All major European and most US and APAC equity indices closed higher. US government bonds closed lower, while most benchmark European bonds were close to flat on the day. European iTraxx and CDX-NA closed slightly wider across IG and high yield. The US dollar, gold, silver, copper, natural gas, and oil all closed higher on the day. Markets will be focusing on tomorrow's 8:30am ET US CPI release for any signs of a slowdown in inflationary pressures.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- Most major US equity indices closed higher, with the DJIA +0.5% and S&P 500 +0.1% closing at all new all-time highs; Russell 2000 +0.2% and Nasdaq -0.5%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +4bps/1.36% yield and 30yr bonds +3bps/2.00% yield. All eyes will be on tomorrow's US CPI report to see how the US government bonds will react to the release, with the market's reaction to last month's release mirroring the rally during the June release until 1:00pm ET when it then mimicked the sell-off that occurred in May.
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/50bps and CDX-NAHY +3bps/293bps.
- The IHS Markit iBoxx Liquid USD High Yield Index reached a record low weighted average yield of 3.87% on 7 July. A key driver of the strength in the US high yield market has been the outperformance of US high yield oil & gas debt. The below graph compares the daily price of WTI alongside the YTD returns (as of 6 Aug) of the IHS Markit iBoxx Liquid USD High Yield Index (blue), the Oil & Gas subindex (green), and the subindex that excludes Oil & Gas constituents (orange). The graph highlights the correlation between the returns of the O&G index versus the price of WTI, as well as how O&G constituents have been a major driver of the exceptional performance of the broader high yield index this year.

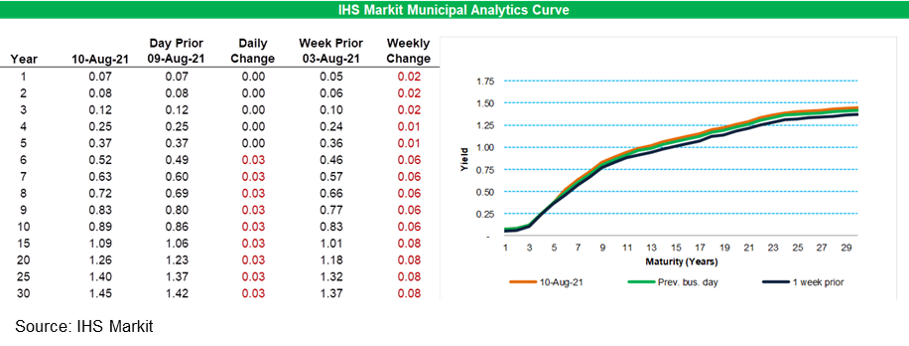
- IHS Markit's AAA Tax-Exempt Municipal Analytics Curve (MAC) sold off 3bps for 6-year and longer paper, with that same part of the curve 6-8bps weaker week-over-week.
- DXY US dollar index closed +0.1%/93.06.
- Gold closed +0.3%/$1,732 per troy oz, silver +0.5%/$23.39 per troy oz, and copper +1.5%/$4.35 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +2.7%/$68.29 per barrel and natural gas closed +0.7%/$4.09 per mmbtu.
- Louisiana's top health official said the state may need to consider enacting new Covid-19 restrictions, warning of a "catastrophic" scenario in hospitals if the current wave of infections does not begin to subside soon. The state health department said there were 2,859 Covid-19 patients in hospital, compared with a high of 2,069 during the winter surge. It also reported 6,088 new cases and 93 additional deaths attributed to coronavirus. On a per-capita basis, Louisiana has recently ranked first- or second-highest in the US in the average number of new cases reported over the previous seven days. Louisiana has one of the lowest vaccination rates in the country with 45 per cent of its residents having received at least one COVID-19 shot. (FT)
- US productivity (output per hour) rose at a 2.3% annual rate in the second quarter, matching our expectation, following an increase of 4.3% in the first quarter that was revised down 1.1 percentage points. (IHS Markit Economists Ken Matheny and Lawrence Nelson)
- Compensation per hour rose at a 3.3% annual rate in the second quarter and at a 1.4% rate in the first quarter. The latter figure was revised down substantially from the previously reported 7.2% increase. Despite the downward revision, compensation per hour has risen at a 6.4% annual rate from the fourth quarter of 2019, far higher than the 2.8% annualized increase in productivity over that span. The marked increase in compensation per hour reflects pandemic-induced effects on employment: employment in lower-wage sectors has declined relative to employment in higher-wage sectors.
- Unit labor costs surged in the early stages of the pandemic, as compensation per hour rose much more than productivity. However, the rise in unit labor costs has slowed on average in more recent quarters. During the first quarter, unit labor costs rose at a 1.0% rate, but this followed a decline of 2.8% in the first quarter (revised down from the previously reported increase of 1.7%). With revisions, unit labor costs declined at a 0.9% rate over the first half of 2021, down from a 1.1% increase over the second half of 2020 and from a 10.1% increase over the first half of 2020.
- Hours rose at a 5.5% rate in the second quarter, continuing a strong recovery that began in the third quarter of 2020. Over the last four quarters, hours have risen 13.6%, reversing more than three-fourths of the 14.5% decline over the first two quarters of 2020.
- As pandemic-induced distortions on labor markets unwind, we expect growth in compensation per hour and productivity to continue to moderate, resulting in moderate growth of unit labor costs.
- A new bill introduced in Congress last week would ban phthalates from food contact substances, including food packaging materials, and require a review of other products to ensure communities of color are not disproportionately exposed to these chemicals. Introduced on August 6, the Preventing Harmful Exposure to Phthalates Act was penned by California Reps. Ted Lieu (D.) and Katie Porter (D.), while Sens. Dianne Feinstein (D-Calif.) and Kirsten Gillibrand (D-N.Y.) introduced companion legislation in the Senate. It comes just days after Rep. Jan Schakowsky (D-Ill.) introduced a bill seeking to change the way FDA evaluates chemicals in foods and create a new FDA office charged with reviewing the safety of at least 10 food chemicals every three years. Top chemical priorities in that bill include PFAS, perchlorate and phthalates. Chemicals in food are gaining the attention of lawmakers, especially after a House committee report shined a light on heavy metals in baby foods and prompted FDA to lay out its new Closer to Zero plan for regulating arsenic, cadmium, lead and mercury in baby and toddler food. Feinstein pointed to the potential for mounting exposure from phthalates from multiple sources on a daily basis, and that regulators have already banned these chemicals from toys and other children's products. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Policy's Joan Murphy)
- Autonomous vehicle (AV) startup Embark Trucks has selected the NVIDIA Drive computing platform to accelerate the development of commercial autonomous software as a service (SaaS) for the trucking industry. The NVIDIA Drive platform will power Embark Universal Interface, a universal autonomous hardware and software stack, as well as Embark Driver software. Ajith Dasari, head of hardware platform at Embark, said, "In order to meet the high safety and performance standards demanded by the Embark Driver software via the EUI, we need an enormous amount of compute power in our trucks. The NVIDIA Drive platform meets this need head-on, and allows us to outfit our partners and customers with the best self-driving hardware and software currently on the market." (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Peer-to-peer car-sharing firm Turo has confidentially filed for an initial public offering (IPO) with the US Securities Exchange Commission (SEC), reports TechCrunch. The number of shares and its price to be offered in the IPO have not yet been determined. The company ended 2020 in a healthy financial position despite the COVID-19 virus pandemic; it laid off one-third of its 330-person workforce and slashed marketing costs to shore up three years of cash. Turo's platform is currently available in more than 5,500 cities in Canada, Germany, the UK, and the US. It has over 450,000 vehicles listed, with more than 850 unique makes and models on its platform, and has a community of 14 million members globally. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Air Products yesterday reported fiscal third-quarter net income up 16% year on year (YOY), to $532.3 million, on net sales up 26%, to $2.60 billion. Adjusted earnings totaled $2.31/share, up 15% YOY but short of analysts' consensus estimate of $2.36/share, as reported by Refinitiv (New York, New York). Volumes up were up 12% YOY, and 6% higher energy-cost pass-through, and 2% higher pricing also boosted sales. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- Industrial gases America segment sales increased 25% YOY, to $1.06 billion, while segment operating income was up 15%, to $286 million. Volumes were up 9% YOY, due to recovery in merchant gases volumes, and prices were up 4%. However, EBITDA margins declined due to higher energy and maintenance costs.
- Industrial gases Asia segment sales rose 15% YOY, to $752 million, while segment operating income was down 1%, to $219 million. Volumes grew 6% YOY, on higher merchant volumes and new plant openings, but this was partly offset by reduced contributions from the Lu'an coal gasification joint venture and higher costs.
- Industrial gases EMEA segment sales increased 45% YOY, to $623 million, while segment operating income was up 33%, to $140 million. Volumes were up 24% YOY, owing to COVID-19 recovery and acquisitions, but margins fell due to higher energy cost pass-through and other cost inflation.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- All major European equity indices closed higher; UK +0.4%, Spain +0.4%, Italy +0.2%, Germany +0.2%, and France +0.1%.
- Most major 10yr European govt bonds closed almost flat, except for Spain -1bp; Italy/Germany/France/UK flat.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +1bp/47bps and iTraxx-Xover +2bps/235bps.
- Brent crude closed +2.3%/$70.63 per barrel.
- The EC's proposals for biofuels in its "Fit For 55" package of policies attempt to correct past mistakes, but they call for tough reforms in sectors with a low appetite for change. The EU must rapidly grow the share of renewable fuels and electricity used by cars, trains, ships, and planes to reach its newly legislated carbon neutrality aim. Today's renewable transportation fuel frontrunner is biofuels—of which around 80% is biodiesel made from food crops like rapeseed—but its carbon-cutting benefits are hamstrung by the use of crops imported from overseas, which results in deforestation that devastates carbon sinks. This may be why the EU has decided to ease off supporting those crops and reshape markets for biofuels in the proposed revision of the Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) published on 14 July. While IHS Markit analysts see crop-based biofuels as the current leaders in the decarbonization of transportation under RED II, under the proposed revision as it is currently worded, states may need to reduce their crop-based biofuels consumption in favor of fuels that use alternate feedstocks. The EC would also like to see, for example, ships and cars use electricity, and new advanced biofuels that come from feedstocks like waste or "energy crops," specific types of trees that grow on land that is not devoted to arable use, or algae, recycled carbon fuels, and electricity-based fuels such as green hydrogen. The EC's proposal seeks to make its fuel wishlist a reality even though these fuels are high in cost and low in availability. (IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Cristina Brooks)
- Irish energy company ESB is taking legal action against four truck-makers that were fined by the European Commission in 2016 for the price fixing of their vehicles in Europe. The Irish Times reports that ESB, which owns a fleet of trucks supplied by the companies affected, has filed High Court proceedings against Volvo Trucks, DAF, Iveco and Daimler, alongside five international entities associated with the vehicle manufacturers. However, it is said to have chosen not to take legal action against their local entities. The ESB declined to comment on the legal cases. The legal action relates to a ruling by the European Commission that fined the four truck-makers EUR2.9 billion for colluding on truck pricing in the European Union (EU) over a 14-year period between 1997 and 2011. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Austrian industrial production (including construction) declined by 1.8% month on month (m/m) in seasonally adjusted, European Union (EU)-harmonized terms in June, extending the previous month's identical -1.8% m/m. The latter was revised down quite heavily from 0.1% m/m initially. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- June's -1.8% partly owed to an above-average decline of construction output (-3.3% m/m), as production ex-construction posted a somewhat smaller drop of -1.3% m/m, equally matching its decline in May
- In year-on-year (y/y) terms, seasonally and calendar-adjusted production ex-construction has, unsurprisingly, fallen further from May's 20.8% to 11.5% in June, linked to the base effect of the initial recovery from the first pandemic wave a year ago.
- Looking at the monthly changes at the data edge in June, the breakdown of industry ex-construction reveals that energy output was the main depressing factor at -4.8% m/m, followed by durable consumer goods (-1.6% m/m). The three other main categories - intermediate, investment, and consumer non-durable goods - actually increased. However, the near-stagnation of investment goods production follows a major decline during April-May (cumulatively by almost 7%), indicating increased uncertainty around mid-2021 about medium-term prospects that contrasts with the surge in activity in February-March.

- Greek consumer prices, measured by the EU-harmonized index of consumer prices, rose by 0.7% year on year (y/y) in July. This followed an increase of 0.6% in June. (IHS Markit Economist Diego Iscaro)
- Although Greece's inflation rate has remained well below the eurozone's average, July's reading was the highest since January 2020.
- Inflation measured by the national index, which gives a higher weight to items such as food and housing costs, stood at 1.4% in July, following 1.0% in June.
- Food prices accelerated sharply in July, rising by 1.7% y/y, an eight-month high. Housing costs also grew at a faster pace in July (4.2% y/y versus 4.0% y/y in June), boosted by the higher prices of fuels/lubricants and heating oil.
- Seven out of the 12 main categories still showed falling prices in July. For example, communication costs decreased by 2.7% y/y, while the prices of miscellaneous goods/services and recreation/culture dropped by 1.2% y/y and 0.8% y/y, respectively.
- New data released by the Banks Association of Turkey (Türkiye Bankalar Birliği: TBB) show the pace of debt restructuring under Temporary Article 32 of the Banking Law accelerated into the middle of the year. The TBB reports that almost TRY25 billion (USD2.9 billion) of loans were restructured in May and June, a sharp spike over the average TRY2.1 billion per month restructured under the program over the previous four months of 2021. The tourism sector was the biggest participant with four firms restructuring TRY7.8 billion in loans in May-June, followed by the energy sector with two firms restructuring a total of TRY5.3 billion and four construction firms restructuring TRY1.7 billion. Since the program was launched in 2019, a total of TRY66.3 billion of loans have been restructured, according to the release. (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Alyssa Grzelak)
- Last month, Turkey extended Temporary Article 32 for an additional two years and it is now to run through 2023 (see Turkey: 22 July 2021: Turkey extends enhanced debt-restructuring framework until 2023 to suppress non-performing loans). Hurryiet Daily News reported that the upper limit on eligible loans to small firms was also increased from TRY25 million to TRY100 million.
- The amount of loans restructured in May-June is equivalent to less than 1% of outstanding loans, but nonetheless would have contributed to lowering the sector's non-performing loan (NPL) ratio, as banks are not required to include restructured loans in their non-performing statistics under measures introduced at the start of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
- Notably, the statistics reported by the TBB only include loans restructured under this specific article, with anecdotal evidence suggesting that many more loans have been restructured voluntarily by individual banks since 2018. As of March 2021, Turkey's official NPL ratio stood at just 3.8%, but IHS Markit calculates a troubled loan ratio closer to 15% when Stage II loans or loans under close monitoring are included.
Asia-Pacific
- Most major APAC equity markets closed higher except for South Korea -0.5%; Hong Kong +1.2%, Mainland China +1.0%, Australia +0.3%, India +0.3%, and Japan +0.2%.
- The Chinese government is eyeing up the opportunities that may be afforded to its new energy vehicles (NEVs) by Russia's move to accelerate the take-up of electric vehicles (EVs), according to a China Daily report. China's Ministry of Commerce is looking to encourage Chinese OEMs making NEVs to look at new opportunities in Russia and other potential export markets. Chinese OEMs and other NEV stakeholders will also be encouraged to seek co-operation on NEV infrastructure, including charging facilities, gas pipeline and power grid optimization, smart services and supplies in rural areas in partnership with Russian companies and government agencies. Zhou Mi, a senior researcher at the Chinese Academy of International Trade and Economic Cooperation, said, "Currently, China's development of NEVs is on a fast track with products enjoying increasing recognition in the global market, especially those for agriculture logistics, mechanical equipment transportation, and short-distance travel [such as electric bicycles]. There is market potential for Chinese NEV manufacturers to export products to Russia." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- SAIC Motor has partnered with telecoms technology company ZTE to build "software-defined" vehicles, reports Reuters. The companies aim to achieve this by collaborating in various fields such as basic software technologies, underlying hardware platforms, cloud computing capability, and intelligent connectivity. ZTE will provide SAIC Motor with its 4G/5G-V2X (vehicle-to-everything) automotive modules and roadside units, as well as a V2X-enabled cloud-controlled platform. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Japan's current-account surplus for June rose by 510.3% year on year (y/y) to JPY905.1 billion (USD8.2 billion) on a non-seasonally adjusted basis but fell by 4.7% month on month (m/m) to JPY1.8 trillion on a seasonally adjusted basis. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- The y/y increase was largely thanks to a trade surplus of JPY648.5 billion, which rose from a deficit of JPY17.2 billion and offset a wider services balance deficit and a decrease in secondary income.
- The improvement in the trade balance reflected a solid rise in exports (up by 47.7% y/y), which outpaced imports (up by 33.8% y/y), thanks to continued solid external demand and also low base effects. That said, the narrower seasonally adjusted trade surplus was due largely to a faster rise in imports (driven by higher production as well as import prices). Primary income continued to rise, largely thanks to improved income from direct investment.
- The Indian government has amended environmental protection rules pertaining to emissions caused by bulk drug manufacturing. The new rules, known as Environment (Protection) Second Amendment Rules, 2021 - which are available here in the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change Ministry notification of 6 August - add tighter parameters for effluent and emission standards to be applied to the production of both bulk drugs, or active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), and pharmaceutical formulations. The new rules will come into force one year from the date of publication of the notification. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Sacha Baggili)
- Vehicle production in the Philippines grew by 48.7% year on year (y/y) to 41,527 units during the first half of 2021 (January-June), according to data released by the ASEAN Automotive Federation (AAF). In June alone, vehicle production in the country stood at 8,011 units, compared with 4,138 units in the same month last year. New vehicle sales in the Philippines stood at 22,550 units in June (up by 44.8% y/y) and were up by 56.1% y/y to 132,767 units during the first half of this. The growth in Philippine vehicle production during the first half of this year was mainly due to an increase in new vehicle demand and a low base of comparison. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)

Posted 10 August 2021 by Ana Moreno, Director, Product Development, IHS Markit and
Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.



