 million units or 1.1% to 92.0 million units; this is a front-loaded adjustment and from the second quarter we expect output levels will be able to accelerate as supply chains return to normal. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- If this is the case, then strong pent-up demand and the pressure to rebuild stock levels is expected to support elevated levels of production in 2024 and 2025, with 2024 now forecast to hit 97.3 million units, up 3.2% compared to the previous forecast and 2025 forecast at 98.9 million units an increase of 2.4%. This is the largest single adjustment to the outlook in what has been a turbulent past nine months.
- So what are the factors behind such a sizeable downgrade? In the first half of the year the primary cause of disruption was the shortage of front-end wafer fabrication for microcontrollers (MCU). This was the particular supply chain that was dented by the ice storm in Texas and the fire at the Renesas Naka 3 facility in Japan. In addition to these events that compounded difficulties in an already constrained supply chain, we began to recognize an issue emerging in early June, which was affecting what are described as back-end processes (packaging and testing) within the semiconductor sector. The back-end issue is focused on operations located in Malaysia and is in direct response to the government's rolling program of lockdown measures. First scheduled to expire by the end of June, the measures were extended through the middle of August and the return to full operational capacity is now not expected until late October.
- Banks and companies were able to sell $175 billion in green bonds through the end of August 2021 that were "fitted" with investments in climate risk reduction and climate-focused, clean-technology solutions, an IHS Markit analysis of the market shows. The 14 September analysis shows that a green bond market has evolved since 2020 that appears to be characterized by especially low interest rates, in part because the debt is explicitly linked to investment in climate-favorable projects, according to IHS Markit Climate and Cleantech Executive Director Peter Gardett, who analyzed bonds issued between March and September of this year. (IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Amena Saiyid)
- Bonds are issued by companies, municipalities, sovereign states or sovereign-backed banks, and other financial institutions as a form of debt that is not a loan or other fixed-income product. Green bonds typically are issued to fund large-scale, capital-intensive green infrastructure projects such as energy efficiency, transit, or renewable power projects that result in positive environmental outcomes, including climate benefits.
- IHS Markit analyzed a subset of more than 140 separate green bond sales in 2021, examining their use of proceeds, language, and their product-level alignment with climate risk reduction methodologies, relying on guidance provided by International Capital Markets Association green bond principles.
- Gardett found that the green bond market is oversubscribed owing to the push for clean energy solutions as part of the transition to a net-zero economy, and because it has evolved from what he called "a 1.0 state of broad and unstandardized tagging of existing bonds to a much more sophisticated and fitted 3.0 state during the summer of 2021."
- Ford has announced that it will spend an additional USD250 million to double production of its F-150 Lightning electric vehicle (EV) pick-up, adding 450 new jobs in Michigan, reports Automotive News. According to the source, the investment and the jobs will be distributed in its Rouge Electric Vehicle Center, Van Dyke Electric Powertrain Center, and Rawsonville Components Plant, helping the automaker to build 80,000 EV pick-ups annually (the original plan was for 40,000 units annually). Executive Chair Bill Ford said, "We knew the F-150 Lightning was special, but the interest from the public has surpassed our highest expectations and changed the conversation around electric vehicles. So we are doubling down, adding jobs and investment to increase production." He added, "This truck and the Ford-UAW workers who are assembling it in Michigan have a chance to make history and lead the electric vehicle movement in America." Ford has doubled its production for its F-150 Lightning based on strong demand, which includes more than 150,000 reservations received by mid-September. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
- Autonomous truck startup Embark has partnered with Ryder System Inc. to establish a nationwide network of up to 100 Embark transfer points in the US, according to a company statement. As part of their partnership, Ryder will provide yard operations, maintenance and fleet management services. Embark intends to carry freight from driverless long-haul trucks to driver-enabled trucks for first- and last-mile delivery through these transfer points. The companies will initially focus on key freight markets in California, Arizona, Texas, Georgia, Tennessee, and Florida, through which Embark will be able to begin operations early next year in preparation for a larger commercial launch in 2024. Over the next five years, Embark and Ryder aim to work with a network of real estate operators to open 100 Embark transfer points across the country. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Colombia's industrial production rose 13.5% year on year (y/y) in July, down slightly from June's 13.9% y/y growth. Although weakening external demand and the global spread of the Delta variant of the COVID-19 virus pose growing risks to the outlook, IHS Markit still expects GDP growth to expand 7.1% this year and 3.4% next year as higher activity in services sectors should support growth in the quarters ahead. (IHS Markit Economist Dariana Tani)
- According to Colombia's National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE), the country's total industrial production index (IPI) continued to rise at a fast pace in July, rising by 13.5%, compared to 13.9% y/y in June; however, this mostly reflects favorable base effects.
- By sub-sectors, manufacturing production grew by 20.1% y/y in July, down slightly from a 20.8% y/y rise in June, mainly driven by the manufacture of food products, chemical substances products and beverages. Electricity and gas supply output, by contrast, rose from 9.3% y/y in June to 9.5% y/y in July while collection, treatment, and water distribution rose by 2.3% y/y in July, after falling by 0.4% y/y in June. Mining and quarrying output was the only component dragging production, with a 0.7% y/y decrease.
- Nevertheless, leading indicators for August such as Colombia's Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI), which is produced by IHS Markit and Davividenda, pointed to a strong but moderating rate of expansion in manufacturing production from July. The PMI index came in at 53.2 in August, down from July's 12-month high of 54.2 but remained above the 50-mark, which separates growth from contraction, for the second consecutive month.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Most major European equity indices closed lower except for Spain +0.3%; France -0.8%, UK -0.9%, Italy -1.0%, and Germany -1.0%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed lower; France/Germany/Spain +2bps and Italy/UK +3bps.
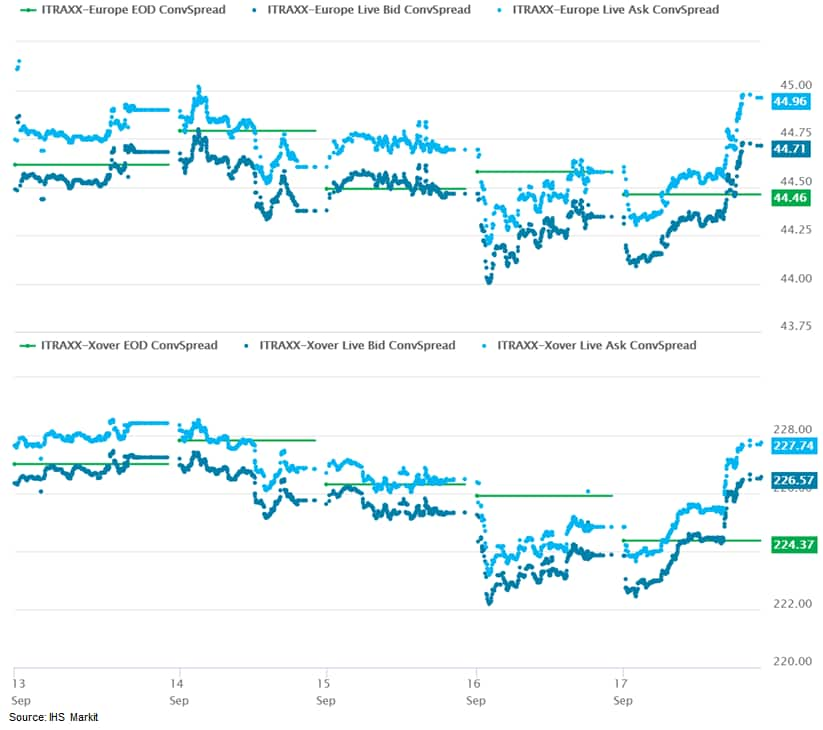
- iTraxx-Europe closed +1bp/45bps and iTraxx-Xover +3bps/227bps, which are both flat week-over-week.
- Brent crude closed -0.4%/$75.34 per barrel.
- SEAT has announced that it is forecasting that the automotive semiconductor supply shortage will affect its vehicle production well into 2022, according to a Reuters report that cited comments from the company. SEAT has joined a growing list of OEMs to publicly acknowledge that the impact of the semiconductor shortage will continue well into next year. In a company statement SEAT said, "The deterioration in the supply of semiconductors now requires reorganizing, planning and adopting new labor protocols." The company added that it had started negotiating a furlough plan with local unions to cancel some working shifts between 27 September and 30 June 2022. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- The central bank of the eight-nation West African Economic and Monetary Union (known by its French acronym of UEMOA) has maintained its benchmark interest rate at 2.0%, the bank's monetary policy committee (MPC) announced on 8 September. The West African CFA franc zone comprises Benin, Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Niger, Senegal, and Togo. (IHS Markit Economist Anton Casteleijn)
- The MPC meeting of the Central Bank of West African States (Banque Centrale des États de l'Afrique de l'Ouest: BCEAO), was held by videoconference under the chairmanship of Tiémoko Kone, governor of the BCEAO. The minimum rate for open-market operations remained at 2.0%, the marginal lending rate at 4.0%, while the reserve requirement ratio for banks in the monetary union also remained unchanged at 3.0%.
- The economic recovery in the UEMOA region gained further momentum in the second quarter of 2021, with a 7.7% increase year-on-year in real GDP, after a 3.4% increase in the previous quarter. The sustained recovery across all sectors was supported mainly by sustained domestic demand strength and exports. The price index of non-energy raw materials exported by countries in the UEMOA region increased by 2.7% in the second quarter of 2021 compared with an increase of 5.1% in the previous quarter.
- Due to a further increase in grants and improved fiscal revenue, the budget deficit for all UEMOA member states was 4.6% of GDP in the second quarter of 2021 compared with the 5.4% of GDP recorded in the second quarter of 2020. The West African bloc's level of foreign-exchange reserves fell slightly to 6.2 months of import cover at the end of June 2021, compared with 6.7 months at the end of March, while the average rate on bank loans fell 6 basis points in the second quarter of 2021 to 6.36%.
Asia-Pacific
- Major APAC equity markets closed mixed; Hong Kong +1.0%, Japan +0.6%, South Korea +0.3%, Mainland China +0.2%, India -0.2%, and Australia -0.8%.
- Mainland China's year-on-year (y/y) real industrial value-added growth declined by 1.1 percentage points to 5.3% in August, the fourth consecutive month of fall since May. Meanwhile, the growth rate, on a two-year (2020-21) average basis, fell to 5.4% from 5.6% in the previous month. The month-on-month growth stayed at 0.3% expansion, unchanged from July's reading but significantly lower than the 2017-19 March average of 0.47%. (IHS Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- By sector, the headline moderation was largely driven by downstream manufacturing and utilities as soaring upstream industrial inflation continued to squeeze profit in mid and downstream sectors, and the chips shortages and unceasingly regional COVID-19 outbreaks disrupted production to some extent. The bright aspect was the continued robustness in high-tech manufacturing, which accelerated to the second highest since the beginning of the year. Meanwhile, value-added growth in mining sector picked up by 1.9 percentage points to 2.5% y/y, reflected in the acceleration of coal production and slower contraction of steel under the authority's supply, ensuring efforts to stabilize commodity prices.
- The service production index dropped by 3 percentage points to 4.8% on a y/y basis and down 1.2 percentage points to 4.4% on a two-year (2020-21) average basis.
- Year-on-year FAI growth continued to decline by 1.4 percentage points to 8.9% through August on higher-base effects. On a 2020-21 average basis, FAI growth further edged down to 4.0% from 4.3% a month ago. Moreover, the m/m growth slowed from 0.18% in July to 0.16% in August.
- By sector, real estate investment deteriorated for six consecutive months since March with the escalating real estate controls. Meanwhile, the cumulative infrastructure investment growth maintained a downward trend in terms of both y/y and 2020-21 average growth, although the estimated de-cumulative figure improved from July.
- The floor space of commercial housing sales continued to slow and the IHS Markit estimated de-cumulative figure fell to contraction in July as housing market purchase controls and mortgage policy tightened in hot cities. Meanwhile, developers' financing growth further slowed to 8.7% on a two-year average basis as bank loans continued to decline, while mortgages and purchasers' deposits expanded at a slower pace.
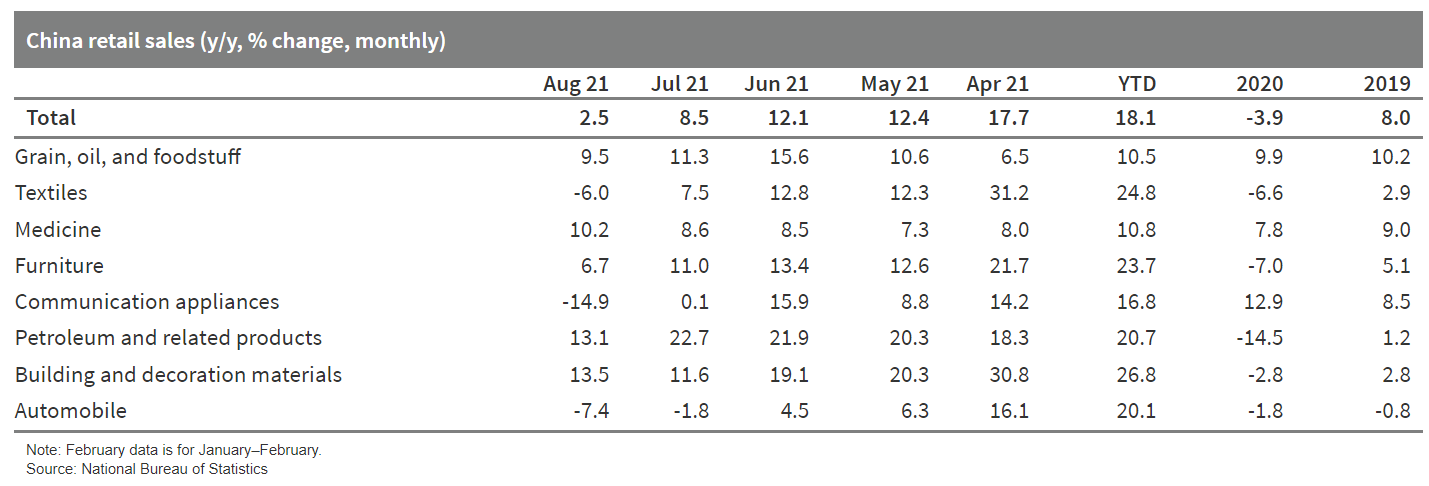
- Year-on-year nominal retail sales fell by 6 percentage points from July to 2.5% in July, the largest drop and the lowest figure since September last year. On a two-year (2020-21) average basis, nominal retail sales growth declined by 2.1 percentage points to 1.5%. Real retail sales growth decelerated by 5.5 percentage points to 0.9% y/y.
- Didi Chuxing's (DiDi) daily active users have reportedly dropped by about 30% since its initial public offering (IPO) in the US that triggered a data security investigation. DiDi's average daily active users dropped to 10.9 million in August from 15.6 million in June, reports the Financial Times (FT). According to the report, the data only reflects the performance of DiDi's main ride-hailing app and does not cover its mini app on WeChat. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- General Motors (GM) has launched its Ultium electric vehicle (EV) platform in China, reports China Daily. The automaker said the cell and other core components to develop the platform have been completely sourced locally. By 2025, GM expects to launch more than 30 EVs based on the Ultium platform worldwide, and more than 20 of them will be introduced to the Chinese market. The Cadillac Lyriq sport utility vehicle (SUV) will be the first Ultium-based model to be unveiled in China in 2022. Mary Barra, chairman and CEO of GM, said, "We believe the inflection point of putting everybody in an EV and transitioning to an all-electric future has arrived, and GM intends to take the lead. China is not only the largest vehicle market. It's also a powerhouse of innovation and the frontier of electric intelligent connected vehicle development and deployment." GM is ramping up a USD35-billion campaign to launch a new generation of electric and automated vehicles powered by its proprietary Ultium battery technology, which it plans to use in key electric models. The state-of-the-art Ultium battery system and third-generation global electric platform will integrate GM's engineering flexibility, technology advances with highly localized manufacturing, and supply chain in China to enhance quality and cost-competitiveness. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Hyundai Motor Group has launched a pilot project to deploy a 'Factory Safety Service Robot' to inspect safety at Kia's plant in South Korea, according to a company statement. The robot is based on Boston Dynamics' quadruped robot, Spot, with applied artificial intelligence (AI), autonomous navigation, teleoperation technologies, and computing payload (AI Processing Service Unit) developed by the automotive group's robotics lab for the robot's usage in various industrial tasks. Hyundai Motor Group said the robot supports late-night security patrols and creates a safer environment for workers. Through the pilot operation at Kia's plant in South Korea, the automotive group will assess its effectiveness and applicability before being deployed to other industrial sites. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- New Zealand's real expenditure-side GDP rose by a seasonally adjusted 2.6% quarter on quarter (q/q) in the June (second) quarter of 2021 as exports - particularly of services - rose significantly, in-turn causing the current-account deficit to narrow from the previous quarter. This surprised on the upside against expectations, benefiting from reduced restrictions and the opening of trans-Tasman travel. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew Vogel)
- The result in the March 2021 quarter was seen as a normalization of conditions, and therefore growth around pre-pandemic levels was expected to follow in the June 2021 quarter. The result surprised on the upside overall, however, as growth exceeded pre-pandemic levels in several areas, seeing expenditure-side GDP up 17.0% year on year (y/y) - although this is distorted by the low base of the 2020 June quarter.
- Although the expenditure and production measures of GDP are theoretically equivalent, there was a slight difference between the two in the June quarter, with economic activity rising 2.8% q/q in real gross value-added terms during the quarter, or 17.4% y/y. Media and government agencies usually focus on production-side GDP as SNZ has determined that the production measure is less volatile.
- Interestingly, growth was driven almost entirely by a huge jump in exports (up 17.0% q/q) against relatively stagnant imports, even as other components of GDP recorded moderate declines during the quarter.

Posted 17 September 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.





