All major US and European equity indices closed higher, while APAC markets were mixed. US and most benchmark European government bonds closed higher. European iTraxx was close to flat across IG and high yield and CDX-NA was slightly tighter on the day. Silver closed higher, gold was flat, and the US dollar, copper, natural gas, and oil were lower on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- All major US equity indices closed higher; Nasdaq +1.8%, S&P 500 +1.1%, Russell 2000 +0.6%, and DJIA +0.6%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -5bps/1.62% yield and 30yr bonds -4bps/2.33% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed -1bp/52bps and CDX-NAHY -4bps/295bps. The worst 15-minute period of performance during the US trading session for 10yr US govt bonds, CDX-NAHY, and the S&P 500 all began between 11:40-11:55am ET.
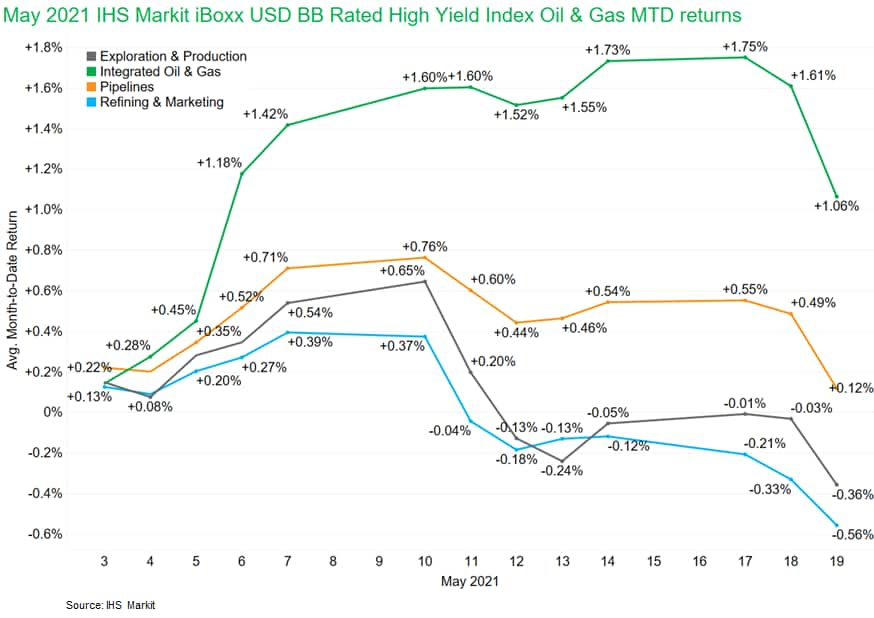
- Integrated Oil & Gas is the best performing energy subsector at +1.06% month-to-date (as of 19 May) within the IHS Markit iBoxx USD BB Rated High Yield Index, while Refining & Marketing is the worst at -0.56% MTD. (IHS Markit Fixed Income Research's Chris Fenske)
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.4%/89.81.
- Gold closed flat/$1,882 per troy oz, silver +0.1%/$28.07 per troy oz, and copper -0.2%/$4.57 per pound.
- Crude oil closed -2.2%/$61.94 per barrel and natural gas closed -1.3%/$2.93 per mmbtu.
- The minutes of the meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) held on 27 and 28 April were released yesterday afternoon (19 May). At that meeting, the Committee maintained the stance of monetary policy, with unanimous support among the voting members. (IHS Markit Economist Ken Matheny
- The target for the federal funds was kept at a range of 0.00- 0.25%, large-scale asset purchases were continued at the rate of approximately $120 billion per month, and the Committee repeated forward guidance for both interest-rate and balance-sheet policies.
- FOMC participants judged the current stance of monetary policy to be appropriate given that the economy remains far from its employment and price-stability objectives amid still-elevated uncertainty.
- A majority of participants, including Chair Jerome Powell, believe it is not yet time to consider when and how to reduce the pace of asset purchases, but a number (i.e., less than a majority) of FOMC participants want to commence such discussions soon if rapid progress toward the Committee's goals continues.
- The discussion evidenced in the minutes does not alter our assumption that interest rate lift-off by the FOMC will occur in 2024 and that large-scale asset purchase will continue at about current rates through this year, followed by a gradual taper in 2022.
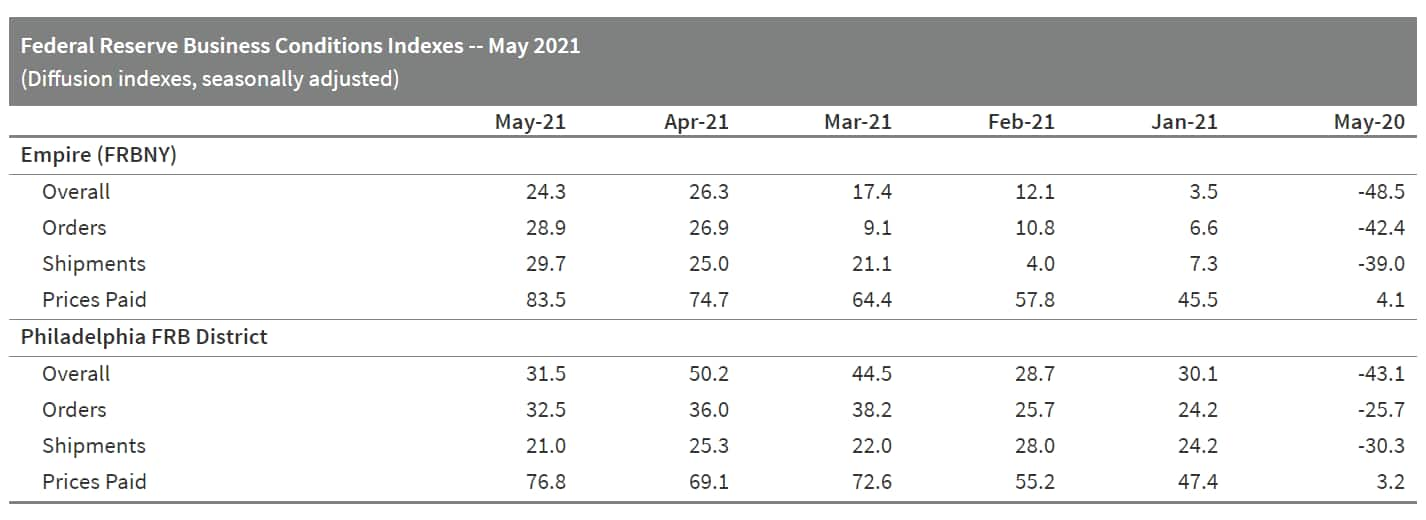
- The Philadelphia Federal Reserve survey of manufacturing activity signaled activity in May that was lower than April's historically high level, but which maintained a string of robust business. The index of current general activity decreased from 50.2 in April to a May reading of 31.5. New orders fell to 32.5 in May from 36.0 in April, a modest decline but continuing a solid run indicating solid demand for goods and providing steady work for production lines. The current shipments index declined modestly to 21.0 in May, the fifth straight month with readings in the 20s. This indicates that manufacturers are able to get product out the door despite challenges from supply-chain disruptions on multiple fronts. The index of current employees dropped to 19.3. (IHS Markit Economist Tom Jackson)
- US seasonally adjusted (SA) initial claims for unemployment insurance fell by 34,000 to 444,000 in the week ended 15 May, its lowest level since the week ended 14 March 2020. The four-week average of 504,750 was also the lowest reading since the week ended 14 March 2020. (IHS Markit Economists Akshat Goel and Patrick Newport)
- Seasonally adjusted continuing claims (in regular state programs) increased by 111,000 to 3,751,000 in the week ended 8 May (though the non-seasonally adjusted number dropped by 10,323). The insured unemployment rate increased a notch to 2.7%.
- Individuals who have exhausted regular benefits are eligible for up to 53 weeks of extended benefits under the PEUC program. In the week ended 1 May, continuing claims for PEUC fell by 150,217 to 5,141,311.
- Independent contractors, self-employed individuals, or individuals who otherwise would not qualify for benefits in regular state programs can apply for claims under the PUA program. There were 95,086 unadjusted initial claims for PUA in the week ended 15 May, an 8,592 decline. In the week ended 1 May, continuing claims for PUA dropped by 678,672 to 6,605,416.
- In the week ended 1 May, the unadjusted total of continuing claims for benefits in all programs fell by 886,568 to 15,975,448.
- Governors in many states—24 at last count—have either enacted or announced an early end to the pandemic-related federal unemployment programs. In addition, at least 36 states have reinstated, or will soon, the requirement that applicants be looking for work to collect benefits.
- Fewer fraudulent claims are partly behind the sustained decline in claims. Two weeks ago, Vermont temporarily disabled its online application process in response to the majority of initial claims being flagged as fraudulent. Initial claims in Vermont then plunged from 6,372 to 337 over the ensuing two weeks.
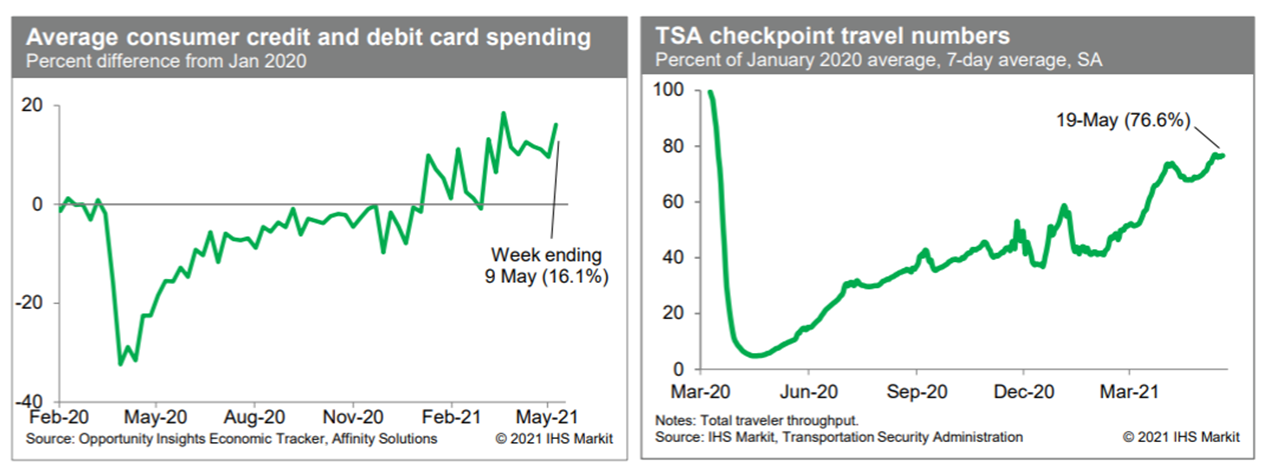
- Average consumer credit- and debit-card spending jumped during the week ending 9 May to 16.1% above the January 2020 level, according to the Opportunity Insights Economic Tracker. This sets up May for more retail and food services sales than are currently implicit in our forecast. We are reviewing this forecast now. Meanwhile, consumption of gasoline moved up last week and remained near the lower end of a normal range. This suggests internal mobility is close to normal. Passenger throughput at US airports, after seasonal adjustment, has been running at roughly 77% of the January 2020 average in recent days. This is up considerably from just a couple of months ago and is indicative of ongoing recovery in the travel sector. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Joel Prakken)
- Strategies to electrify heating and driving in New England will raise demand for power during this decade, but will not put the regional grid at risk of shortages, said the New England Independent System Operator (ISO-NE), which manages planning, the power market, and transmission grid for Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Kevin Adler)
- Electrification of heating and transportation are considered critical to enabling the US to continue to reduce its GHG emissions. Transportation accounted for 29% of US GHG emissions in 2019, and commercial/residential heating and cooling accounted for 13%, according to the US Environmental Protection Agency.
- About 1.2 million air-source heat pumps (ASHPs) are expected to be installed in New England homes by 2030, driving up power demand in the heating sector by 2,526 GWh by the end of the decade, or 1.5%. By 2030, ISO-NE expects nearly 19% of homes will have heat pumps.
- Overall electric power demand is expected to increase by a total of about 17% by 2030 to 165,116 GWh from 140,836 GWh in 2020, ISO-NE said in the "2021-2030 Forecast Report of Capacity, Energy, Loads, and Transmission."
- Every New England state has a heat pump incentive program, which offers rebates based on the estimated per-ton CO2 reductions delivered. At the upper end, Massachusetts offers up to $1,500 for the installation of a heat pump, and Maine offers up to $1,200.
- Electric vehicle (EV) purchases also will see rapid growth, induced by falling costs, improving battery range, and state-level incentives to switch away from internal combustion engines (ICE). ISO-NE projects 1.02 million EVs will be on the road in New England by 2030, with nearly half to be purchased in Massachusetts. The new cars will require an additional 3,554 GWh of grid electricity in 2030, or 2.7% of all grid demand.
- Ford and SK Innovation are reported to be ready to announce plans for a new electric vehicle (EV) battery joint venture (JV), according to media reports. Reuters initially reported the story and says that the JV would be for battery production in the United States and could eventually include a jointly owned plant to produce battery cells. Neither company has commented on the report, although Ford has scheduled an announcement for 20 May. According to Reuters, the talks between Ford and SK Innovations moved quickly after the battery supplier settled a technology dispute with competitor LG Chem. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- May Mobility is testing a Toyota Sienna equipped with its next-generation autonomous kit on public roads in Ann Arbor, Michigan (United States), according to a company statement. The company has also announced plans to work with Toyota to add the automated vehicle to public shuttle fleets in 2022. The model features Toyota's Vehicle Control Interface (VCI), allowing for "seamless technology integration and robust operation of key vehicle control systems, such as steering, brakes, and acceleration". (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- TuSimple has partnered with a produce grower and distributor Giumarra and the Associated Wholesale Grocers (AWG) to launch an autonomous delivery pilot, according to a company statement. TuSimple's autonomous trucks transported fresh watermelons along a 900-mile route from Giumarra's facility in Nogales (Arizona) to AWG's distribution center in Oklahoma City (Oklahoma). The run normally takes 24 hours and 6 minutes with human drivers and traditional trucks, while TuSimple's autonomous systems allowed a 42% faster run of 14 hours and six minutes. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Waymo is reportedly talking to outside investors about raising additional external investment of as much as USD4 billion. The company has also planned to spin out from its parent firm Alphabet Inc. and eventually go public, reports Bloomberg. This signals that development of autonomous technology continues to be capital-intensive. Last year, Waymo raised USD2.25 billion in an external funding round, which later expanded to USD3 billion. This marked the first external infusion of capital. Waymo recently lost six key executives, including its CEO and CFO, among others. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- European equity markets closed higher; Germany +1.7%, France +1.3%, UK +1.0%, Italy +0.9%, and Spain +0.6%.
- Most 10yr European govt bonds closed lower except for Germany flat; Italy -6bps, France/Spain -2bps, and UK -1bp.
- iTraxx-Europe closed flat/52bps and iTraxx-Xover -3bps/258bps.
- Brent crude closed -2.3%/$65.11 per barrel.
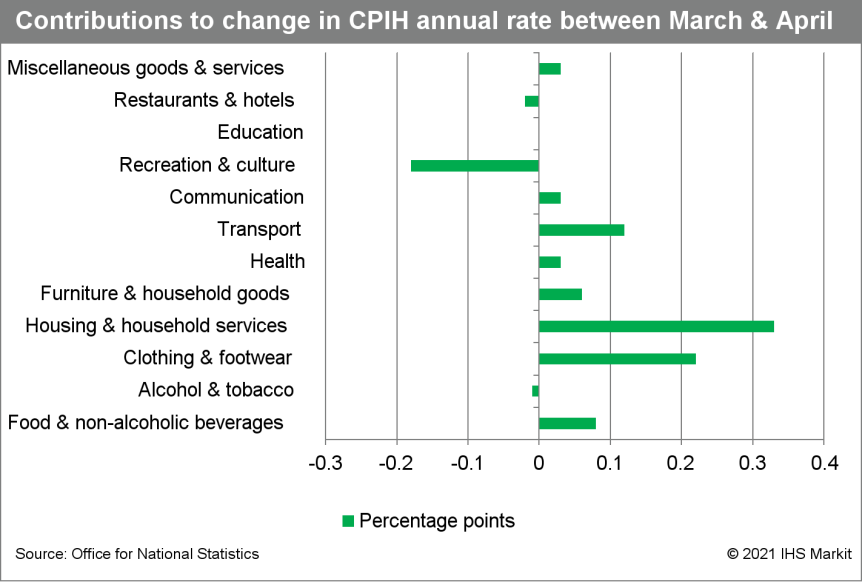
- The Office for National Statistics (ONS) has reported that the United Kingdom's 12-month rate of consumer price index (CPI) inflation more than doubled to 1.5% in April from 0.7% in the previous month. During 2020, inflation averaged 0.9%, well below the Bank of England's target of 2.0%. A breakdown of the inflation rate in April reveals continued price gains for several consumer-facing services, namely communications (+1.7% year on year [y/y]), recreation and culture (+2.2% y/y), and education (+2.1% y/y). (IHS Markit Economist Raj Badiani)
- Tesla has again been linked with investment into the UK. Sources at the UK government's recently founded Office for Investment have told the Daily Telegraph that calls have been made by the office to regional development agencies looking for them to urgently submit potential locations for a new manufacturing facility. Authorities spoken to about a site with around 250 hectares of land include Teesside and the West Midlands. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Eurostat's "final" release has confirmed April's rise in eurozone Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) inflation from 1.3% to 1.6%, the highest level in two years (although in line with the initial market consensus expectation). The cumulative acceleration since December 2020 stands at 1.9 percentage points, with a surge in energy inflation responsible for the bulk of the increase, along with various special factors early in 2021. (IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- Mercedes-Benz Trucks is running trials with its new Mercedes-Benz GenH2 hydrogen truck, according to a company statement. The truck has been undertaking track trials since last month and will move onto road trials later this year, while customer trials will begin in 2023. The first series-produced GenH2 Trucks are expected to be handed over to customers starting in 2027. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- Maire Tecnimont subsidiary NextChem has signed an agreement with Mytilineos to develop engineering activities for the implementation of a green hydrogen plant via electrolysis in Italy. The project, which will convert renewable energy from one of Mytilineos' solar plants into green hydrogen, to be followed by other plants as well, aims to provide local off-takers with a carbon neutral energy carrier alternative, enabling effective decarbonization. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's William Cunningham)
- Inflation has accelerated in Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries as energy prices are bouncing back, while core inflation is not moderating. IHS Markit is forecasting higher inflation compared with 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Vaiva Seckute)
- Average annual harmonized inflation in Central and Eastern European countries has accelerated from 1% in December 2020 to 2.7% in April this year. The main reason behind the faster price growth was higher energy prices. While energy prices had been decreasing in 2020 in most of the countries, they rose up to almost 20% in April this year.
- Two exceptions are Czechia and Slovakia, where energy prices rose very little in April. This can be partly explained by only moderate declines in energy prices last year.
- Core inflation remained above the EU average in most countries, and has recently accelerated in many countries. Core inflation was the highest in Poland, at 5.2% in April, compared with 1.2% in the EU. Core inflation remained below the EU average in Croatia and Slovenia.

- The Russian beverage market is facing the effects of the Covid-19, when: Russian consumers have increasingly been buying more beverages in aluminum cans. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jana Sutenko)
- The shortage of aluminum cans was reported to RBC by two large beer producers in Russia, as well as several soft drink companies. The shortage was also confirmed by the Union of Producers of Soft Drinks (Soyuznapitki).
- The deficit of aluminum cans has been observed for the last three months. Currently, suppliers are primarily supplying cans under contracts for the largest and most marginal brands -- in particular, Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, which has created problems for other manufacturers of soft drinks. The shortage of aluminum containers was also reported by beer giant AB InBev Efes (manufacturer BUD, Stella Artois, Velkopopovický Kozel, Corona Extra, etc).
- According to the retail audit of the research company NielsenIQ, sales of soft drinks in aluminum cans grew at the fastest pace in the last year. In the period between April 2020 to March 2021, sales rose 14% year-on-year/y in both value and volume. For comparison, sales of drinks in plastic bottles increased by 7% over the same period, while sales in glass bottles fell by 9%.
- The shortage of aluminum cans is associated with the changes in consumers' behavior. B, who, because of the closure of restaurants, bars and other establishments, they have switched to home consumption. Foodservice spilled over into retail, where the share of usage of cans is traditionally large.
- Saudi Arabia's consumer price index edged up by 0.2% on the month in April, according to GASTAT. Year on year, price inflation accelerated mildly to 5.2% from 5.0% in March. (IHS Markit Economist Ralf Wiegert)
- Although inflation accelerated, the pace remained below IHS Markit's expectations as we had assumed a stronger impact of food prices due to the beginning of Ramadan in April.
- Food prices were among the forces that pushed the price index the strongest in April relative to March, with prices for food and beverages increasing by 0.4%. Transport costs also increased by 0.8% as vehicles prices accelerated.
- Rents for housing, on the other hand, declined and forced the related price index for housing, water, electricity, gas, and other fuels to drop by 0.2%.
- Saudi consumer prices will most likely return to deflation mode once the impact of the value-added tax (VAT) rate hike wears off in July 2021. However, we expect the annual price increase to eventually turn positive again over the course of the second half of the year. We still do not expect a major acceleration of price inflation further out; price forces are still muted, and they remain anchored by the Saudi riyal's dollar peg.
- South Africa's annual headline inflation rate edged up to 4.4% in April from 3.2% in the previous month, latest figures from statistical service Statistics South Africa (StatsSA) show. The biggest contributors to the annual price gains during April included food and non-alcoholic beverages (1.1 percentage point), transport costs (1.5 percentage point), miscellaneous goods and services (0.7 percentage point), and housing and utilities (0.6 percentage point). (IHS Markit Economist Thea Fourie)
- In April, food and non-alcoholic beverages inflation accelerated to 6.7% y/y, while transport costs were pushed up by higher fuel prices (up 21.4% y/y) and maintenance costs (up 7.8% y/y).
- Administrative service costs, particularly water and other services (up 5.9% y/y) and electricity and fuels (up 6.7% y/y), were primarily responsible for the higher inflation in the housing and utilities category. StatsSA reported that inflation for regulated administrative prices averaged 11.3% in April - well above headline inflation.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Australia +1.3%, Japan +0.2%, Mainland China -0.1%, South Korea -0.3%, Hong Kong -0.5%, and India -0.7%.
- Baidu Apollo has signed a strategic co-operation agreement with Hesai Technology, reports Caixin Global. Under this partnership, Hesai will supply its LiDAR sensor for Baidu's fifth-generation autonomous vehicle (AV), which is expected to achieve mass production in the third quarter of this year. The vehicle will be used for the commercialization of its robotaxi services. LiDAR sensors are necessary for AVs as they measure distance via pulses of laser light and generate 3D maps of the world around them. Hesai claims that the customized LiDAR will improve accuracy by about 2 cm and has an object detection radius that is 1.5 times wider compared to the leading products currently in the market. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Chinese automaker Chongqing Changan Automobile Company (Changan) plans to introduce a new premium electric vehicle (EV) auto brand in co-operation with Huawei and CATL in China this month, reports Gasgoo. Codenamed AB Auto, the brand will be an independent brand from Changan New Energy. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
- Japan's private machinery orders (excluding volatiles) - a leading indicator for capital expenditure - rose by 3.7% month on month (m/m) in March following two consecutive months of declines. The improvement reflected a 9.5% m/m increase in orders from non-manufacturing (excluding volatiles) following two consecutive months of decreases, offsetting a 0.1% m/m drop in orders from manufacturing. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- Orders from governments continued to rise, moving up 2.7% m/m in March following a 17.0% m/m increase in the previous month.
- Orders from overseas fell sharply, dropping 53.9% m/m in March following a 76.2% m/m increase in February, largely because of the dropout of one-off factors.
- The third consecutive month of decline in orders from manufacturing was due largely to continued falls in orders from shipbuilding and non-ferrous metals and drops in orders from other transport equipment, as well as the first decrease in 10 months in orders from general-purpose and production machinery. On the other hand, the improvement in orders from non-manufacturing was thanks largely to solid rises in orders from transportation and postal service, information services, and other miscellaneous non-manufacturing groupings.
- Although Southeast Asia largely avoided the high rates of COVID-19 infections witnessed in many Western countries in 2020, there has recently been a concerning increase in the rates of new infections and fatalities in the region. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Janet Beal and Brendan Melck)
- Malaysia's heath ministry reported 45 deaths associated with COVID-19 on 17 May, the highest daily number recorded since the beginning of the pandemic, while daily new cases remain persistently high at about 6,000. According to a Sky News report, intensive care unit (ICU) beds are becoming scarce and the government is failing to act decisively on which regions of the country to place under stricter lockdown measures.
- In Thailand, daily recorded new case numbers are reaching record highs, with a record 35 fatalities and 2,473 new cases announced by the government on 18 May.
- Taiwan, which has previously been held up as an example of containing the spread of COVID-19, has registered its highest weekly new recorded case numbers in the past week (1,302).
- In Indonesia, where new cases reached a peak in February, recent regional spikes in new case numbers have fueled fears that large-scale movement around the country during the Eid al-Fitr celebrations could lead to another major new spike.
- The upsurge in cases in Southeast Asia is forcing governments to impose lockdown measures again, while Western European countries and the US are recording substantial reductions in new cases and deaths
- ABB has won a contract from the Provincial Electricity Authority (PEA) in Thailand to install more than 120 fast-charging stations for electric vehicles (EVs) across the country by the end of 2021, according to a company statement. Specifically, 124 units of ABB's Terra 54 fast-charging station will be installed at 62 filling stations owned by Thai oil and energy conglomerate Bangchak Corporation and at PEA offices in 40 provinces across the country. Construction has already begun, and the first 40 ABB superchargers at filling stations are already in operation. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- The Swiss multinational Nestlé has announced the start of construction of its Nestlé Bandaraya factory in Batang, Central Java in Indonesia. The new USD220 million facility will produce liquid milk under the Bear brand, as well as Milo and Nescafé ready-to-drink beverages, in order to fulfill the growing demand. It will be ready for commercial production in 2023 and will apply state-of-the-art technology to ensure the highest environmental standards. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jana Sutenko)
- The Malaysian government plans to offer tax incentives to accelerate the development of electric vehicles (EVs) in the country, reports Bernama, citing Malaysia Automotive, Robotics and IoT Institute (MARii) CEO Datuk Madani Sahari. The government has prepared an accelerated EV policy under the National Automotive Policy (NAP) 2020. The government could bring the proposal to the cabinet by June for approval, before announcing it in July. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
Posted 20 May 2021 by Chris Fenske, Head of Capital Markets Research, Global Markets Group, S&P Global Market Intelligence
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.





