Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Oct 16, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 16 October 2020
European equity markets closed higher across the region, while US and APAC markets closed mixed. Benchmark European government bonds were higher across the region, while US bonds were slightly lower. iTraxx indices closed tighter across IG and high yield, while a late-day sell-off in the US resulted in CDX-NAIG closing flat and CDX-NAHY slightly wider after being tighter for most of the day. The US dollar, Brent crude, and gold closed lower on the day, while silver and WTI closed higher.
Americas
- US equity markets closed mixed; DJIA +0.4%, S&P 500 flat, Russell 2000 -0.3%, and Nasdaq -0.4%. The S&P 500 closed +0.2% on the week and 1.8% below Monday's intraday high for the week.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +1bp/0.75% yield and 30yr bonds +1bp/1.53% yield.
- The U.S. budget shortfall ballooned to more than $3.1 trillion in the government's fiscal year ended in September, Treasury Department data showed Friday. The deficit as a share of the economy surged to 16%, the largest since 1945, based on second-quarter gross domestic product. At the end of the financial crisis in 2009, the ratio was close to 10% before slowly narrowing through 2015. (Bloomberg)
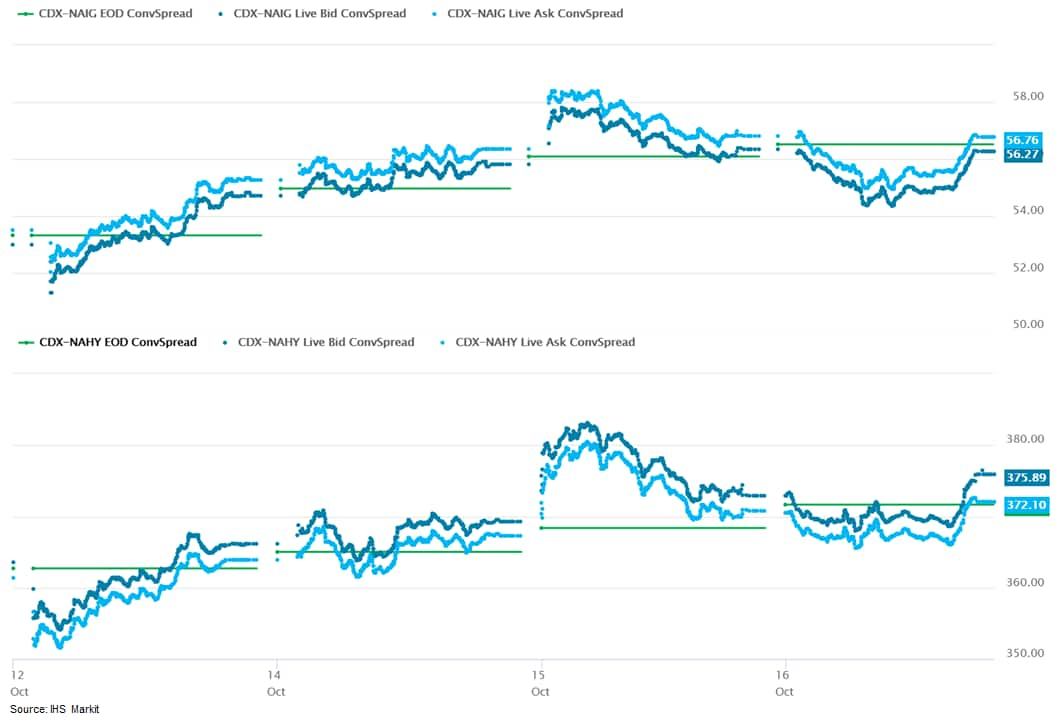
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/57bps and CDX-NAHY closed +2bps/374bps,
which is +3bps and +5bps week-over-week, respectively.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.1%/93.72.
- Gold closed -0.1%/$1,906 per ounce and silver +0.8%/$24.41 per ounce.
- Crude oil closed +0.4%/$41.12 per barrel.
- US total retail trade and food services sales increased 1.9% in
September; core retail sales were stronger than expected, resulting
in a 0.9 percentage point upward revision to our third- and
fourth-quarter estimates of real personal consumption expenditures
(PCE) growth. (IHS Markit Economists James Bohnaker and David
Deull)
- Motor vehicle and parts dealers enjoyed another solid month as sales increased 3.6% in September to 10.9% growth on a 12-month basis. Strong demand for home improvement and socially distanced recreation has not wavered—sales at building materials and sporting goods retailers were 19.1% and 14.4% higher on a 12-month basis, respectively.
- Clothing and clothing accessory stores (up 11.0%) and department stores (up 9.7%) had a positive month, likely due to last-minute back-to-school shopping. Electronics and appliance stores (down 1.6%) sales backtracked in September despite increased remote learning this school season.
- Restaurant and bar sales continued to see gradual improvement with a 2.1% increase in September, yet remained down 14.4% from 12 months earlier. Food services sales may stall as outdoor dining becomes unmanageable in parts of the country with colder temperatures moving in.
- Nonstore retail sales continued to improve as sales increased 0.5% in September and were up 23.8% on a 12-month basis. Online sales growth could accelerate further during the holiday shopping season.
- Retail sales again beat expectations as consumers divert more of their spending money to retail goods while much of the service sector is shuttered. We expect that spending on goods will begin to unwind in the next couple quarters, acting as a drag on overall PCE growth.
- US total industrial production (IP) declined 0.6% in September,
in contrast to expectations for a moderate increase. This report is
consistent with our view that the broad economic recovery has
essentially stalled, setting up fourth-quarter GDP for a sharp
deceleration. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence
Nelson)
- The details from this report that feed directly into our GDP tracking—vehicle assemblies, utilities IP, mining IP, and computer IP—were, on balance, above our assumptions, implying a small (0.1 percentage point) upward revision to our estimate of third-quarter GDP growth. A subsequent report out this morning on retail inventories more than reversed this. We currently look for 33.0% annualized GDP growth in the third quarter followed by 4.6% growth in the fourth quarter.
- Manufacturing IP declined 0.3% in September. The industrial detail within manufacturing IP was mixed. Of note was a 4.0% decline in IP of motor vehicles and parts. Excluding this industry, manufacturing IP was flat.
- Mining IP rose 1.7% in September, but remained well below the pre-pandemic trend.
- Utilities IP dropped 5.6% in September, as unseasonably mild temperatures led to a larger-than-normal decline in the demand for air conditioning.
- As of September, total IP had reversed 57% of the spring contraction, but IP has made no progress since July. The momentum for IP heading into the fourth quarter is weak.
- The US University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index rose 0.8
point (1.0%) to 81.2 in the preliminary October reading, a marginal
improvement from September and the highest since March. The reading
is consistent with our expectation for slowing growth in consumer
spending in the fourth quarter. (IHS Markit Economists David Deull
and James Bohnaker)
- The Consumer Sentiment Index was 9.4 points above the April trough, but, at 19.8 points beneath its February level, it continued to signal a much more pessimistic outlook in the COVID-19 era. It is comparable to levels seen in 2014, partway through the recovery from the Great Recession.
- The October increase was driven by improving expectations; the index measuring consumer expectations increased 3.2 points to 78.8. In contrast, the index of views on current conditions fell 2.9 points to 84.9.
- Consumer sentiment rose 1.8 point to 79.0 among households earning less than $75,000 a year but slipped 0.8 point to 82.8 among households with earnings above that threshold.
- Buying conditions were mixed in October. The index of buying conditions for large household durable goods fell by 7 points to 107, and the index for vehicles fell 12 points to 115, a notable downswing to the lowest level since 2011. In contrast, the index of buying conditions for homes increased 10 points to 142, an eight-month high.
- The expected one-year inflation rate edged up 0.1 percentage point to 2.7%, while expected five-year inflation swung down 0.3 percentage point to 2.4%, the lowest since March.
- Movement in the Consumer Sentiment index since its plunge in March and April has been minimal relative to that drop, indicating that in spite of lapsing fiscal support to businesses and households on the one hand, and improvement in equity markets on the other, consumers' views on the economy are not easily changed—a condition likely to persist until the pandemic is overcome.
- PQ Group announced plans to sell microspheres unit to private equity, explore options for sodium silicates. The performance materials business generated $363.0 million in revenue and $76.7 million in adjusted EBITDA during 2019. The company has also announced plans to explore a possible sale of its sodium silicate and silicate derivatives unit, called performance chemicals. That unit, PQ's largest reporting segment, generated $685.1 million in revenue and $154.3 million in adjusted EBITDA in 2019. It operates in diversified end markets, including food and beverage, coatings, and personal care. The plans are both part of a strategy to focus PQ on its catalysts and refining services businesses, which are "well positioned to use its technology and service offerings to help customers drive sustainability by more efficiently producing the lightweight polymers and clean fuels that are expected be in high demand going forward," says PQ Group CEO Belgacem Chariag. The performance chemicals and performance materials segments account for over 60% of PQ Group's annual revenues. The performance materials sale is expected to close by the end of this year. Proceeds from the sale will go toward reducing debt and funding a special dividend of up to $1.84/share. Goldman Sachs and Harris Williams are acting as financial advisors to PQ, while Ropes & Gray is acting as legal advisor. Kirkland & Ellis is acting as legal advisor to The Jordan Company. No timetable has been given for the potential sale of the performance chemicals segment. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory's Vincent Valk)
- Distributor Barentz announced intentions to acquire Maroon Group. Terms of the transaction, including purchase price, were not disclosed. Barentz is backed by private equity firm Cinven (London, UK), while Maroon Group has been owned by CI Capital Partners (New York, New York), another private equity firm. The deal is expected to close later this year. Maroon Group, which is active in the personal care, cleaning, pharma, food ingredient, and CASE (coatings, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers) markets, significantly increases Barentz's presence in North America. The company has about $500 million/year in revenue and around 300 employees. "Our product portfolios are very complementary," says Hidde van der Wal, CEO of Barentz. "We have no conflicts of interest and we can learn a lot from each other. Maroon Group has significant scale in North America—the biggest economy of the world, where we were small, until today." Barentz's global presence was "the deciding factor" in the deal, according to Maroon Group CEO Terry Hill. "This creates tremendous opportunities to strengthen our business in North America and internationally," he adds. Hill and Maroon Group's existing management team will continue to run the business under Barentz. CI Capital Partners acquired Maroon Group in 2014. The company has completed 11 acquisitions under CI's ownership, increasing revenues by 450% and adding new end markets, according to CI. Maroon Group has around 5,700 customers in the US and Canada. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory's Vincent Valk)
- In a Medium.com blog post, CEO of Cruise Automation, Dan Ammann announced that Cruise, which is owned by General Motors (GM), will put its autonomous vehicles (AVs) on the streets of San Francisco without a backup driver by the end of 2020. Ammann wrote, "Before the end of the year, we'll be sending cars out onto the streets of SF [San Francisco] — without gasoline and without anyone at the wheel. Because safely removing the driver is the true benchmark of a self-driving car, and because burning fossil fuels is no way to build the future of transportation. It will be a low key, quiet moment. But the echo could be loud." The announcement comes as Cruise received a permit on 15 October from the California DMV to remove the human backup driver from the company's autonomous test cars. "We're not the first company to receive this permit, but we're going to be the first to put it to use on the streets of a major US city," Ammann wrote. A spokesperson for Cruise Automation confirmed to IHS Markit that the permit allows Cruise to test five vehicles in the city center for ongoing testing, which is the number that Cruise requested in its permit application, although Cruise has not yet asked for the necessary permit to have public passengers in the vehicle. The test vehicles are the Cruise AVs, based on the Chevrolet Bolt electric vehicle (EV), not the concept Cruise Origin due to start production in 2021. Although putting the Cruise AVs on the streets of San Francisco is an important step, it is also the next step in the company testing and proving out the ability of the vehicles to operate safely and integrated with usual traffic. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Fisker has announced an agreement with Magna for the production of its Ocean SUV at Magna's European assembly facility, starting in the fourth quarter of 2022. The move is in line with Fisker's strategy and plans to work with another company on production, and both the backing of Magna and the selection of a production location could increase confidence in Fisker's plans to go public. Fisker also says that, while initial production of the Ocean will be at Magna's facility in Europe, the company is also considering production in the US in 2023. Fisker's market sales launch is due in the US and Europe simultaneously. Fisker has also confirmed that its production target at Magna's facility is 50,000 units in 2023, with the scale of production in 2022 depending on when during the fourth quarter it starts and how well its ramping up goes. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- According to data from the Colombian National Department of
Statistics (Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadística:
DANE), industrial production contracted 12.2% year on year (y/y) in
August, while retail sales fell 17.1%. (IHS Markit Economist
Lindsay Jagla)
- In yearly terms, industrial production remains well below 2019 levels, with all four industrial sectors contracting y/y. Manufacturing drove this decline in August, falling 10.3% y/y, due primarily to contractions in food and beverages production (-5.4% and -16.8% y/y, respectively).
- Contractions in mining and quarrying also played a role. This sector declined 23.1% y/y in August as crude oil and natural gas extraction fell 15.4% y/y and coal mining dropped 39.6% y/y.
- Retail sales fell 17.1% y/y, driven mainly by declines in fuel purchases for motor vehicles as well as a decrease in purchases of motor vehicles themselves. Four out of 19 merchandise lines grew in yearly terms: household furniture and appliances, sound and video equipment, cleaning supplies, and personal computer and telecoms equipment.
- Due to the global outbreak of the COVID-19 virus and the subsequent social isolation measures that shuttered the Colombian economy, industrial production and retail sales hit rock bottom in April, falling 29.4% and 42.3% y/y, respectively. Since then, both indicators have shown signs of recovery, expanding month on month (m/m) in May, June, and July.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- European equity markets closed higher across the region; France +2.0%, Italy +1.7%, Germany +1.6%, UK +1.5%, and Spain +0.5%.
- Most 10yr European govt bonds closed higher, except for UK flat; Italy -5bps, Spain -4bps, France -2bps, and Germany -1bp.
- The UK's credit rating was downgraded by Moody's late on Friday evening as analysts at the agency warned of scarring to the country's economy from the coronavirus pandemic. The rating agency cut its grade one notch to Aa3, equivalent to a double-A minus rating from rival S&P Global, while adding that its outlook was "stable". Moody's said it believed growth would be "meaningfully weaker" than it had previously believed and that the country's economy had been struggling even before the pandemic reached Britain. (FT)
- Italy achieved its first negative-yield term bond sale on 13
October. (IHS Markit Economist Brian Lawson)
- On 13 October it placed EUR3.75 billion of January 2024 BTPs at -0.14%, with demand of EUR5.244 billion. It had offered EUR3.25-3.75 billion at the maturity.
- On the same day, it also sold EUR2.25 billion of seven-year debt, the maximum of a range of EUR1.75-2.25 billion, at 0.34%, with EUR3.95 billion of interest, alongside EUR1.5 billion of September 2050 debt at 1.48%.
- At the same time, Italy's 10-year bond traded to a new low of 0.63%, while Greece's 10-year yield reached 0.77%, also an all-time low.
- Underlying this improvement is the growing cumulative stimulus under the ECB's PEPP facility, which purchased EUR126.77 billion of public-sector securities during August and September.
- The programs held EUR95.2 billion of Italian government debt at end-September, with net purchases in the latest two-month period of EUR21.8 billion.
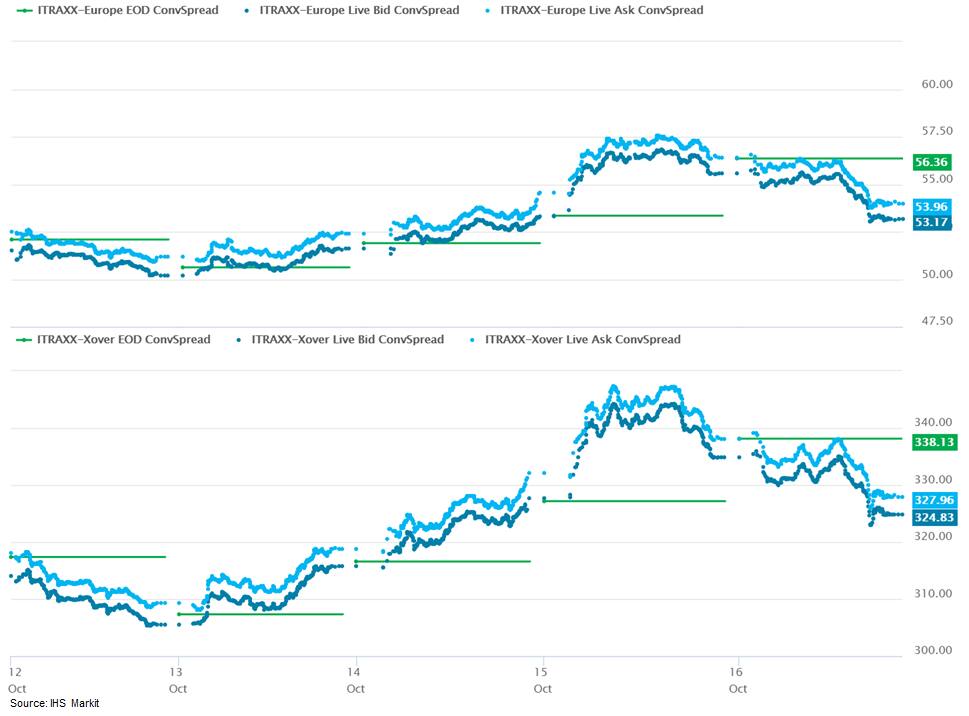
- iTraxx-Europe closed -3bps/54bps and iTraxx-Xover
-12bps/326bps, which is +1bp and +9bps week-over-week,
respectively.
- Brent crude closed -0.5%/$42.93 per barrel.
- The European Commission has adopted an EU sustainable chemicals strategy. The strategy includes actions that prohibit the use of the most harmful chemicals in consumer products such as toys, childcare articles, cosmetics, detergents, food contact materials, and textiles, unless proven essential for society, and ensures that all chemicals are used more safely and sustainably, the Commission says. The strategy sets out concrete actions to make chemicals safe and sustainable by design, and to ensure that chemicals can deliver their benefits without harming the planet, and both current and future generations, according to the Commission. Several innovation and investment actions "will be foreseen to accompany the chemicals industry through this transition," it says, although no further details were provided. The strategy also draws the attention of EU member states to the possibilities of the Recovery and Resilience Facility to invest in the green and digital transition of EU industries, including in the chemical sector, according to the Commission. European chemical industry association Cefic has cautiously welcomed the proposals adopted in the new strategy, but says a sectoral Green Deal for chemicals is still needed and has warned that an uncoordinated policy risks undermining the role the EU's homegrown industry can play. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) also welcomed the strategy, saying it looked forward to supporting its implementation.
- The French economy declined by substantially more than the
eurozone average during the first half of 2020. French GDP fell by
12.3% year on year (y/y), well above the decline of 9.0% y/y in the
eurozone. (IHS Markit Economist Diego Iscaro)
- There are many reasons for this underperformance. In relation to Germany, for example, the second-quarter lockdown was stricter and, for example, tourism plays a more important role in the economy.
- However, one of the main reasons is actually methodological, and relates to the way the French statistical office decided to measure the output produced by the non-healthcare public sector during the lockdown.
- In France, there was a strict lockdown between March and May, most schools were closed and many other public services were not provided. Therefore, the statistical office took the view that output in the non-healthcare public sector had collapsed during the second quarter.
- Real public consumption was therefore estimated to have declined by 7.2% during the first half of the year, being a substantial drag on the economy. This contrasts with Germany, where real government spending rose by 3.2% during the first six months of 2020, or even Italy where it declined by just 1.0% during the same period.
- While this helps to explain part of the underperformance of France (and countries such as Belgium and Slovakia) during the first half of the year, as the economy started to reopen in May we estimate that government consumption rebounded strongly in during the third quarter. As a result, France's GDP is likely to have increased by substantially more than the eurozone average during the period.
- We currently estimate French real GDP to have rebounded by 13.2% quarter on quarter (q/q) during the third quarter. The third-quarter first estimate will be published on 30 October.
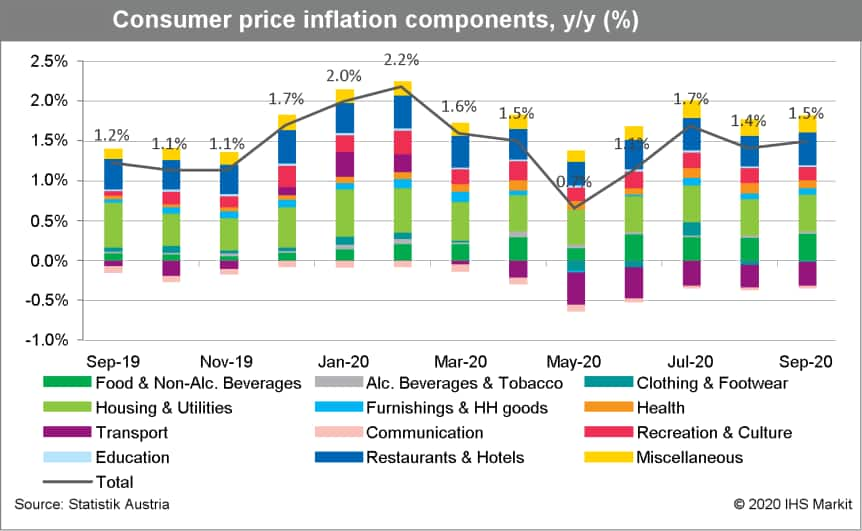
- Statistik Austria data show that consumer prices increased by
0.6% month on month (m/m) in September, about 0.1 percentage point
lower than the long-term average for the month. Headline inflation
according to the national measure thus rebounded from 1.4% year on
year (y/y) to 1.5% y/y, compared with May's interim four-year low
of 0.7%. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- The EU-harmonised measure, which displays a different seasonal pattern (relatively higher weights for fuel and restaurants and hotels, and lower weights for insurance services and housing maintenance), increased more strongly at 1.0% m/m, but this is a seasonal phenomenon. Its annual rate actually softened from 1.4% y/y to 1.3% y/y. Nevertheless, at 1.6 percentage points, this represents the largest positive gap with the eurozone average (-0.3%) ever recorded, almost three times the 0.6% average differential during 2011-19.
- There was not any single major factor causing Austria's inflation to remain as high, relatively speaking. That said, clothing and footwear, food, household goods, and hotels and restaurants were the main boosting forces for the annual rate. Healthcare and recreation and culture exerted the most downward pressure.
- Energy prices remained essentially flat (-0.1% m/m), which also applies to mineral-oil products and household energy individually. Owing to base effects, the annual decline of energy prices deepened from -6.6% to -7.2%.
- Only 4 of the 12 main Classification of Individual Consumption According to Purpose (COICOP) groups of goods and services posted a softening rate, while upward pressure came from six categories (housing and utilities and alcohol and tobacco retained the inflation rates seen in August).
- The prices of seasonal goods increased by 1.0% m/m in
September, leading to a rise in their y/y rate from 5.1% to 6.2%.
This means that the index excluding seasonal goods, while also
posting a 0.6% m/m like the headline measure, showed a slightly
softer picture (from 1.3% y/y in August to 1.4% y/y in
September).
- ZITY, a car-sharing service by Renault and Ferrovial, has deployed 100 vehicles with telemetry and driving assistance solutions in Spain. This deployment is a result of ZITY's partnership with Telefónica, Geotab, and Mobileye, reports Europa Press. The collaboration is part of a nine-month pilot project, called Safe Driving, the aim of which is to offer greater safety and a better experience to users. Telefónica will analyze the areas of opportunity for ZITY's Renault ZOE vehicles and will also contribute in designing the final solution. Meanwhile, the trial will involve vehicles integrated with the Geotab Go device, a fleet management platform, and Geotab's Go Talk, a voice message platform. The pilot will also feature Mobileye's driving assistance system, which uses a single camera and helps in reducing accidents. In 2017, ZITY was launched in Madrid (Spain) and currently has 800 cars deployed in the service in the city. This year, ZITY introduced the service in Paris to replace Moov'in, which it launched with ADA in 2018. Ridecell has been selected as the platform provider for the service, which will enable ZITY users to access facilities such as contactless rental, payment, verification, and on-demand scheduling through the app. Recently, the European Commission approved the creation of a car-sharing alliance between Renault Group and Ferrovial to involve the acquisition of Car Sharing Mobility Services, also known as ZITY Hub. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Evonik Industries sales totaled €2.92 billion, down 9.6% YOY, while adjusted EBITDA was €519 million, €24 million or 4.4% less than in the prior-year period, but €48 million higher than the consensus estimate of €471 million, as compiled by Vara Research. "This result is clearly above market expectations and is therefore pre-released today," it says. During the third quarter, an improving month-on-month trend became apparent, which further accelerated in September and produced the better-than-expected results, according to Evonik. The main drivers were the specialty additives and smart materials divisions, it says. Specialty additive sales fell by 10% YOY to €777 million, while adjusted EBITDA declined by 8% to €214 million, but beating consensus. Sales of smart materials declined 5% YOY to €790 million, with adjusted EBITDA dropping 13% to €137 million, also beating analysts' consensus expectations. Evonik's nutrition and care business recorded sales that were 2% lower YOY at €715 million, but with an 18% increase in adjusted EBITDA to €140 million, slightly below consensus. Sales of its performance materials decreased 27% YOY to €444 million, with adjusted EBITDA down 43% to €28 million, beating consensus. The company has also provided an updated outlook for 2020, saying it now expects adjusted EBITDA to be in the range €1.8-2.0 billion, compared with €2.15 billion in 2019. The sales outlook remains unchanged at €11.5-13.0 billion, compared with €13.1 billion in 2019, it says.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Hong Kong +0.9%, India +0.6%, Mainland China +0.1%, Japan -0.4%, Australia -0.5%, and South Korea -0.8%.
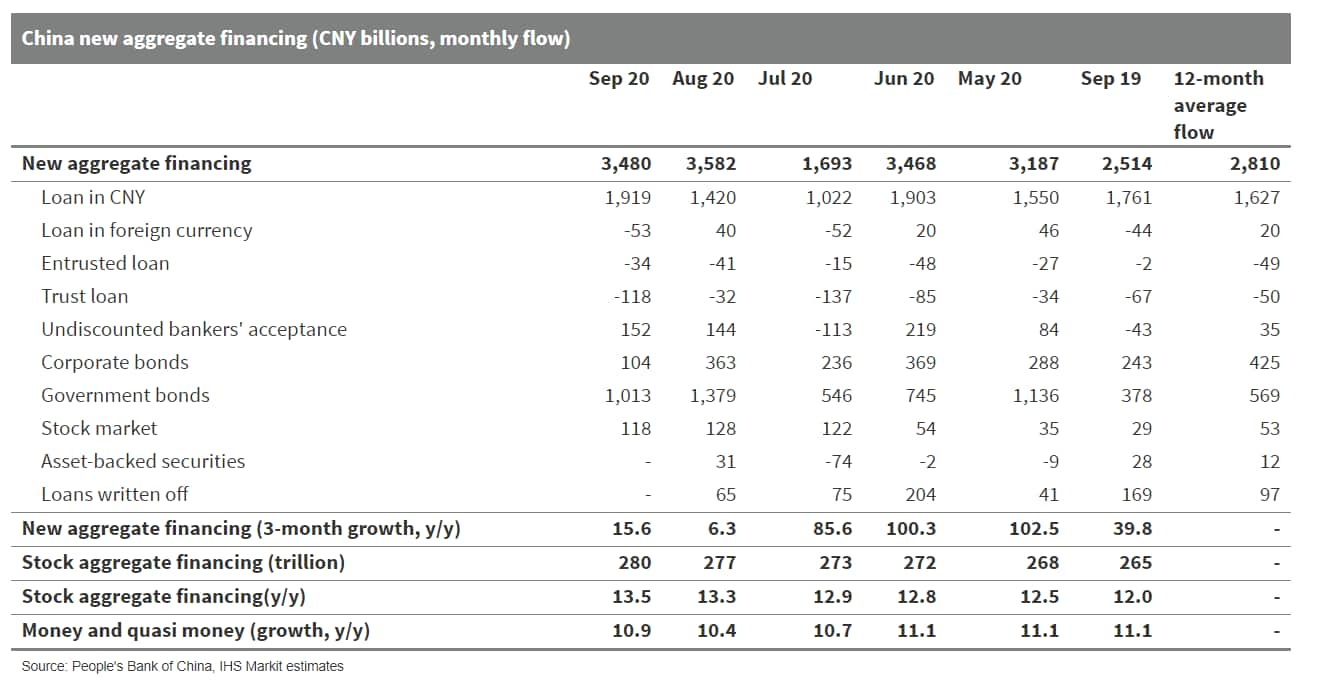
- China's new aggregate financing, the widest measure of net new
financing to the real economy, increased CNY3.48 trillion in
September 2020, up CNY965.8 billion from the amount a year ago,
according to the release of the People's Bank of China (PBOC). The
stock total social financing (TSF) increased 13.5% year on year
(y/y), 0.2 percentage points up from August. (IHS Markit Economist
Yating Xu)
- Rising local government leverage remained a major contributor to the TSF increase. Local government bond issuance reached CNY1.01 trillion in September, CNY630 billion higher than the year-ago level, but softening from July and August. Meanwhile, new bank loans continued to expand as a result of sustained growth recovery.
- Corporate medium- and long-term loans increased CNY1.1 trillion, nearly doubling y/y, in line with the rise in the export order index and domestic order index in the central bank's third-quarter 2020 entrepreneurs survey.
- New household medium- and long-term loans maintained their strong momentum since June, rising CNY142 billion from a year ago in September.
- Undiscounted bankers' acceptance rose CNY1.09 trillion from a year ago, marking the sixth consecutive month of increase. However, other off-balance sheet loans, including entrusted loans and trust loans, declined.
- Broad money supply (M2) growth rebounded to 10.9% y/y following three consecutive months of decline. Acceleration in credit expansion and increase in government spending were the two major contributors to M2 growth. M1 maintained its upward trend as strong housing sales and government spending supported corporates' current deposits.
- TSF increased by CNY29.6 trillion in the first three quarters of 2020, up CNY9 trillion y/y. New bank loans rose to CNY16.26 trillion, falling short of the annual target of CNY20 trillion.
- TSF and M2 are expected to remain strong in the fourth quarter as relatively low financing costs and low inventory levels may continue to help corporations and households increase their leverage.
- Local government financing will keep growing in the fourth
quarter, albeit at a slower pace compared with in the third
quarter. The remaining CNY1.78 trillion in local government bonds
has yet to be issued in the fourth quarter, compared with the
CNY2.93 trillion worth of government bonds issued in the third
quarter.
- In the week ending 16 October 2020, China saw corn starch purchasing price for processing surge to CNY3,000 per ton (USD441/ton), five-year high, according to Chinese media outlet Wenhua Caijing. The market sentiment in the consuming regions has been influenced by the news, in which the pace of harvesting is slower than usual as some crops had fallen due to the weather in the northeast. Some processors are actively stocking up on corn as the supply of high-quality grains is expected to be tight. Meanwhile, the stock in the processing industry is relatively low, indicating a need for replenishment. As of 14 October, total stock of corn starch processors was 579,000 tons, a reduction of 4.3% compared with the same period of last year. The price fluctuation before and after the 1 October national public holiday has triggered some panic ordering. Overall sales are dynamic. This week, the average price of corn starch in the domestic spot market in producing regions was CNY2,829.52/ton, an increase of CNY72.85/ton compared with the average price before the National Day. On the husbandry side, the number of livestocks has recovered and pigs are growing in weight and size, so demand for feed is growing accordingly. Additionally, demand for corn starch for packaging material has risen. China's ecommerce big discount day is 11 November (Single's Day), equivalent to the US Black Friday. The sales season consume substantial packaging material. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Hope Lee)
- Shares in China's leading animal health business recently climbed to their highest ever valuation on the Shanghai Stock Exchange. China Animal Husbandry Industry Company (CAHIC) saw it shares peak at around CNY20.50 ($3) each last month. The firm has been publicly listed since 1999. According to Bloomberg data, China's stock market value has hit a record high of more than $10 trillion on the back of the country's strong economic recovery during the COVID-19 pandemic. The data shows China's stock market is the second largest in the world, behind that of the US ($39tn). This current peak takes the total value of China's stock market past its previous high in 2015 - a time when the country witnessed an equities bubble. 2015 also marked the last time CAHIC's shares were valued higher than CNY15 each. CAHIC has shown resilience in the face of COVID-19 and African swine fever (ASF). In 2019, the firm's revenues dropped 10%. This was a much smaller dip than Jinyu Group - China's second-largest animal health company - and other major domestic players. Other leading Chinese animal health firms on the Shanghai Stock Exchange such as Jinyu Group and Pulike Biological Engineering have also witnessed strong share prices recently. Jinyu's stock valuation reached an all-time high of around CNY31 each in August. The firm's share price has been climbing steadily this year, despite it reporting a major impact from ASF on it 2019 financials. In September, Pulike's valuation eclipsed CNY30 per share for the first time since 2015. In addition, Tianjin Ringpu Bio-Technology's shares climbed over CNY27 for the first time in the firm's 10 years as a listed entity on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. (IHS Markit Animal Health's Joseph Harvey)
- CWind Taiwan announced that it has been awarded Taiwan's first balance of plant (BOP) contract for the Formosa 1 Offshore Wind Farm, as it moves into its operational phase. The contract will see the continued involvement of CWind's crew transfer vessel (CTV) Ocean Surveyor 3, that had been involved in previous crew transfer charters and marine survey work during the construction and maintenance phases of the wind farm. Under the contract, CWind will also provide its in-house technicians, which include its first batch of Taiwanese technicians to graduate from its Global Wind Organization (GWO) training school. These graduates will work alongside senior technicians from its European parent company. The scope of work, to commence in September 2020, will include the topside inspection and maintenance services to the 22 turbines in the project, including internal and external inspections and painting. The wind farm has a capacity of 128 MW, and was delivered in two phases. Phase 1 consists of two 4 MW turbines, and Phase 2 consists of 20 6 MW turbines delivered by Siemens Gamesa. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
- Japan is seeking to set up a commercial hydrogen fuel supply chain by around 2030 to support the reduction of carbon emissions, according to Reuters, citing a statement from the country's Industry Minister Hiroshi Kajiyama. The country is trying to speed up technological developments to scale up a transportation system for hydrogen using ships by around 2030. Kajiyama said that his ministry has asked for a hydrogen budget of USD800 million for 2021, up by 20% from 2020. Separately, Kawasaki Heavy Industries plans to ship liquefied hydrogen from Australia to Japan early next year. Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) outlined plans for a "hydrogen society" vision in March 2016 associated with the Olympic Games, which were scheduled to take place in Tokyo in 2020 but were postponed owing to the COVID-19 virus outbreak. The plan aimed to have 160 hydrogen filling stations and 40,000 hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles (FCVs) in use by 2020. By 2030, the ministry aims to expand this 20-fold to 800,000 FCV units, with at least 320 filling stations across the country. Japan has been aggressively pursuing improvements in its hydrogen infrastructure to support the adoption of FCVs. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
- South Korea's largest mobile carrier SK Telecom plans to spin off its mobility business unit into a new company called T Map Mobility, reports Reuters. The new company will receive a direct investment of USD50 million from Uber. In addition, T Map Mobility will form a separate ride-hailing joint venture (JV) with Uber, which will invest USD100 million for a 51% stake. The JV will combine the expertise of T Map Mobility's mapping technology and Uber's ride-hailing technology and is expected to begin operations in the first half of 2021. This gives Uber an opportunity to expand in South Korea's ride-hailing market, which is dominated by local player Kakao's mobility unit. Uber which currently offers premium taxi-hailing and registered taxi-hailing services in South Korea was earlier subjected to tough competition and opposition from taxi drivers and regulations. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Hyundai has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with South Korean government entities, energy companies, and other local companies to establish Korea Hydrogen Energy Network (Kohygen), a special-purpose company, reports The Korea Herald. The agreement is part of the government's Green New Deal policy, which involves joint efforts with corporations to foster hydrogen fuel-cell mobility. Kohygen, which will officially begin operations in February 2021, will install 10 gaseous hydrogen refueling stations starting next year. It will also establish more than 25 liquid hydrogen refueling stations in 2023. Along with Hyundai, Korea District Heating Corporation and seven energy companies, including SK Energy, GS Caltex, and S-Oil are participating in Kohygen. This latest development is in line with the South Korean government's wider aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, generate new growth momentum for its automotive industry, and reduce its heavy reliance on imported oil. Hydrogen fuel has a strong potential to revive sluggish manufacturing businesses, including small and medium-sized enterprises, which in turn will create new jobs. Last year, the government revealed a roadmap to increase the adoption of fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) in the country. It aims to produce 6.2 million FCEVs and build 1,200 hydrogen refilling stations across the country by 2040. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-16-october-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-16-october-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+16+October+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-16-october-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 16 October 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-16-october-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+16+October+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-16-october-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




